C# WPF入门学习主线篇(三十三)—— 使用ICommand实现命令绑定
C# WPF入门学习主线篇(三十三)—— 使用ICommand实现命令绑定
在MVVM模式中,命令绑定是将用户交互(如按钮点击)与ViewModel中的方法连接起来的一种机制。使用ICommand接口可以实现这一功能,从而将UI逻辑与业务逻辑分离。本文将详细介绍如何使用ICommand实现命令绑定,并通过一个示例来演示具体的实现步骤。
一、ICommand接口概述
ICommand接口定义了执行命令的基本方法和事件,包括:
- Execute(object parameter): 定义命令执行的逻辑。
- CanExecute(object parameter): 确定命令是否可以执行。
- CanExecuteChanged: 当命令的执行状态发生变化时触发的事件。
通过实现ICommand接口,可以将用户的操作与ViewModel中的命令进行绑定。
二、创建RelayCommand类
为了简化ICommand的实现,我们可以创建一个通用的RelayCommand类。这个类将实现ICommand接口,并封装命令的执行逻辑和执行条件。
using System; using System.Windows.Input; public class RelayCommand : ICommand { private readonly Action _execute; private readonly Func _canExecute; public RelayCommand(Action execute, Func canExecute = null) { _execute = execute; _canExecute = canExecute; } public bool CanExecute(object parameter) { return _canExecute == null || _canExecute(parameter); } public void Execute(object parameter) { _execute(parameter); } public event EventHandler CanExecuteChanged { add { CommandManager.RequerySuggested += value; } remove { CommandManager.RequerySuggested -= value; } } }三、在ViewModel中使用RelayCommand
接下来,我们在ViewModel中定义命令并绑定到UI。在这个示例中,我们将实现一个简单的应用程序,其中包含一个按钮,点击按钮后更新文本框的内容。
1. 创建Model
首先,定义一个简单的Model类:
public class Person { public string Name { get; set; } public int Age { get; set; } }2. 创建ViewModel
接下来,创建ViewModel类,定义命令并绑定Model的数据:
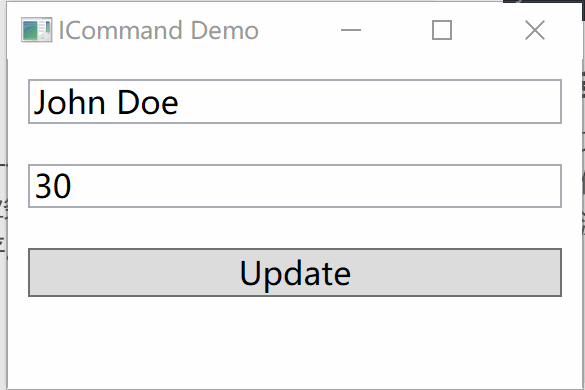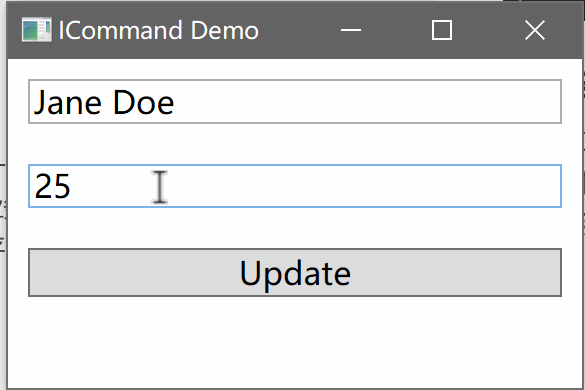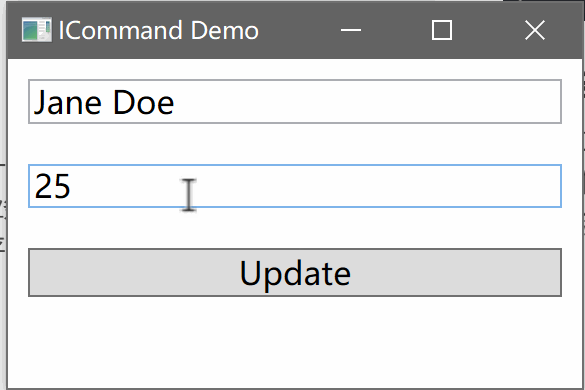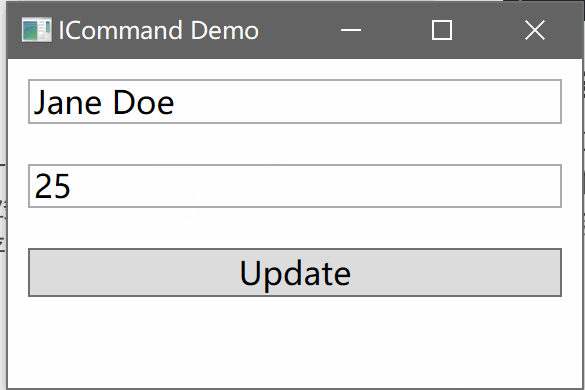
using System.ComponentModel; using System.Windows.Input; public class PersonViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged { private Person _person; public PersonViewModel() { _person = new Person { Name = "John Doe", Age = 30 }; UpdateCommand = new RelayCommand(UpdatePerson); } public string Name { get { return _person.Name; } set { if (_person.Name != value) { _person.Name = value; OnPropertyChanged(nameof(Name)); } } } public int Age { get { return _person.Age; } set { if (_person.Age != value) { _person.Age = value; OnPropertyChanged(nameof(Age)); } } } public ICommand UpdateCommand { get; } private void UpdatePerson(object parameter) { Name = "Jane Doe"; Age = 25; } public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged; protected void OnPropertyChanged(string propertyName) { PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName)); } }3. 创建View
