(五)共享模型之无锁
问题提出
有如下需求,保证 account.withdraw 取款方法的线程安全
interface Account {
// 获取余额
Integer getBalance();
// 取款
void withdraw(Integer amount);
static void demo(Account account) {
List ts = new ArrayList();
long start = System.nanoTime();
for (int i = 0; i {
account.withdraw(10);
}));
}
ts.forEach(Thread::start);
ts.forEach(t -> {
try {
t.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
});
long end = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println(account.getBalance() + " cost: " + (end-start)/1000_000 + " ms");
}
}
原有实现并不是线程安全的
class AccountUnsafe implements Account {
private Integer balance;
public AccountUnsafe(Integer balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
@Override
public Integer getBalance() {
return balance;
}
@Override
public void withdraw(Integer amount) {
balance -= amount;
}
}
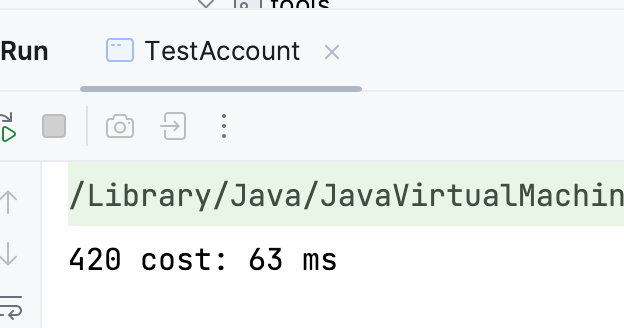
执行测试
class TestAccount {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AccountUnsafe accountUnsafe = new AccountUnsafe(1000);
Account.demo(accountUnsafe);
}
}
执行结果
同时有多个线程并发对变量 balance 进行操作,产生线程安全问题
解决思路-锁
首先想到的是给 Account 对象加锁
class AccountUnsafe implements Account {
private Integer balance;
public AccountUnsafe(Integer balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
@Override
public synchronized Integer getBalance() {
return balance;
}
@Override
public synchronized void withdraw(Integer amount) {
balance -= amount;
}
}
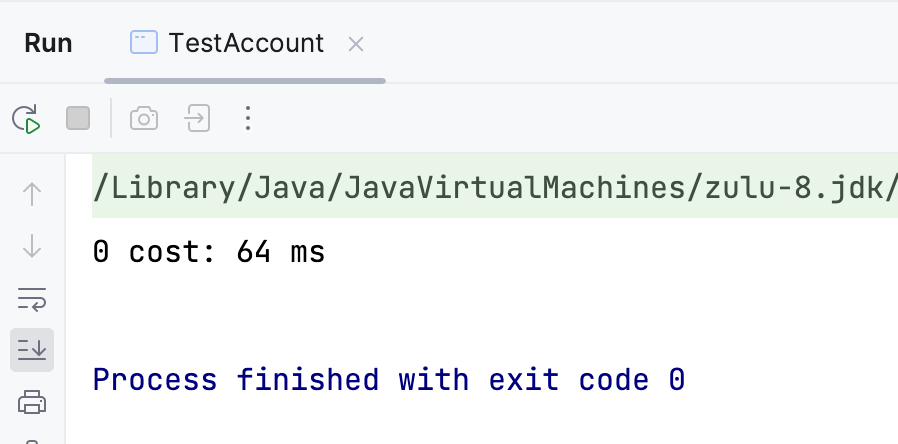
加锁后执行结果
解锁思路-无锁
class AccountSafe implements Account {
private AtomicInteger balance;
public AccountSafe(AtomicInteger balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
@Override
public Integer getBalance() {
return balance.get();
}
@Override
public void withdraw(Integer amount) {
while(true) {
int prev = balance.get();
int next = prev - amount;
if (balance.compareAndSet(prev, next)) {
break;
}
}
}
}
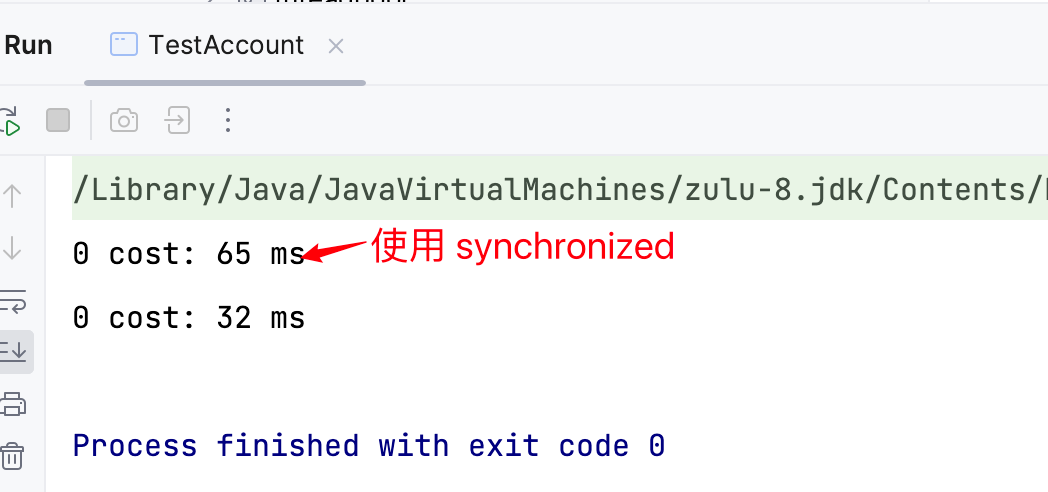
测试代码
class TestAccount {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AccountUnsafe accountUnsafe = new AccountUnsafe(10000);
AccountSafe accountSafe = new AccountSafe(new AtomicInteger(10000));
Account.demo(accountUnsafe);
Account.demo(accountSafe);
}
}
执行结果
CAS 与 volatile
前面看到的 AtomicInteger 的解决方法,内部并没有用锁来保护共享变量的线程安全。那么它是如何实现的呢?
