【数据结构初阶】顺序表
温馨提示:这篇文章已超过428天没有更新,请注意相关的内容是否还可用!
顺序表
- 1.线性表
- 2.顺序表
- 2.1概念以及结构
- 2.1.1静态顺序表
- 2.1.2动态顺序表
- 3.顺序表的实现
- 3.1初始化内容
- 3.2初始化函数
- 3.3销毁函数
- 3.4打印函数
- 3.5扩容函数
- 3.6尾插
- 3.6尾删函数
- 3.7头插函数
- 3.8头删函数
- 3.9查找函数
- 3.10插入函数
- 3.11删除函数
- 3.12修改函数
- 4. 顺序表的问题
- 5.相关题目
- 全部码源
1.线性表
线性表(linear list)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。 线性表是一种在实际中广泛使
用的数据结构,常见的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串…
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就说是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的,线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储。
2.顺序表
2.1概念以及结构
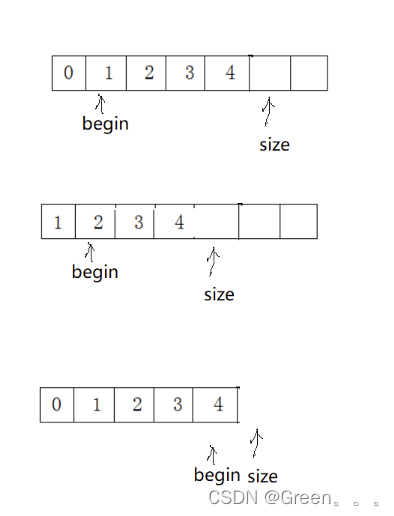
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
顺序表一般可以分为:
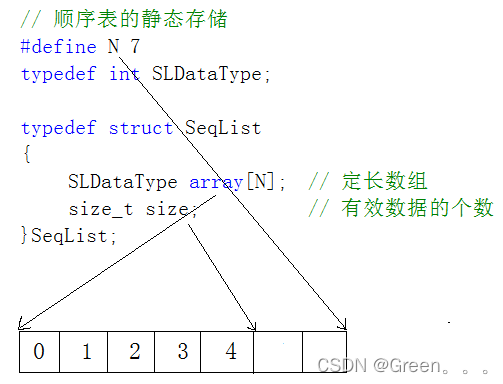
2.1.1静态顺序表
静态顺序表:使用定长数组存储元素。
// 静态顺序表 #define N 7 typedef int SLDataType; struct SeqList { SLDataType a[N]; int size; }SeqList;2.1.2动态顺序表
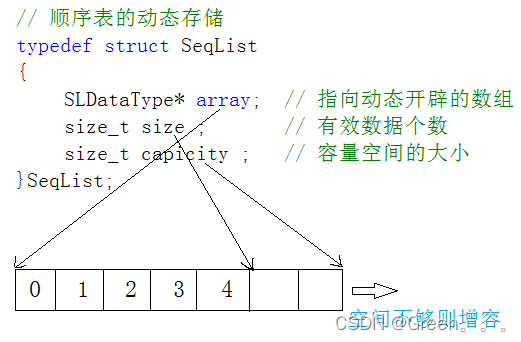
动态顺序表:使用动态开辟的数组存储
// 动态顺序表 typedef int SLDataType; typedef struct SeqList { SLDataType* a; int size; // 存储有效数据个数 int capacity; // 空间大小 }SL;3.顺序表的实现
3.1初始化内容
顺序表包含文件:
- SeqList.h—函数的声明和库函数的包含
- SeqList.c—用来测试你写的顺序表能不能用
- test.c—用来测试你写的顺序表能不能用
函数的声明和库函数的包含及接口实现:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #pragma once #include #include #include // 动态顺序表 typedef int SLDataType; typedef struct SeqList { SLDataType* a; int size; // 存储有效数据个数 int capacity; // 空间大小 }SL; // 管理数据 -- 增删查改 void SLInit(SL* ps); void SLDestroy(SL* ps); void SLPrint(SL* ps); void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps); // 头插头删 尾插尾删 void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x); void SLPopBack(SL* ps); void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x); void SLPopFront(SL* ps); // 返回下标,没有找打返回-1 int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x); // 在pos位置插入x void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x); // 删除pos位置的值 void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos); void SLModify(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x);3.2初始化函数
SeqList.h
void SLInit(SL* ps);
SeqList.c
void SLInit(SL* ps) { assert(ps); ps->a = (SLDataType*)malloc(sizeof(SLDataType) * 4); if (ps->a == NULL) { perror("malloc failed"); exit(-1); //return; } ps->size = 0; ps->capacity = 4; }用malloc开辟数组a的空间大小,对size,capacity进行初始化
3.3销毁函数
SeqList.h
void SLDestroy(SL* ps);
SeqList.c
