信号量——Linux并发之魂
欢迎来到 破晓的历程的 博客
VPS购买请点击我 引言
今天,我们继续学习Linux线程本分,在Linux条件变量中,我们对条件变量的做了详细的说明,今天我们要利用条件变量来引出我们的另一个话题——信号量内容的学习。
1.复习条件变量
在上一期博客中,我们没有对条件变量做具体的使用,所以,这里我们通过一份代码来复习一下,接下来,我们实现基于BlockingQueue的生产者消费者模型。
1.1何为基于BlockingQueue的生产者消费者模型
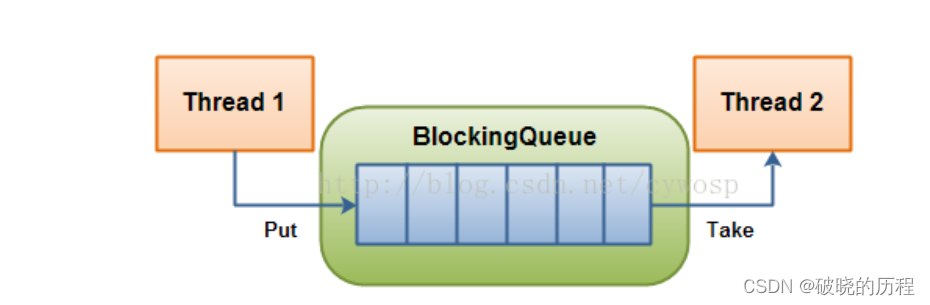
BlockingQueue在多线程编程中阻塞队列(Blocking Queue)是一种常用于实现生产者和消费者模型的数据结构。其与普通的队列区别在于,当队列为空时,从队列获取元素的操作将会被阻塞,直到队列中被放入了元素;当队列满时,往队列里存放元素的操作也会被阻塞,直到有元素被从队列中取出(以上的操作都是基于不同的线程来说的,线程在对阻塞队列进程操作时会被阻塞)
如图:
1.2分析该模型
这里我想写多个生产线程和多个消费线程的模型
我们来分析一下。
- 首先生产任务的过程和消费任务的过程必须是互斥关系,不可以同时访问该队列(此时,这个队列是共享资源)。
- 当队列满时,生产线程就不能再生产任务,必须在特定的条件变量下等待;同理当队列为空时,消费线程就不能再消费任务,也必须在特定的条件变量下等待。
所以,类应这样设计:
template
class BlockQueue
{
public:
BlockQueue(const int &maxcap=gmaxcap):_maxcap(maxcap)
{
pthread_mutex_init(&_mutex,nullptr);
pthread_cond_init(&_pcond,nullptr);
pthread_cond_init(&_ccond,nullptr);
}
void push(const T&in)//输入型参数,const &
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&_mutex);
while(is_full())
{
pthread_cond_wait(&_pcond,&_mutex);
}
_q.push(in);
pthread_cond_signal(&_ccond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_mutex);
}
void pop(T*out)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&_mutex);
while(is_empty())
{
pthread_cond_wait(&_ccond,&_mutex);
}
*out=_q.front();
_q.pop();
pthread_cond_signal(&_pcond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_mutex);
}
~BlockQueue()
{
pthread_mutex_destroy(&_mutex);
pthread_cond_destroy(&_ccond);
pthread_cond_destroy(&_pcond);
}
private:
bool is_empty()
{
return _q.empty();
}
bool is_full()
{
return _q.size()==_maxcap;
}
private:
std::queue _q;
int _maxcap; //队列中元素的上线
pthread_mutex_t _mutex;
pthread_cond_t _pcond; //生产者对应的条件变量
pthread_cond_t _ccond;
};
由于我们不知道存储的数据类型,所以这里我们选择使用泛型编程的方式。
接下来就是要生产任务,为了可以观察到整个生产和消费任务的过程,我们可以生成两个随机数,然后进行运算。代码如下:
class CalTask
{
using func_t = function;
public:
CalTask() {}
CalTask(int x, int y, char op, func_t func)
:_x(x),_y(y),_op(op),_callback(func)
{}
string operator()()
{
int result=_callback(_x,_y,_op);
char buffer[1024];
snprintf(buffer,sizeof buffer,"%d %c %d=%d",_x,_op,_y,result);
return buffer;
}
string toTaskstring()
{
char buffer[1024];
snprintf(buffer,sizeof buffer,"%d %c %d=?",_x,_op,_y);
return buffer;
}
private:
int _x;
int _y;
char _op;
func_t _callback;
};
const char*oper="+-*/%";
int mymath(int x,int y,char op)
{
int result=0;
switch(op)
{
case '+':
result=x+y;
break;
case '-':
result=x-y;
break;
case '*':
result=x*y;
break;
case '/':
if(y==0)
{
cerr
result=x/y;
}
break;
case '%':
if(y==0)
{
cerr
result=x%y;
}
default:
break;
}
return result;
}
public:
BlockQueue(const int &maxcap=gmaxcap):_maxcap(maxcap)
{
pthread_mutex_init(&_mutex,nullptr);
pthread_cond_init(&_pcond,nullptr);
pthread_cond_init(&_ccond,nullptr);
}
void push(const T&in)//输入型参数,const &
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&_mutex);
while(is_full())
{
pthread_cond_wait(&_pcond,&_mutex);
}
_q.push(in);
pthread_cond_signal(&_ccond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_mutex);
}
void pop(T*out)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&_mutex);
while(is_empty())
{
pthread_cond_wait(&_ccond,&_mutex);
}
*out=_q.front();
_q.pop();
pthread_cond_signal(&_pcond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_mutex);
}
~BlockQueue()
{
pthread_mutex_destroy(&_mutex);
pthread_cond_destroy(&_ccond);
pthread_cond_destroy(&_pcond);
}
private:
bool is_empty()
{
return _q.empty();
}
bool is_full()
{
return _q.size()==_maxcap;
}
private:
std::queue
using func_t = function}
CalTask(int x, int y, char op, func_t func)
:_x(x),_y(y),_op(op),_callback(func)
{}