在View(XAML文件)中,绑定命令和数据上下文:
4. 设置DataContext
在代码隐藏文件中,将ViewModel实例绑定到View的DataContext:
using System.Windows; namespace WpfApp { public partial class MainWindow : Window { public MainWindow() { InitializeComponent(); this.DataContext = new PersonViewModel(); } } }四、完整代码示例
MainWindow.xaml
MainWindow.xaml.cs
using System.Windows; namespace WpfApp { public partial class MainWindow : Window { public MainWindow() { InitializeComponent(); this.DataContext = new PersonViewModel(); } } }Person.cs
public class Person { public string Name { get; set; } public int Age { get; set; } }PersonViewModel.cs
using System.ComponentModel; using System.Windows.Input; public class PersonViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged { private Person _person; public PersonViewModel() { _person = new Person { Name = "John Doe", Age = 30 }; UpdateCommand = new RelayCommand(UpdatePerson); } public string Name { get { return _person.Name; } set { if (_person.Name != value) { _person.Name = value; OnPropertyChanged(nameof(Name)); } } } public int Age { get { return _person.Age; } set { if (_person.Age != value) { _person.Age = value; OnPropertyChanged(nameof(Age)); } } } public ICommand UpdateCommand { get; } private void UpdatePerson(object parameter) { Name = "Jane Doe"; Age = 25; } public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged; protected void OnPropertyChanged(string propertyName) { PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName)); } }RelayCommand.cs
using System; using System.Windows.Input; public class RelayCommand : ICommand { private readonly Action _execute; private readonly Func _canExecute; public RelayCommand(Action execute, Func canExecute = null) { _execute = execute; _canExecute = canExecute; } public bool CanExecute(object parameter) { return _canExecute == null || _canExecute(parameter); } public void Execute(object parameter) { _execute(parameter); } public event EventHandler CanExecuteChanged { add { CommandManager.RequerySuggested += value; } remove { CommandManager.RequerySuggested -= value; } } }五、总结
通过本文,我们详细介绍了如何在WPF应用程序中使用ICommand实现命令绑定,并通过一个具体的示例演示了如何实现命令绑定。使用命令绑定可以将用户交互与ViewModel中的命令连接起来,从而实现UI逻辑与业务逻辑的分离,提高代码的可维护性和可测试性。希望本文能帮助你更好地理解和应用ICommand接口,提高WPF开发的水平。
文章版权声明:除非注明,否则均为主机测评原创文章,转载或复制请以超链接形式并注明出处。