秋招突击——7/17——复习{二分查找——搜索插入位置、搜索二维矩阵,}——新作{链表——反转链表和回文链表,子串——和为K的子数组}
文章目录
- 引言
- 新作
- 二分模板
- 二分查找——搜索插入位置
- 复习实现
- 搜索二维矩阵
- 复习实现
- 新作
- 反转链表
- 个人实现
- 参考实现
- 回文链表
- 个人实现
- 参考实现
- 和为K的子数组
- 个人实现
- 参考实现
- 总结
引言
- 今天算法得是速通的,严格把控好时间,后面要准备去面试提前批了,项目得赶紧过!
- 今天复习一个模板,然后在整理一个模板!
新作
二分模板
void binSearch(int[] nums,int l,int r){ while(l int mid = (l + r + 1) > 1; if(nums[mid] >= tar) l = mid; else r = mid - 1;二分查找——搜索插入位置
- 题目链接
- 第一次做
- 第二次做
复习实现
- 这里是使用左边界的
class Solution { public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int tar) { int l = 0,r = nums.length - 1; while(l > 1; if(nums[mid] > tar) r = mid; else if(nums[mid] == tar) return mid; else l = mid + 1; } if(nums[l]右边界
class Solution { public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int tar) { int l = 0,r = nums.length - 1; while(l > 1; if(nums[mid]搜索二维矩阵
- 题目链接
- 第一次做
复习实现
- 这道题两种实现方式,一种是做两次二分查找,不过要明确好使用左边界还是右边界,是找第一个小的值还是第一个大的值,然后再确定是否存在,不存在直接跳出。这种比较耗时。
- 还有一种坐标转换,将所有的元素排成一个序列,然后从左到右进行查询,确定到具体的目标是转成对应二维矩阵的信息,进行比较!
class Solution { public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] mat, int tar) { // define the row and col of array int m = mat.length; int n = mat[0].length; // binSearch on the conversion of the index int l = 0; int r = m * n - 1; while(l > 1; if(mat[mid / n][ mid % n] >= tar) r = mid; else l = mid + 1; } return mat[l / n][ l % n] == tar; } }我靠,这样写,出奇的顺利,差不多五分钟就写完了!
新作
反转链表
题目链接
个人实现
- 这个就是常规的反转链表,很常见!
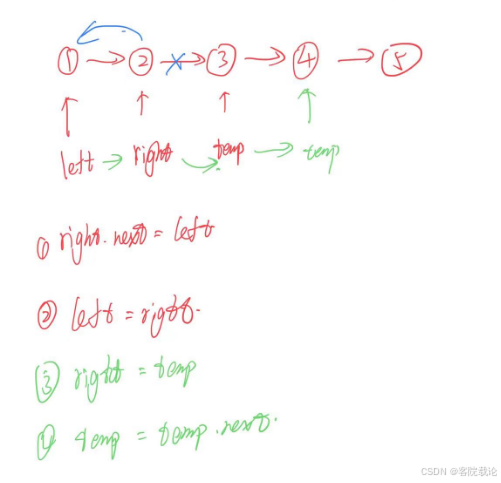
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { // handle the edge situation if(head == null || head.next == null) return head; // define dummy head to store the head node ListNode dummy = new ListNode(); dummy.next = head; // reverse the node list ListNode left = dummy.next; ListNode right = left.next; ListNode temp = right.next; left.next = null; while(temp != null){ right.next = left; left = right; right = temp; temp = temp.next; } right.next = left; left = right; dummy.next = right; return dummy.next; } }写是写出来了,但是太散了,还是要参考一下啊
参考实现
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { // handle the edge situation if(head == null || head.next == null) return head; // define dummy head to store the head node ListNode dummy = new ListNode(); dummy.next = head; // reverse the node list ListNode left = null; ListNode right = dummy.next;; while(right != null){ ListNode temp = right.next; right.next = left; left = right; right = temp; } dummy.next = left; return dummy.next; } }总结
- 其实我的代码有很多重复的地方,完全没有必要,总结下来:
- 反转链表两节点,next和pre,临时保存用temp,最终返回是pre。
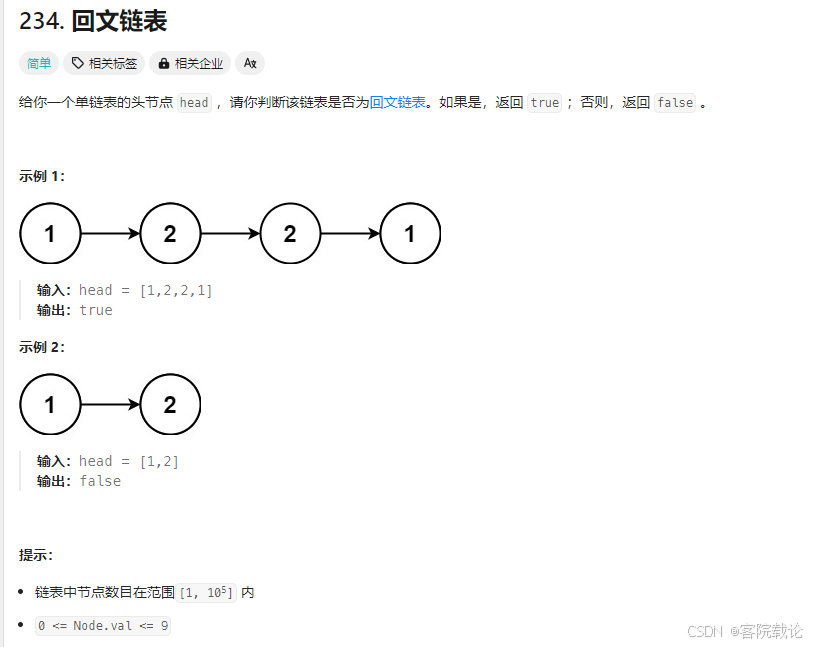
回文链表
题目链接
注意
- 链表节点数最少为1,直接返回
- 链表的值不用担心越界
- 要求时间复杂度是O(n),空间复杂度是O(1)
个人实现
- 这个是回文链表,也就双指针可以做,因为空间复杂度是O(1),并没有办法使用其他的数据结构,所以想想看,双指针怎么遍历。
- 如果节点数是奇数,一定不会是回文字符串,直接返回false
- 如果节点数是偶数,那么就要找到中间的节点数,直接将字符串进行拼接,然后再用反转不就行了!