void SLDestroy(SL* ps) { assert(ps); free(ps->a); ps->a = NULL; ps->capacity = ps->size = 0; }3.4打印函数
SeqList.h
void SLPrint(SL* ps);
SeqList.c
void SLPrint(SL* ps) { assert(ps); for (int i = 0; i size; i++) { printf("%d ", ps->a[i]); } printf("\n"); }3.5扩容函数
SeqList.h
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps);
SeqList.c
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps) { assert(ps); // 满了要扩容 if (ps->size == ps->capacity)//先检查空间是否够用 { SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->a, ps->capacity * 2(sizeof(SLDataType)));//一般2倍扩容 if (tmp == NULL) { perror("realloc failed"); exit(-1); } ps->a = tmp; ps->capacity *= 2; } }补:
3.6尾插
SeqList.h
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x);
SeqList.c
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x) { assert(ps); SLCheckCapacity(ps); ps->a[ps->size] = x; ps->size++; //SLInsert(ps, ps->size, x); }3.6尾删函数
SeqList.h
void SLPopBack(SL* ps);
SeqList.c
void SLPopBack(SL* ps) { assert(ps); // 温柔的检查 //if (ps->size == 0) //return; // 暴力的检查 assert(ps->size > 0); //ps->a[ps->size - 1] = 0; ps->size--; //SLErase(ps, ps->size - 1); }3.7头插函数
SeqList.h
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x);
SeqList.c
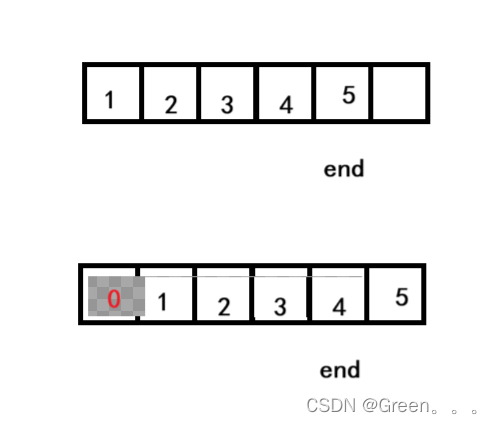
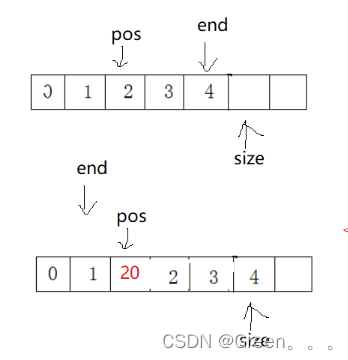
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x) { assert(ps); SLCheckCapacity(ps); // 挪动数据 int end = ps->size - 1; while (end >= 0) { ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end]; --end; } ps->a[0] = x; ps->size++; //SLInsert(ps, 0, x); }3.8头删函数
SeqList.h
void SLPopFront(SL* ps);
SeqList.c
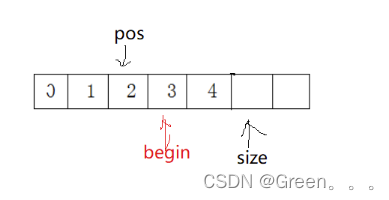
void SLPopFront(SL* ps) { assert(ps); assert(ps->size > 0); int begin = 1; while (begin size) { ps->a[begin - 1] = ps->a[begin]; ++begin; } ps->size--; //SLErase(ps, 0); }3.9查找函数
SeqList.h
// 返回下标,没有找打返回-1 int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x);
SeqList.c
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x) { assert(ps); for (int i = 0; i size; i++) { if (ps->a[i] == x) { return i; } } return -1; }3.10插入函数
SeqList.h
// 在pos位置插入x void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x);
SeqList.c
// 在pos位置插入x void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x) { assert(ps); assert(pos >= 0 && pos size);//插入数字是否在数组内 SLCheckCapacity(ps);检查是否需要扩容 int end = ps->size - 1; while (end >= pos) { ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end]; --end; } ps->a[pos] = x; ps->size++; }3.11删除函数