public void withdraw(Integer amount) {
// 需要不断尝试,直到成功为止
while(true) {
// 比如拿到了旧值 1000
int prev = balance.get();
// 在这个基础上 1000 - 10 = 990
int next = prev - amount;
/*
* compareAndSet 正式做这个检查的,在 set 前,先比较 prev 与当前值
* 不一致了,next 作废,返回 false 表示失败
* 比如,别的线程已经做了减法,当前值已经被减成了 990
* 那么本线程的这次 990 就作废了,进入 while 下次循环重试
* 一致,以 next 设置为新值,返回 true 表示成功
*/
if (balance.compareAndSet(prev, next)) {
break;
}
}
}
其中的关键是 compareAndSet,它的简称就是 CAS (也有 Compare And Swap 的说法),它必须是原子操作。
:::tips
**注意 **
其实 CAS 的底层是 lock cmpxchg 指令(X86 架构),在单核 CPU 和多核 CPU 下都能够保证【比较-交换】的原子性
- 在多核状态下,某个核执行到带 lock 的指令时,CPU 会让总线锁住,当这个核把此指令执行完毕,再开启总线。这个过程中不会被线程的调度机制所打断,保证了多个线程对内存操作的准确性,是原子 的。
:::
volatile
获取共享变量时,为了保证该变量的可见性,需要使用 volatile 修饰。
它可以用来修饰成员变量和静态成员变量,可以避免线程从自己的工作缓存中查找变量的值,必须到主存中获取它的值,线程操作 volatile 变量都是直接操作主存,即一个线程对 volatile 变量的修改,对另一个线程可见。
:::tips
注意:
volatile 仅仅保证了共享变量的可见性,让其他线程能看到最新值,但不能解决指令交错问题(不能保证原子性)
:::
CAS 必须借助 volatile 才能读取到共享变量的最新值来实现【比较并交换】的效果。
为什么无锁效率高
- 无锁情况下,即使重试失败,线程始终在高速运行,没有停歇2,而 synchronized 会让线程在没有获得锁的时候,发生上下文切换,进入阻塞,打个比喻:线程就好像告诉跑道上的赛车,高速运行时,速度超快,一旦发生上下文切换,就好比赛车要减速、熄火,等被唤醒又得重新打火、启动、加速…恢复到高速运行,代价比较大
- 但无锁情况下,因为线程要保持运行,需要额外 CPU 的支持,CPU 在这里就好比高速跑道,没有额外的跑道,线程想高速运行也无从谈起,虽然不会进入阻塞,但由于没有分到时间片,仍然会进入可运行状态,还是会导致上下文切换。
CAS 的特点
结合 CAS 和 volatile 可以实现无锁并发,适用于线程数少、多核 CPU 的场景下。
- CAS 是基于乐观锁的思想:最乐观的估计,不怕别的线程来修改共享变量,就算改了也没关系,我吃亏点再重试呗。
- synchronized 是基于悲观锁的思想:最悲观的估计,得防着其它线程来修改共享变量,我上了锁你们都别想改,我改完了解开锁,你们才有机会。
- CAS 体现的是无锁并发、无阻塞并发
- 因为没有使用 synchronized,所以线程不会陷入阻塞,这是效率提升的因素之一
- 但如果竞争激烈,可以想到重试必然频繁发生,反而效率会受影响
原子整数
J.U.C 并发包提供了:
- AtomicBoolean
- AtomicInteger
- AtomicLong
以 AtomicInteger 为例:
AtomicInteger i = new AtomicInteger(0); // 获取并自增(i = 0, 结果 i = 1, 返回 0),类似于 i++ System.out.println(i.getAndIncrement()); // 自增并获取(i = 1, 结果 i = 2, 返回 2),类似于 ++i System.out.println(i.incrementAndGet()); // 自减并获取(i = 2, 结果 i = 1, 返回 1),类似于 --i System.out.println(i.decrementAndGet()); // 获取并自减(i = 1, 结果 i = 0, 返回 1),类似于 i-- System.out.println(i.getAndDecrement()); // 获取并加值(i = 0, 结果 i = 5, 返回 0) System.out.println(i.getAndAdd(5)); // 加值并获取(i = 5, 结果 i = 0, 返回 0) System.out.println(i.addAndGet(-5)); // 获取并更新(i = 0, p 为 i 的当前值, 结果 i = -2, 返回 0) // 其中函数中的操作能保证原子,但函数需要无副作用 System.out.println(i.getAndUpdate(p -> p - 2)); // 更新并获取(i = -2, p 为 i 的当前值, 结果 i = 0, 返回 0) // 其中函数中的操作能保证原子,但函数需要无副作用 System.out.println(i.updateAndGet(p -> p + 2)); // 获取并计算(i = 0, p 为 i 的当前值, x 为参数1, 结果 i = 10, 返回 0) // 其中函数中的操作能保证原子,但函数需要无副作用 // getAndUpdate 如果在 lambda 中引用了外部的局部变量,要保证该局部变量是 final 的 // getAndAccumulate 可以通过 参数1 来引用外部的局部变量,但因为其不在 lambda 中因此不必是 final System.out.println(i.getAndAccumulate(10, (p, x) -> p + x)); // 计算并获取(i = 10, p 为 i 的当前值, x 为参数1, 结果 i = 0, 返回 0) // 其中函数中的操作能保证原子,但函数需要无副作用 System.out.println(i.accumulateAndGet(-10, (p, x) -> p + x));
原子引用
为什么需要原子引用类型?