string operator()()
{
int result=_callback(_x,_y,_op);
char buffer[1024];
snprintf(buffer,sizeof buffer,"%d %c %d=%d",_x,_op,_y,result);
return buffer;
}
string toTaskstring()
{
char buffer[1024];
snprintf(buffer,sizeof buffer,"%d %c %d=?",_x,_op,_y);
return buffer;
}
private:
int _x;
int _y;
char _op;
func_t _callback;
};
const char*oper="+-*/%";
int mymath(int x,int y,char op)
{
int result=0;
switch(op)
{
case '+':
result=x+y;
break;
case '-':
result=x-y;
break;
case '*':
result=x*y;
break;
case '/':
if(y==0)
{
cerr
cerr
result=x%y;
}
default:
break;
}
return result;
}
BlockQueue
int x=rand()%10+1;
int y=rand()%5+1;
int opercode=rand()%(sizeof(oper));
CalTask T(x,y,oper[opercode],mymath);
bqs-push(T);
cout
BlockQueue
CalTask T;
bqs-pop(&T);
cout
BlockQueue
pthread_create(&p[i],nullptr,productor,&bqs);
pthread_create(&c[i],nullptr,consumer,&bqs);
}
for(int i=0;i
pthread_join(p[i],nullptr);
pthread_join(c[i],nullptr);
}
}
private:
void P(sem_t &sem)
{
int n = sem_wait(&sem);
assert(n == 0); // if
(void)n;
}
void V(sem_t &sem)
{
int n = sem_post(&sem);
assert(n == 0);
(void)n;
}
public:
RingQueue(const int &cap = gcap): _queue(cap), _cap(cap)
{
int n = sem_init(&_spaceSem, 0, _cap);
assert(n == 0);
n = sem_init(&_dataSem, 0, 0);
assert(n == 0);
_productorStep = _consumerStep = 0;
pthread_mutex_init(&_pmutex, nullptr);
pthread_mutex_init(&_cmutex, nullptr);
}
// 生产者
void Push(const T &in)
{
// ?: 这个代码 有没有优化的可能
// 你认为:现加锁,后申请信号量,还是现申请信号量,在加锁?
P(_spaceSem); // 申请到了空间信号量,意味着,我一定能进行正常的生产
pthread_mutex_lock(&_pmutex);
_queue[_productorStep++] = in;
_productorStep %= _cap;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_pmutex);
V(_dataSem);
}
// 消费者
void Pop(T *out)
{
// 你认为:现加锁,后申请信号量,还是现申请信号量,在加锁?
P(_dataSem);
pthread_mutex_lock(&_cmutex);
*out = _queue[_consumerStep++];
_consumerStep %= _cap;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_cmutex);
V(_spaceSem);
}
~RingQueue()
{
sem_destroy(&_spaceSem);
sem_destroy(&_dataSem);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&_pmutex);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&_cmutex);
}
private:
std::vector
using func_t = std::function}
Task(int x, int y, char op, func_t func)
:_x(x), _y(y), _op(op), _callback(func)
{}
std::string operator()()
{
int result = _callback(_x, _y, _op);
char buffer[1024];
snprintf(buffer, sizeof buffer, "%d %c %d = %d", _x, _op, _y, result);
return buffer;
}
std::string toTaskString()
{
char buffer[1024];
snprintf(buffer, sizeof buffer, "%d %c %d = ?", _x, _op, _y);
return buffer;
}
private:
int _x;
int _y;
char _op;
func_t _callback;
};
const std::string oper = "+-*/%";
int mymath(int x, int y, char op)
{
int result = 0;
switch (op)
{
case '+':
result = x + y;
break;
case '-':
result = x - y;
break;
case '*':
result = x * y;
break;
case '/':
{
if (y == 0)
{
std::cerr
if (y == 0)
{
std::cerr
char name[128];
snprintf(name, sizeof(name), "thread[0x%x]", pthread_self());
return name;
}
void *ProductorRoutine(void *rq)
{
// RingQueue
// version1
// int data = rand() % 10 + 1;
// ringqueue-Push(data);
// std::cout
// RingQueue
//version1
// int data;
// ringqueue-Pop(&data);
// std::cout
srand((unsigned int)time(nullptr) ^ getpid() ^ pthread_self() ^ 0x71727374);
// RingQueue
免责声明:我们致力于保护作者版权,注重分享,被刊用文章因无法核实真实出处,未能及时与作者取得联系,或有版权异议的,请联系管理员,我们会立即处理! 部分文章是来自自研大数据AI进行生成,内容摘自(百度百科,百度知道,头条百科,中国民法典,刑法,牛津词典,新华词典,汉语词典,国家院校,科普平台)等数据,内容仅供学习参考,不准确地方联系删除处理! 图片声明:本站部分配图来自人工智能系统AI生成,觅知网授权图片,PxHere摄影无版权图库和百度,360,搜狗等多加搜索引擎自动关键词搜索配图,如有侵权的图片,请第一时间联系我们,邮箱:ciyunidc@ciyunshuju.com。本站只作为美观性配图使用,无任何非法侵犯第三方意图,一切解释权归图片著作权方,本站不承担任何责任。如有恶意碰瓷者,必当奉陪到底严惩不贷!