SeqList.h
// 删除pos位置的值 void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos);
SeqList.c
// 删除pos位置的值 void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos) { assert(ps); assert(pos >= 0 && pos size);//插入数字是否在数组内 int begin = pos + 1; while (begin size) { ps->a[begin - 1] = ps->a[begin]; ++begin; } ps->size--; }3.12修改函数
SeqList.h
void SLModify(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x);
SeqList.c
void SLModify(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x) { assert(ps); assert(pos >= 0 && pos size); ps->a[pos] = x; }4. 顺序表的问题
- 中间/头部的插入删除,时间复杂度为O(N)
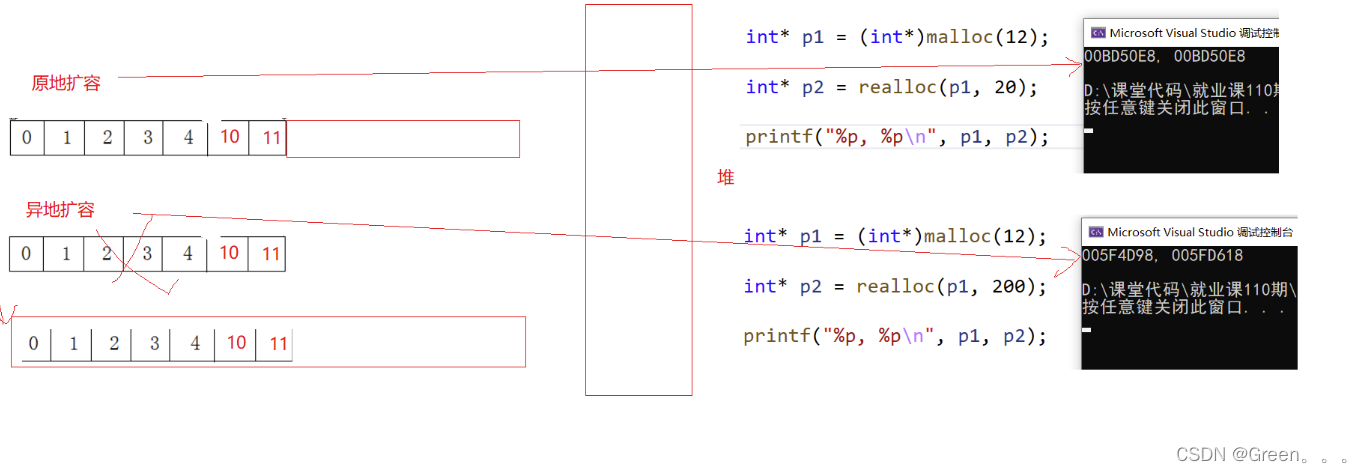
- 增容需要申请新空间,拷贝数据,释放旧空间。会有不小的消耗。
- 增容一般是呈2倍的增长,势必会有一定的空间浪费。例如当前容量为100,满了以后增容到200,我们再继续插入了5个数据,后面没有数据插入了,那么就浪费了95个数据空间。
5.相关题目
- 原地移除数组中所有的元素val,要求时间复杂度为O(N),空间复杂度为O(1)。OJ
- 删除排序数组中的重复项。OJ链接
- 合并两个有序数组。OJ链接
全部码源
SeqList.h
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #pragma once #include #include #include 静态顺序表 //#define N 1000 //typedef int SLDataType; // //struct SeqList //{ // SLDataType a[N]; // int size; //}; // 动态顺序表 typedef int SLDataType; typedef struct SeqList { SLDataType* a; int size; // 存储有效数据个数 int capacity; // 空间大小 }SL; // 管理数据 -- 增删查改 void SLInit(SL* ps); void SLDestroy(SL* ps); void SLPrint(SL* ps); void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps); // 头插头删 尾插尾删 void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x); void SLPopBack(SL* ps); void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x); void SLPopFront(SL* ps); // 返回下标,没有找打返回-1 int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x); // 在pos位置插入x void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x); // 删除pos位置的值 void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos); void SLModify(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x);SeqList.c
#include"SeqList.h" void SLInit(SL* ps) { assert(ps); ps->a = (SLDataType*)malloc(sizeof(SLDataType) * 4); if (ps->a == NULL) { perror("malloc failed"); exit(-1); //return; } ps->size = 0; ps->capacity = 4; } void SLDestroy(SL* ps) { assert(ps); free(ps->a); ps->a = NULL; ps->capacity = ps->size = 0; } void SLPrint(SL* ps) { assert(ps); for (int i = 0; i size; i++) { printf("%d ", ps->a[i]); } printf("\n"); } void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps) { assert(ps); // 满了要扩容 if (ps->size == ps->capacity) { SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->a, ps->capacity * 2 * (sizeof(SLDataType))); if (tmp == NULL) { perror("realloc failed"); exit(-1); } ps->a = tmp; ps->capacity *= 2; } } void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x) { assert(ps); SLCheckCapacity(ps); ps->a[ps->size] = x; ps->size++ //SLInsert(ps, ps->size, x); } void SLPopBack(SL* ps) { assert(ps); // 温柔的检查 //if (ps->size == 0) //return; //暴力的检查 assert(ps->size > 0); //ps->a[ps->size - 1] = 0; ps->size--; //SLErase(ps, ps->size - 1); } void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x) { assert(ps); SLCheckCapacity(ps); // 挪动数据 int end = ps->size - 1; while (end >= 0) { ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end]; --end; } ps->a[0] = x; ps->size++; SLInsert(ps, 0, x); } void SLPopFront(SL* ps) { assert(ps); assert(ps->size > 0); int begin = 1; while (begin size) { ps->a[begin - 1] = ps->a[begin]; ++begin; } ps->size--; //SLErase(ps, 0); } int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x) { assert(ps); for (int i = 0; i size; i++) { if (ps->a[i] == x) { return i; } } return -1; } // 在pos位置插入x void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x) { assert(ps); assert(pos >= 0 && pos size); SLCheckCapacity(ps); int end = ps->size - 1; while (end >= pos) { ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end]; --end; } ps->a[pos] = x; ps->size++; } // 删除pos位置的值 void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos) { assert(ps); assert(pos >= 0 && pos size); int begin = pos + 1; while (begin size) { ps->a[begin - 1] = ps->a[begin]; ++begin; } ps->size--; } void SLModify(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x) { assert(ps); assert(pos >= 0 && pos size); ps->a[pos] = x; }test.c
#include"SeqList.h" void TestSeqList1() { SL sl; SLInit(&sl); SLPushBack(&sl, 1); SLPushBack(&sl, 2); SLPushBack(&sl, 3); SLPushBack(&sl, 4); SLPushBack(&sl, 5); SLPushBack(&sl, 6); SLPushBack(&sl, 6); SLPushBack(&sl, 0); SLPushBack(&sl, 0); SLPrint(&sl); SLPopBack(&sl); SLPopBack(&sl); SLPrint(&sl); SLPopBack(&sl); SLPopBack(&sl); SLPopBack(&sl); SLPopBack(&sl); SLPopBack(&sl); SLPopBack(&sl); SLPopBack(&sl); //SLPopBack(&sl); //SLPopBack(&sl); /*SLPopBack(&sl); SLPopBack(&sl); SLPopBack(&sl); SLPopBack(&sl);*/ SLPrint(&sl); SLPushBack(&sl, 1); SLPushBack(&sl, 2); SLPrint(&sl); SLDestroy(&sl); } void TestSeqList2() { SL sl; SLInit(&sl); SLPushBack(&sl, 1); SLPushBack(&sl, 2); SLPushBack(&sl, 3); SLPushBack(&sl, 