- AtomicReference
- AtomicMarkableReference
- AtomicStampedReference
有如下方法:
public interface DecimalAccount { // 获取余额 BigDecimal getBalance(); // 取款 void withdraw(BigDecimal amount); static void demo(DecimalAccount account) { List ts = new ArrayList(); for (int i = 0; i { account.withdraw(BigDecimal.TEN); })); } ts.forEach(Thread::start); ts.forEach(t -> { try { t.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } }); System.out.println(account.getBalance()); } }使用 CAS 锁实现安全的取款操作
class DecimalAccountCas implements DecimalAccount { private AtomicReference balance; public DecimalAccountCas(BigDecimal balance) { this.balance = new AtomicReference(balance); } @Override public BigDecimal getBalance() { return (BigDecimal) balance.get(); } @Override public void withdraw(BigDecimal amount) { while(true) { BigDecimal prev = getBalance(); BigDecimal next = prev.subtract(amount); if(balance.compareAndSet(prev, next)) { break; } } } }测试
class TestDecimalAccountCas { public static void main(String[] args) { DecimalAccount.demo(new DecimalAccountCas(new BigDecimal("10000"))); } }输出结果:
ABA 问题及解决
AtomicReference
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestABA") public class TestABA { static AtomicReference ref = new AtomicReference("A"); public static void main(String[] args) { log.debug("main start..."); // 获取值 A String prev = ref.get(); other(); sleep(1000); // 尝试改为 C log.debug("change A->C, {}", ref.compareAndSet(prev, "C")); } private static void other() { new Thread(() -> { log.debug("change A->B, {}", ref.compareAndSet(ref.get(), "B")); }, "t1").start(); sleep(500); new Thread(() -> { log.debug("change B->A, {}", ref.compareAndSet(ref.get(), "A")); }, "t2").start(); } private static void sleep(long time) { try { Thread.sleep(time); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }输出:
21:34:33.971 [main] - main start... 21:34:33.997 [t1] - change A->B, true 21:34:34.503 [t2] - change B->A, true 21:34:35.508 [main] - change A->C, true
主线程仅能判断出共享变量的值与最初值 A 是否相同,不能感知到这种从 A 改为 B 又改回 A 的情况,如果主线程希望:只要有其他线程【动过了】共享变量,那么自己的 CAS 计算失败,这时,仅比较值是不够的,需要再加一个版本号。
AtomicStampedReference
