数据结构之栈与队列详解
温馨提示:这篇文章已超过387天没有更新,请注意相关的内容是否还可用!
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、栈
- 1.栈的概念及定义
- 2.栈的实现
- (1)栈的结构
- (2)StackInit(初始化)
- (3)StackPush(压栈)
- (4)StackPop(出栈)
- (5)StackTop(取栈顶的元素)
- (6)StackEmpty(检查栈是否为空)
- (7)StackDestroy(销毁栈)
- 3.完整代码
- (1)头文件
- (2)源文件
- 二、队列
- 1.队列的概念及定义
- 2.队列的实现
- (1)队列的结构
- (2)QueueInit(初始化)
- (3)QueuePush(入队)
- (4)QueuePop(出队)
- (5)QueueFront(获取头部元素)
- (6)QueueBack(获取尾部元素)
- (7)QueueEmpty(检查队列是否为空)
- 3.完整代码
- (1)头文件
- (2)源文件
- 结语
前言
栈和队列是一种特殊的线性结构,他与之前学的线性结构不同,栈和队列是拥有一种特殊规则的线性结构,虽然它是用数组或者链表实现,但是只有符合这种规则才能被称作栈或者队列
一、栈
1.栈的概念及定义
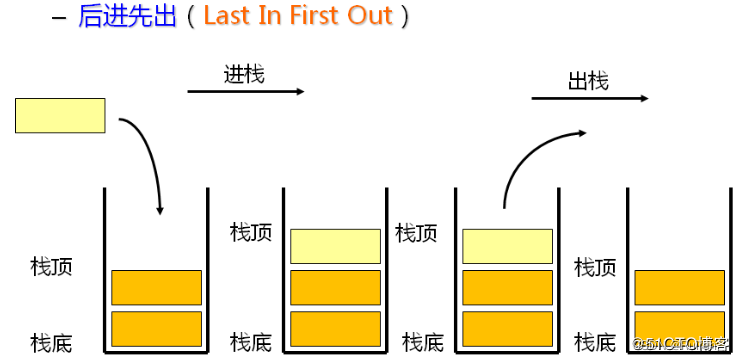
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。
2.栈的实现
栈的实现有两种实现,但是我们可以想想栈的特点,后进先出,我们只对尾部操作,那么是不是用数组刚好合适,虽然用链表也可以,但是数组的尾插的损耗更加小一点,所以我这里就一数组来进行讲解
我这里用动态的数组来实现栈
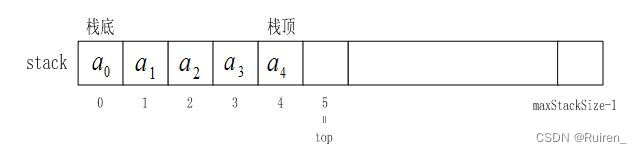
(1)栈的结构
typedef int STDataType;//方便存储各种数据 typedef struct Stack { STDataType* a; int top;//栈顶位置,如果等于capacity=0时为空 int capacity;//容量 }ST;(2)StackInit(初始化)
void StackInit(ST* ps) { assert(ps); ps->a = NULL; ps->top = 0;//初始化时如果top是0,即top指向栈顶上的后一位,所以取出元素时需要减一 ps->capacity = 0; }(3)StackPush(压栈)
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x) { assert(ps); if (ps->top == ps->capacity) { int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4: ps->capacity * 2; STDataType* temp = (STDataType * )realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType)*newcapacity); if (temp == NULL) { printf("realloc fail\n"); exit(-1); } ps->a = temp; ps->capacity = newcapacity; } ps->a[ps->top] = x; ps->top++; }这里的代码参考动态数组的实现
(4)StackPop(出栈)
void StackPop(ST* ps) { assert(ps); assert(ps->top > 0); ps->top--; }(5)StackTop(取栈顶的元素)
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps) { assert(ps); assert(ps->top > 0); return ps->a[ps->top - 1];//这里需要减一是因为top指向栈顶上的后一位,如果还不理解就看初始化代码 }(6)StackEmpty(检查栈是否为空)
布尔类型的数据在c使用需要加stdbool头文件
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps) { return ps->top == 0; }(7)StackDestroy(销毁栈)
void StackDestroy(ST* ps) { assert(ps); free(ps->a); ps->a = NULL; ps->capacity = 0; ps->top = 0; }3.完整代码
(1)头文件
#pragma once #include #include #include #include typedef int STDataType; typedef struct Stack { STDataType* a; int top; int capacity; }ST; void StackInit(ST* ps); void StackDestroy(ST* ps); void StackPush(ST* ps,STDataType x); void StackPop(ST* ps); STDataType StackTop(ST* ps); bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);(2)源文件
#include"Stack.h" void StackInit(ST* ps) { assert(ps); ps->a = NULL; ps->top = 0;//初始化时如果top是0,即top指向栈顶上的后一位 ps->capacity = 0; } void StackDestroy(ST* ps) { assert(ps); free(ps->a); ps->a = NULL; ps->capacity = 0; ps->top = 0; } void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x) { assert(ps); if (ps->top == ps->capacity) { int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4: ps->capacity * 2; STDataType* temp = (STDataType * )realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType)*newcapacity); if (temp == NULL) { printf("realloc fail\n"); exit(-1); } ps->a = temp; ps->capacity = newcapacity; } ps->a[ps->top] = x; ps->top++; } void StackPop(ST* ps) { assert(ps); assert(ps->top > 0); ps->top--; } STDataType StackTop(ST* ps) { assert(ps); assert(ps->top > 0); return ps->a[ps->top - 1]; } bool StackEmpty(ST* ps) { return ps->top == 0; }至此,栈算是搞完了,接下来讲队列