- 遍历一遍,保存为字符串,先判定数量,数量一致,在使用字符串的操作。
- 看错了,回文是从前往后读,和从后往前读是一致的!
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) { ListNode temp = head; StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder(""); // traverse the list and judge the length while(temp != null){ str.append("" + temp.val); temp = temp.next; } String substr1 = str.toString(); //System.out.println(substr1 ); String substr2 = str.reverse().toString(); //System.out.println(substr2 ); return substr1.equals(substr2); } }问题
将int转成String
- String.valueOf(4);
- Integer.toString(4);
- “” + 4
StringBuilder的相关操作
- 添加元素:append,可以添加char,int还有string
- 删除元素:delete(start_idx,end_idx),删除这段索引之间的字符串
- 转为String:toString
- 获取子串:substring(start_idx,end_idx),注意,一定要是小写
- 获取长度:length(),除了collection是用size,其他都是使用length,不过string系列的要加括号
- 字符串比较相等,使用equals,不要使用==,需要转为string
- 字符串反转,reverse(),只能使用stringBuilder进行调用
这题做的不容易,补充了好多知识,真不容易!
参考实现
- 参考样例实现了三个方法
方法一
- 将数组保存为数组,然后的使用双指针进行反向遍历,跟我的很像。
方法二
- 使用栈实现逆序遍历,然后正向读取数据,然后的入栈,在逐个出栈,就是反向遍历单链表了。
方法三——快慢指针
- 两倍快指针到了终点,然后慢指针就是中点
- 反转两个链表,分别进行比较,然后再反转回来!
逆序遍历出栈入栈,确定中点快慢指针
和为K的子数组
- 题目链接
注意
- 必须要连续的序列,并且不能为空
- 可以为1个,可能是两个
- k是目标值,不会越界
- 数组是没有任何顺序的
个人实现
- 数组没有任何顺序,所以不能使用两数之和的方式进行计算,这里得想办法,表示一下两者的关系。
- 这里没有对时间复杂度做出要求,所以我们可以尝试直接暴力搜索去做。
- 实现思路如下
- 将前i项的序列保存为字典,O(n)
- 遍历每一个索引,并在字典中找到对应的索引值,找到了就符合条件,找不到跳过。O(n*n),最坏是平方。
- S[k] - S[i] = k,i public int subarraySum(int[] nums, int k) { // res == result int res = 0; // define the array to store the value of the sum int m = nums.length; int[] sumN = new int[m]; sumN[0] = nums[0]; // handle the special situation if(m == 1 && nums[0] != k) return 0; Map sumN[i] = nums[i] + sumN[i - 1]; //System.out.println(sumN[i]); List int resTar = sumN[r] - k; if(map.containsKey(resTar)){ for(int x : map.get(resTar)){ if(x
- 题目链接
- 使用栈实现逆序遍历,然后正向读取数据,然后的入栈,在逐个出栈,就是反向遍历单链表了。
- 将数组保存为数组,然后的使用双指针进行反向遍历,跟我的很像。
- 参考样例实现了三个方法
- 这个是回文链表,也就双指针可以做,因为空间复杂度是O(1),并没有办法使用其他的数据结构,所以想想看,双指针怎么遍历。
- 反转链表两节点,next和pre,临时保存用temp,最终返回是pre。
- 其实我的代码有很多重复的地方,完全没有必要,总结下来:
- 这个就是常规的反转链表,很常见!
- 这里是使用左边界的
免责声明:我们致力于保护作者版权,注重分享,被刊用文章因无法核实真实出处,未能及时与作者取得联系,或有版权异议的,请联系管理员,我们会立即处理! 部分文章是来自自研大数据AI进行生成,内容摘自(百度百科,百度知道,头条百科,中国民法典,刑法,牛津词典,新华词典,汉语词典,国家院校,科普平台)等数据,内容仅供学习参考,不准确地方联系删除处理! 图片声明:本站部分配图来自人工智能系统AI生成,觅知网授权图片,PxHere摄影无版权图库和百度,360,搜狗等多加搜索引擎自动关键词搜索配图,如有侵权的图片,请第一时间联系我们,邮箱:ciyunidc@ciyunshuju.com。本站只作为美观性配图使用,无任何非法侵犯第三方意图,一切解释权归图片著作权方,本站不承担任何责任。如有恶意碰瓷者,必当奉陪到底严惩不贷!