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestABA") public class TestABA { static AtomicStampedReference ref = new AtomicStampedReference("A", 0); public static void main(String[] args) { log.debug("main start..."); // 获取值 A String prev = ref.getReference(); int stamp = ref.getStamp(); log.debug("版本 {}", stamp); other(); sleep(1000); // 尝试改为 C log.debug("change A->C, {}", ref.compareAndSet(prev, "C", stamp, stamp + 1)); } private static void other() { new Thread(() -> { log.debug("change A->B, {}", ref.compareAndSet(ref.getReference(), "B", ref.getStamp(), ref.getStamp() + 1)); }, "t1").start(); log.debug("更新版本为 {}", ref.getStamp()); sleep(500); new Thread(() -> { log.debug("change B->A, {}", ref.compareAndSet(ref.getReference(), "A", ref.getStamp(), ref.getStamp() + 1)); }, "t2").start(); log.debug("更新版本为 {}", ref.getStamp()); } private static void sleep(long time) { try { Thread.sleep(time); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }输出为:
22:06:25.993 [main] - main start... 22:06:25.994 [main] - 版本 0 22:06:26.022 [t1] - change A->B, true 22:06:26.022 [main] - 更新版本为 0 22:06:26.528 [t2] - change B->A, true 22:06:26.528 [main] - 更新版本为 1 22:06:27.533 [main] - change A->C, false
AtomicStampedReference 可以给原子引用加上版本号,追踪原子应用整个的变化过程,如:A -> B -> A -> C,通过 AtomicStampedReference,我们可以知道,引用变量中途被更改了几次。
但是有时候,并不关心引用变量更改了几次,只是单纯的关心是否更改过,所以就有了 AtomicMakableReference。
AtomicMakableReference
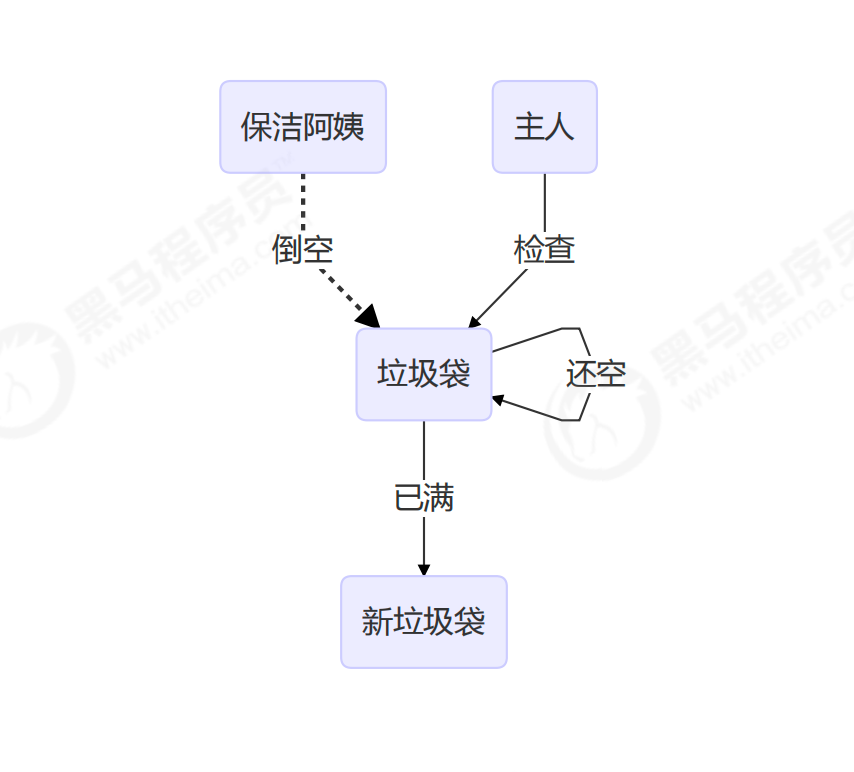
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestABAAtomicMarkableReference") public class TestABAAtomicMarkableReference { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { GarbageBag bag = new GarbageBag("装满垃圾了"); AtomicMarkableReference ref = new AtomicMarkableReference(bag, true); log.debug("main start..."); GarbageBag prev = ref.getReference(); log.debug(prev.toString()); new Thread(() -> { log.debug("打扫卫生的线程 start..."); bag.setDesc("空垃圾袋"); ref.compareAndSet(bag, bag, true, false); log.debug(bag.toString()); }, "保洁阿姨").start(); Thread.sleep(1000); log.debug("想换一只新垃圾袋?"); boolean success = ref.compareAndSet(prev, new GarbageBag("空的垃圾袋"), true, false); log.debug("换了么?" + success); log.debug(ref.getReference().toString()); } } class GarbageBag { String desc; public GarbageBag(String desc) { this.desc = desc; } public void setDesc(String desc) { this.desc = desc; } @Override public String toString() { return "GarbageBag{" + "desc='" + desc + '\'' + '}'; } }输出结果:
22:43:40.296 [main] - main start... 22:43:40.297 [main] - GarbageBag{desc='装满垃圾了'} 22:43:40.322 [保洁阿姨] - 打扫卫生的线程 start... 22:43:40.322 [保洁阿姨] - GarbageBag{desc='空垃圾袋'} 22:43:41.327 [main] - 想换一只新垃圾袋? 22:43:41.328 [main] - 换了么?false 22:43:41.328 [main] - GarbageBag{desc='空垃圾袋'}注释掉打扫卫生线程代码,再观察输出
22:45:29.014 [main] - main start... 22:45:29.015 [main] - GarbageBag{desc='装满垃圾了'} 22:45:30.017 [main] - 想换一只新垃圾袋? 22:45:30.017 [main] - 换了么?true 22:45:30.017 [main] - GarbageBag{desc='空的垃圾袋'}**原子数组 **
- AtomicIntegerArray
- AtomicLongArray
- AtomicReferenceArray
有如下方法:
public class Test27 { /** 参数1,提供数组、可以是线程不安全数组或线程安全数组 参数2,获取数组长度的方法 参数3,自增方法,回传 array, index 参数4,打印数组的方法 */ // supplier 提供者 无中生有 ()->结果 // function 函数 一个参数一个结果 (参数)->结果 , BiFunction (参数1,参数2)->结果 // consumer 消费者 一个参数没结果 (参数)->void, BiConsumer (参数1,参数2)-> private static void demo(Supplier arraySupplier, Function lengthFunc, BiConsumer putConsumer, Consumer printConsumer) { List ts = new ArrayList(); T array = arraySupplier.get(); int length = lengthFunc.apply(array); for (int i = 0; i { for (int j = 0; j t.start()); ts.forEach(t -> { try { t.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } }); printConsumer.accept(array); } public static void main(String[] args) { // 不安全的数组 System.out.print("不安全的数组:"); demo( () -> new int[10], array -> array.length, // 此处通过泛型确定 Fuction 接口中的 T 为 int 型数组 (array, index) -> array[index]++, array -> System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)) ); // 安全的数组 System.out.print("安全的数组:"); demo( () -> new AtomicIntegerArray(10), array -> array.length(), // 此处通过泛型确定 Fuction 接口中的 T 为 int 型数组 (array, index) -> array.getAndIncrement(index), array -> System.out.println(array) ); } }输出结果:
不安全的数组:[9131, 9043, 9256, 9288, 9221, 9231, 9212, 9212, 9199, 9225] 安全的数组:[10000, 10000, 10000, 10000, 10000, 10000, 10000, 10000, 10000, 10000]
字段更新器
- AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater // 域字段
- AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater
- AtomicLongFieldUpdater
利用字段更新器,可以针对对象的某个域(Field)进行原子操作,只能配合 volatile 修饰的字段使用,否则会出现异常:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Must be volatile type
public class Test40 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Student stu = new Student(); AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater updater = AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater.newUpdater(Student.class, String.class, "name"); new Thread(() -> { stu.name = "李四"; }).start(); Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println(updater.compareAndSet(stu, null, "张三")); System.out.println(stu); } } class Student { volatile String name; @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + '}'; } }输出:
false Student{name='李四'}原子累加器
累加器性能比较
public class Test41 { private static void demo(Supplier addSupplier, Consumer action) { T adder = addSupplier.get(); long start = System.nanoTime(); List ts = new ArrayList(); for (int i = 0; i { for (int j = 0; j t.start()); ts.forEach(t -> { try { t.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } }); long end = System.nanoTime(); System.out.println(adder + " cost:" + (end - start)/1000_000); } }比较 AtomicLong 与 LongAdder
public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("累加器 LongAdder:"); for (int i = 0; i new LongAdder(), adder -> adder.increment()); } System.out.println("--------------------------------"); System.out.println("累加器 AtomicLong:"); for (int i = 0; i new AtomicLong(), adder -> adder.getAndIncrement()); } }输出
累加器 LongAdder: 2000000 cost:14 2000000 cost:14 2000000 cost:4 2000000 cost:4 2000000 cost:5 -------------------------------- 累加器 AtomicLong: 2000000 cost:33 2000000 cost:26 2000000 cost:27 2000000 cost:27 2000000 cost:25
性能提升的原因很简单,就是在有竞争时,设置多个累加单元,Thread-0 累加 Cell[0],而 Thread-1 累加 Cell[1]…最后将结果汇总。这样它们在累加时操作的不同的 Cell 变量,因为减少了 CAS 重试失败,从而提高性能。
源码之 LongAdder
LongAdder 类有几个关键域
// 累加单元数组,懒惰初始化 transient volatile Cell[] cells; // 基础值,如果没有竞争,则用 cas 累加这个域 transient volatile long base; // 在 cells 创建或扩容时,置为 1,表示加锁 transient volatile int cellBusy;
cas 锁
// 不要用于实践!!! public class LockCas { private AtomicInteger state = new AtomicInteger(0); public void lock() { while (true) { if (state.compareAndSet(0, 1)) { break; } } } public void unlock() { log.debug("unlock..."); state.set(0); } }测试
LockCas lock = new LockCas(); new Thread(() -> { log.debug("begin..."); lock.lock(); try { log.debug("lock..."); sleep(1); } finally { lock.unlock(); } }, "t1").start(); new Thread(() -> { log.debug("begin..."); lock.lock(); try { log.debug("lock..."); } finally { lock.unlock(); } }, "t2").start();输出
18:27:07.198 c.Test42 [t1] - begin... 18:27:07.202 c.Test42 [t1] - lock... 18:27:07.198 c.Test42 [t2] - begin... 18:27:08.204 c.Test42 [t1] - unlock... 18:27:08.204 c.Test42 [t2] - lock... 18:27:08.204 c.Test42 [t2] - unlock...
原理之伪共存
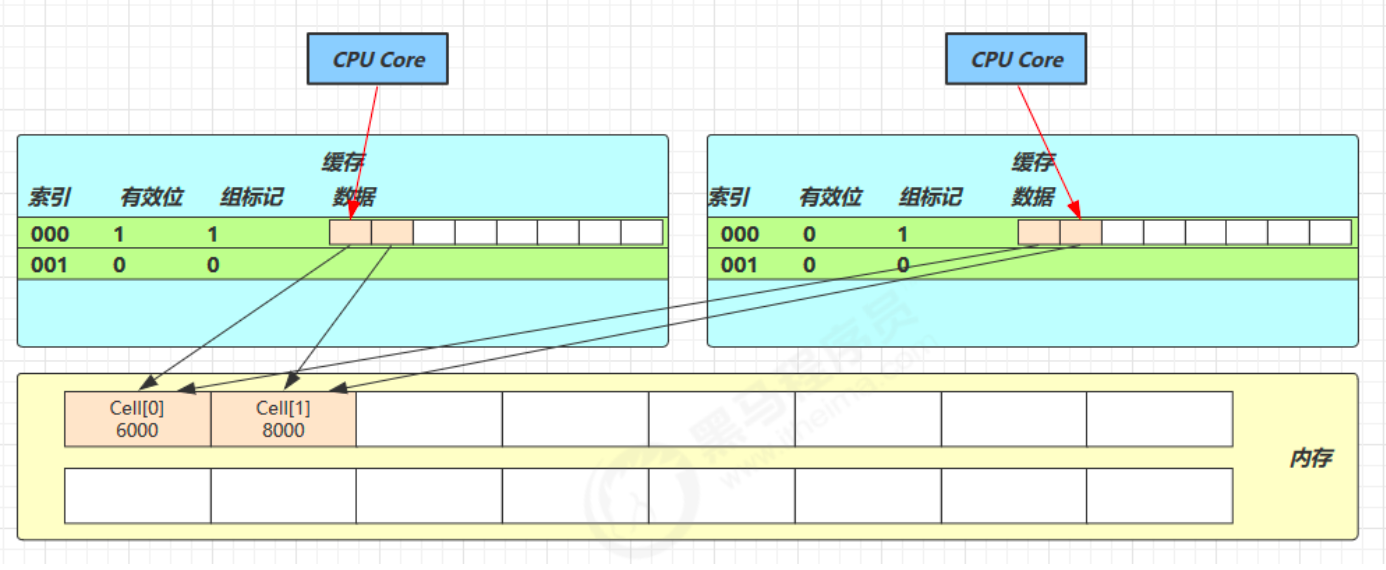