二、队列
1.队列的概念及定义
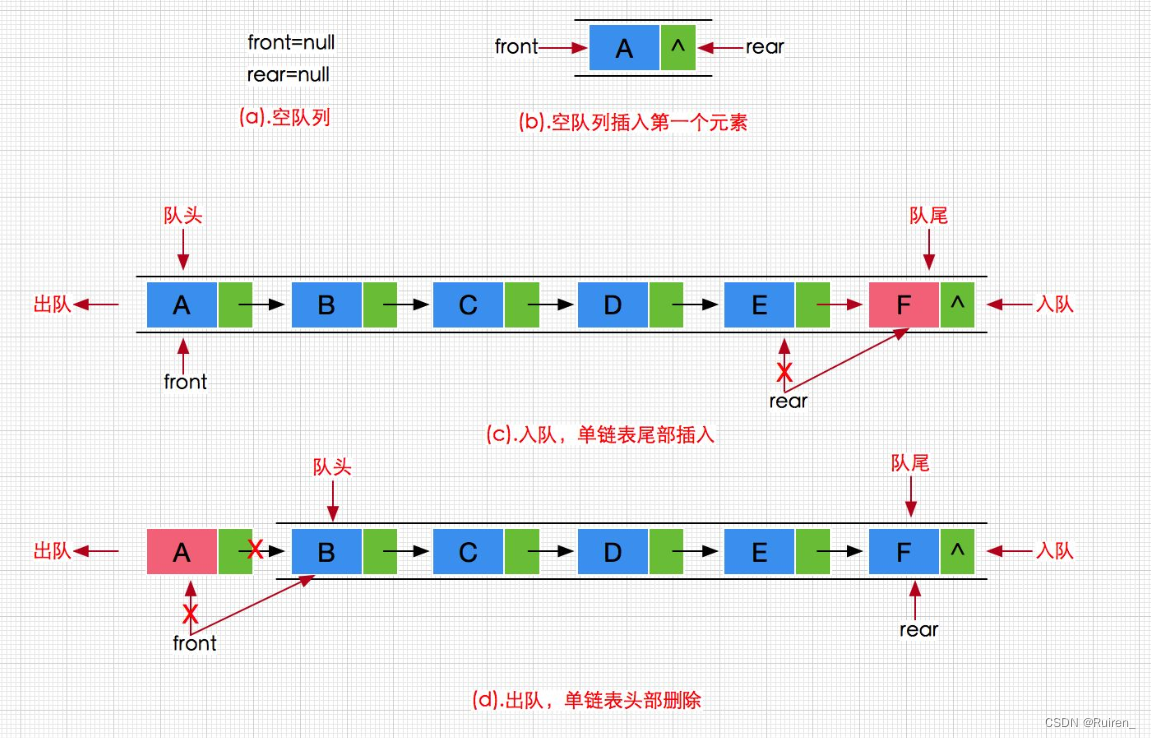
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out) 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
2.队列的实现
队列需要能够对头和尾操作,所以数组是不好实现的,我们用链表来实现
(1)队列的结构
队列的特点与排队购物差不多,我们要能够控制头的出和尾的进,所以与栈不一样,我们需要头和尾的位置所以我们就要实现成下面的样子
typedef int QDataType; typedef struct QueueNode//队列的节点 { struct QueueNode* next; QDataType data; }QN; typedef struct Queue//存储了头和尾,方便我们直接对头和尾操作 { QN* head; QN* tail; }Queue;此处的实现可以参考我前面的文章链表
(2)QueueInit(初始化)
void QueueInit(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); pq->head = NULL; pq->tail = NULL; }(3)QueuePush(入队)
尾入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x) { assert(pq); QN* newnode = (QN*)malloc(sizeof(QN)); newnode->data = x; newnode->next = NULL; if (pq->head == NULL) { pq->head = pq->tail = newnode; } else { pq->tail->next = newnode; pq->tail = newnode; } }(4)QueuePop(出队)
头出
void QueuePop(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); QN* next = pq->head->next; free(pq->head); pq->head = next; if (pq->head == NULL) { pq->tail = NULL; } }(5)QueueFront(获取头部元素)
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); return pq->head->data; }(6)QueueBack(获取尾部元素)
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq->tail)); return pq->tail->data; }(7)QueueEmpty(检查队列是否为空)
布尔类型需要包括头文件stdbool
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); return pq->head == NULL; }3.完整代码
(1)头文件
#pragma once #include #include #include #include typedef int QDataType; typedef struct QueueNode { struct QueueNode* next; QDataType data; }QN; typedef struct Queue { QN* head; QN* tail; }Queue; void QueueInit(Queue* pq); void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq); void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x); void QueuePop(Queue* pq); QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq); QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq); int QueueSize(Queue* pq); bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);(2)源文件
#include"Queue.h" void QueueInit(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); pq->head = NULL; pq->tail = NULL; } void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); QN* cur = pq->head; while (cur) { QN* next = cur->next; free(cur); cur = next; } } void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x) { assert(pq); QN* newnode = (QN*)malloc(sizeof(QN)); newnode->data = x; newnode->next = NULL; if (pq->head == NULL) { pq->head = pq->tail = newnode; } else { pq->tail->next = newnode; pq->tail = newnode; } } void QueuePop(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); QN* next = pq->head->next; free(pq->head); pq->head = next; if (pq->head == NULL) { pq->tail = NULL; } } QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); return pq->head->data; } QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq->tail)); return pq->tail->data; } bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); return pq->head == NULL; }结语
好了,栈和队列算是讲完了,如果有什么不妥之处欢迎指正,谢谢