4); SLPushBack(&sl, 5); SLPrint(&sl); SLPushFront(&sl, 10); SLPushFront(&sl, 20); SLPushFront(&sl, 30); SLPushFront(&sl, 40); SLPrint(&sl); SLDestroy(&sl); } void TestSeqList3() { SL sl; SLInit(&sl); SLPushBack(&sl, 1); SLPushBack(&sl, 2); SLPushBack(&sl, 3); SLPushBack(&sl, 4); SLPushBack(&sl, 5); SLPrint(&sl); SLPopFront(&sl); SLPopFront(&sl); SLPrint(&sl); SLPopFront(&sl); SLPopFront(&sl); SLPopFront(&sl); //SLPopFront(&sl); SLPrint(&sl); SLPushBack(&sl, 4); SLPushBack(&sl, 5); SLPrint(&sl); SLDestroy(&sl); } void TestSeqList4() { SL sl; SLInit(&sl); SLPushBack(&sl, 1); SLPushBack(&sl, 2); SLPushBack(&sl, 3); SLPushBack(&sl, 4); SLPushBack(&sl, 5); SLPushFront(&sl, -1); SLPushFront(&sl, -2); SLPrint(&sl); SLInsert(&sl, 3, 40); SLPrint(&sl); int x; scanf("%d", &x); int pos = SLFind(&sl, x); if (pos != -1) { SLInsert(&sl, pos, x * 10); } SLPrint(&sl); SLDestroy(&sl); } void TestSeqList5() { SL sl; SLInit(&sl); SLPushBack(&sl, 1); SLPushBack(&sl, 2); SLPushBack(&sl, 3); SLPushBack(&sl, 4); SLPushBack(&sl, 5); SLPrint(&sl); SLErase(&sl, 2); SLPrint(&sl); int x; scanf("%d", &x); int pos = SLFind(&sl, x); if (pos != -1) { SLErase(&sl, pos); } SLPrint(&sl); SLDestroy(&sl); } void TestSeqList6() { SL sl; SLInit(&sl); SLPushBack(&sl, 1); SLPushBack(&sl, 2); SLPushBack(&sl, 3); SLPushBack(&sl, 4); SLPushBack(&sl, 5); SLPrint(&sl); SLModify(&sl, 2, 20); sl.a[2] = 20; SLPrint(&sl); /*int x; scanf("%d", &x); int pos = SLFind(&sl, x); if (pos != -1) { SLModify(&sl, pos, x*10); } SLPrint(&sl);*/ int pos, x; scanf("%d%d", &pos, &x); //sl.a[pos] = x; SLModify(&sl, pos, x); SLPrint(&sl); SLDestroy(&sl); } void TestSeqList7() { /*SL* sl = NULL; SLInit(sl); SLPushBack(sl, 1); SLPushBack(sl, 2); SLPushBack(sl, 3); SLPushBack(sl, 4); SLPushBack(sl, 5); SLPrint(sl);*/ SL sl; SLInit(&sl); SLPushBack(&sl, 1); SLPushBack(&sl, 2); SLPushBack(&sl, 3); SLPushBack(&sl, 4); SLPushBack(&sl, 5); SLPrint(&sl); SLPopFront(&sl); SLDestroy(&sl); } //int main() //{ // TestSeqList7(); // // return 0; //} return 0; }💘不知不觉,【数据结构初阶】顺序表以告一段落。通读全文的你肯定收获满满,让我们继续为数据结构学习共同奋进!!!
免责声明:我们致力于保护作者版权,注重分享,被刊用文章因无法核实真实出处,未能及时与作者取得联系,或有版权异议的,请联系管理员,我们会立即处理! 部分文章是来自自研大数据AI进行生成,内容摘自(百度百科,百度知道,头条百科,中国民法典,刑法,牛津词典,新华词典,汉语词典,国家院校,科普平台)等数据,内容仅供学习参考,不准确地方联系删除处理! 图片声明:本站部分配图来自人工智能系统AI生成,觅知网授权图片,PxHere摄影无版权图库和百度,360,搜狗等多加搜索引擎自动关键词搜索配图,如有侵权的图片,请第一时间联系我们,邮箱:ciyunidc@ciyunshuju.com。本站只作为美观性配图使用,无任何非法侵犯第三方意图,一切解释权归图片著作权方,本站不承担任何责任。如有恶意碰瓷者,必当奉陪到底严惩不贷!