其中 Cell 即为累加单元
abstract class Striped64 extends Number { // 防止缓存行伪共享 @sun.misc.Contended static final class Cell { volatile long value; Cell(long x) { value = x; } // 最重要的方法, 用 cas 方式来进行累加, cmp 表示旧值, val 表示新值 final boolean cas(long cmp, long val) { return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapLong(this, valueOffset, cmp, val); } // 省略不重要代码 } }得从缓存说起
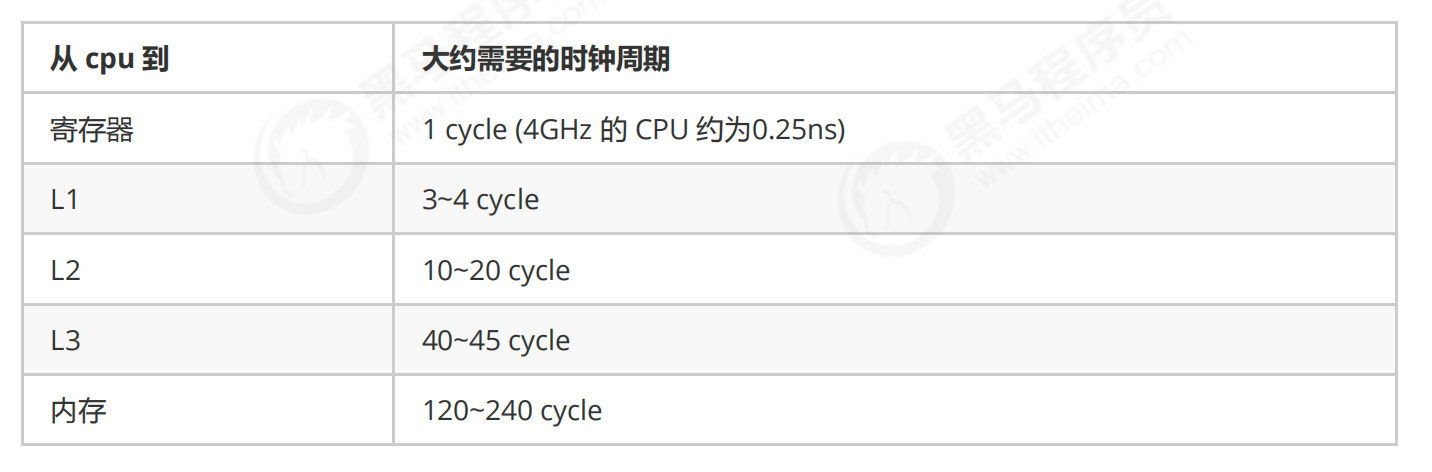
缓存与内存的速度比较
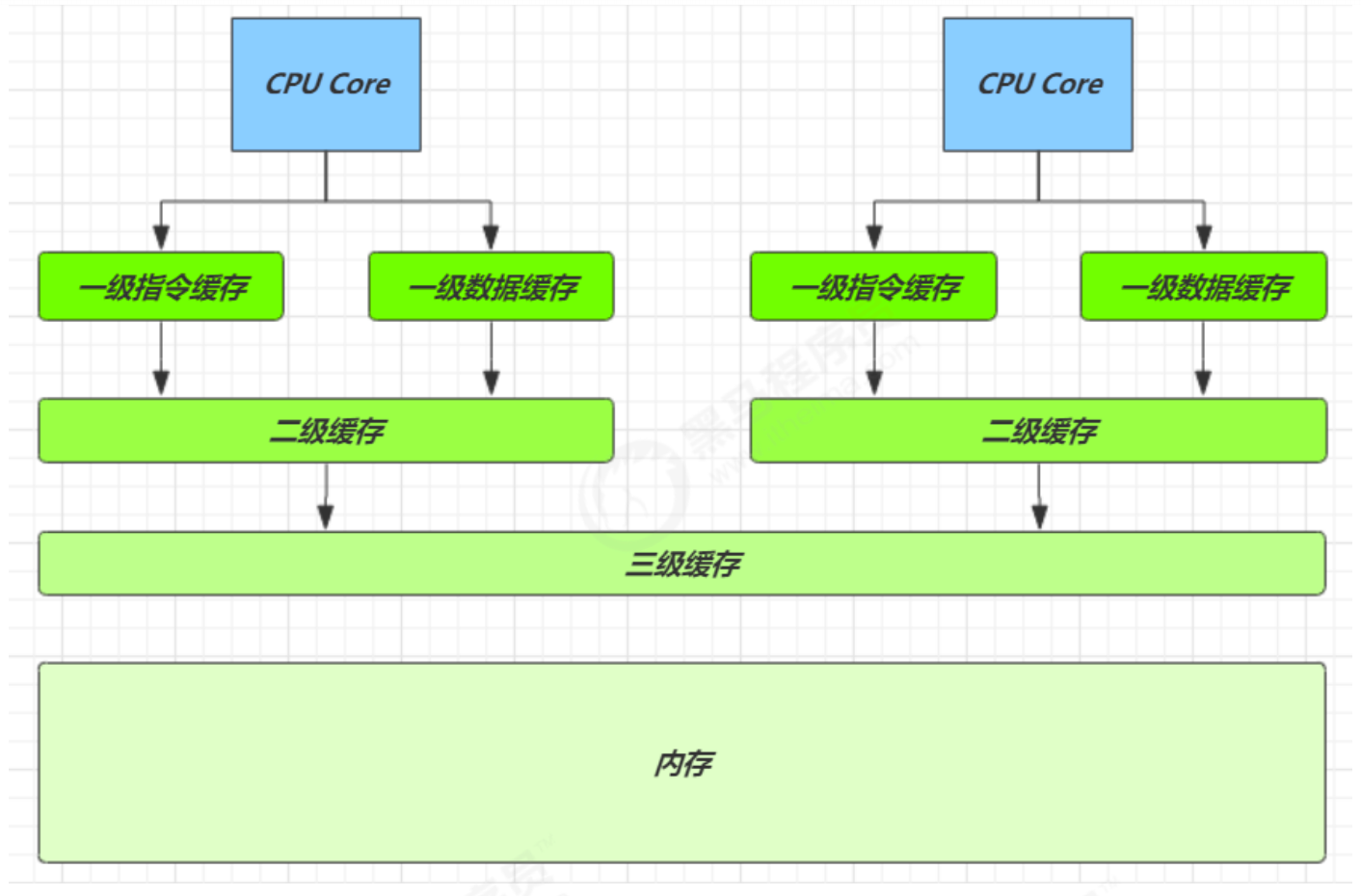
因为 CPU 与 内存的速度差异很大,需要靠预读数据至缓存来提升效率。
而缓存以缓存行为单位,每个缓存行对应着一块内存,一般是 64 byte(8 个 long)
缓存的加入会造成数据副本的产生,即同一份数据会缓存在不同核心的缓存行中
CPU 要保证数据的一致性,如果某个 CPU 核心更改了数据,其它 CPU 核心对应的整个缓存行必须失效
因为 Cell 是数组形式,在内存中是连续存储的,一个 Cell 为 24 字节(16 字节的对象头和 8 字节的 value),因此缓存行可以存下 2 个 Cell 对象。这样问题来了:
- Core-0 要修改 Cell[0]
- Core-1 要修改 Cell[1]
- 一个 Core 对应一个线程,一个线程负责修改一个 Cell。
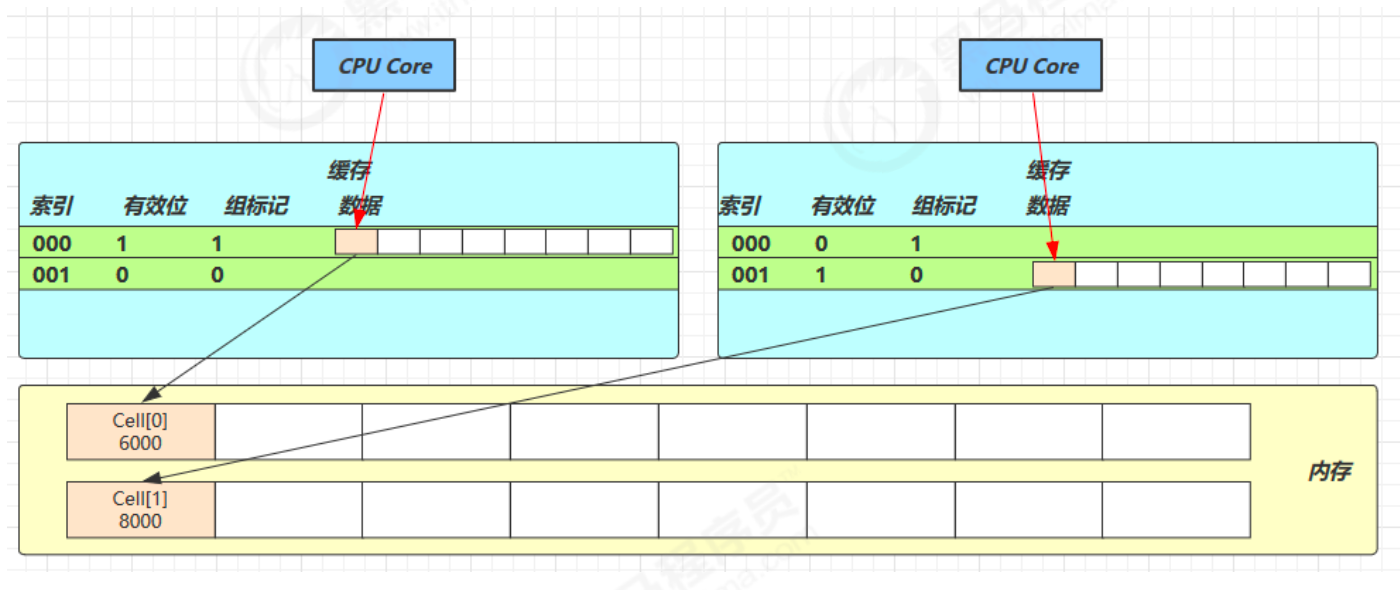
无论谁修改成功,都会导致对方 Core 的缓存行失效,比如 Core-0 中Cell[0]=6000, Cell[1]=8000要累加Cell[0]=6001, Cell[1]=8000,这时会让 Core-1 的缓存行失效
@sun.misc.Contended 用来解决这个问题,它的原理是在使用此注解的对象或字段的前后各增加 128 字节大小的 padding,从而让 CPU 将对象预读至缓存时占用不同的缓存行,这样,不会造成对方缓存行的失效。
累加主要调用下面的 add 方法:
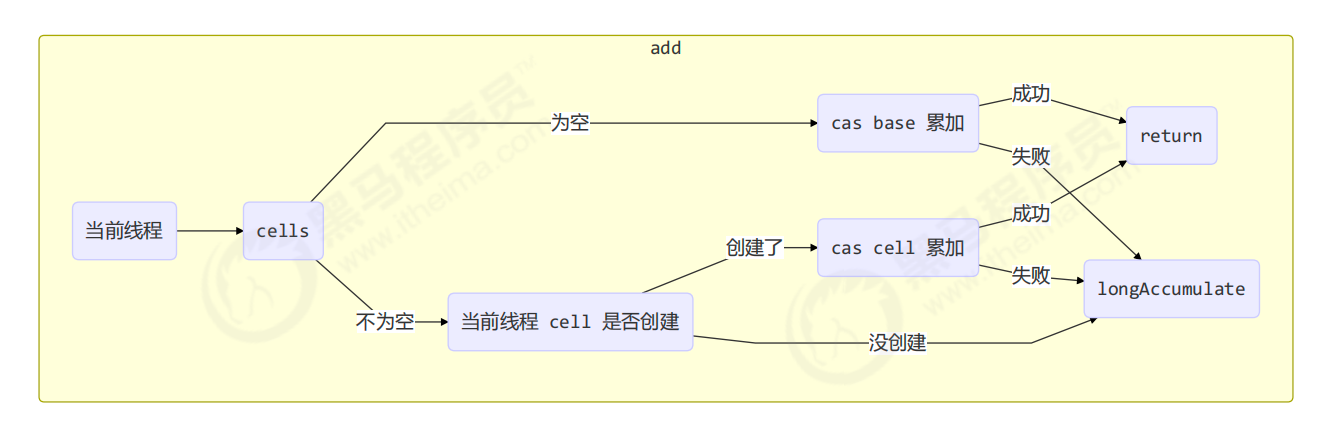
public class LongAdder extends Striped64 implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 7249069246863182397L; /** * Creates a new adder with initial sum of zero. */ public LongAdder() { } /** * Adds the given value. * * @param x the value to add */ public void add(long x) { // as 为累加单元数组 // b 为基础值 // x 为累加值 Cell[] as; long b, v; int m; Cell a; // 进入 if 的两个条件 // 1. as 有值, 表示已经发生过竞争, 进入 if // 2. cas 给 base 累加时失败了, 表示 base 发生了竞争, 进入 if // base 是父类 Striped64 中的 volatile 变量 // base:基值,主要在无争用时使用,但也在表初始化竞争期间用作回退。通过 CAS 更新。 // casBase:父类方法 if ((as = cells) != null || !casBase(b = base, b + x)) { // uncontended 表示 cell 没有竞争 boolean uncontended = true; // as 还没有创建 if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1)add 流程图:
abstract class Striped64 extends Number { // CPU 数量,要限制 Cell 数组的大小 static final int NCPU = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(); // Cell 数组。当非 null 时,size 是 2 的幂 transient volatile Cell[] cells; // 基值,主要在无争用时使用,但也在表初始化竞争期间用作回退。通过 CAS 更新。 transient volatile long base; // 调整大小和/或创建 Cell 数组时使用的自旋锁(通过 CAS 锁定) transient volatile int cellsBusy; final boolean casBase(long cmp, long val) { return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASE, cmp, val); } final void longAccumulate(long x, LongBinaryOperator fn, boolean wasUncontended) { int h; // 当前线程还没有对应的 cell, 需要随机生成一个 h 值用来将当前线程绑定到 cell if ((h = getProbe()) == 0) { // 初始化 probe ThreadLocalRandom.current(); // force initialization // h 对应新的 probe 值, 用来对应 cell h = getProbe(); wasUncontended = true; } // collide 为 true 表示需要扩容 boolean collide = false; // True if last slot nonempty for (;;) { Cell[] as; Cell a; int n; long v; // 已经有了 cells if ((as = cells) != null && (n = as.length) > 0) { // 还没有 cell if ((a = as[(n - 1) & h]) == null) { // 为 cellsBusy 加锁, 创建 cell, cell 的初始累加值为 x // 成功则 break, 否则继续 continue 循环 if (cellsBusy == 0) { // Try to attach new Cell Cell r = new Cell(x); // Optimistically create if (cellsBusy == 0 && casCellsBusy()) { boolean created = false; try { // Recheck under lock Cell[] rs; int m, j; if ((rs = cells) != null && (m = rs.length) > 0 && rs[j = (m - 1) & h] == null) { rs[j] = r; created = true; } } finally { cellsBusy = 0; } if (created) break; continue; // Slot is now non-empty } } collide = false; } // 有竞争, 改变线程对应的 cell 来重试 cas else if (!wasUncontended) // CAS already known to fail wasUncontended = true; // Continue after rehash // cas 尝试累加, fn 配合 LongAccumulator 不为 null, 配合 LongAdder 为 null else if (a.cas(v = a.value, ((fn == null) ? v + x : fn.applyAsLong(v, x)))) break; // 如果 cells 长度已经超过了最大长度, 或者已经扩容, 改变线程对应的 cell 来重试 cas else if (n >= NCPU || cells != as) collide = false; // At max size or stale // 确保 collide 为 false 进入此分支, 就不会进入下面的 else if 进行扩容了 else if (!collide) collide = true; // 加锁 else if (cellsBusy == 0 && casCellsBusy()) { // 加锁成功, 扩容 try { if (cells == as) { // Expand table unless stale Cell[] rs = new Cell[n cellsBusy = 0; } collide = false; continue; // Retry with expanded table } // 改变线程对应的 cell h = advanceProbe(h); } // 还没有 cells, 尝试给 cellsBusy 加锁 else if (cellsBusy == 0 && cells == as && casCellsBusy()) { // 加锁成功, 初始化 cells, 最开始长度为 2, 并填充一个 cell boolean init = false; try { // Initialize table if (cells == as) { Cell[] rs = new Cell[2]; rs[h & 1] = new Cell(x); cells = rs; init = true; } } finally { cellsBusy = 0; } // 成功则 break; if (init) break; } // 上两种情况失败, 尝试给 base 累加 else if (casBase(v = base, ((fn == null) ? v + x : fn.applyAsLong(v, x)))) break; // Fall back on using base } } } Cell[] as = cells; Cell a; long sum = base; if (as != null) { for (int i = 0; i