Java基础(十九):集合框架
目录
- 一、Java集合框架体系
- 二、Collection接口及方法
- 1、添加
- 2、判断
- 3、删除
- 4、其它
- 三、Iterator(迭代器)接口
- 1、Iterator接口
- 2、迭代器的执行原理
- 3、foreach循环
- 四、Collection子接口1:List
- 1、List接口特点
- 2、List接口方法
- 3、List接口主要实现类:ArrayList
- 4、List的实现类之二:LinkedList
- 5、List的实现类之三:Vector
- 五、Collection子接口2:Set
- 1、Set接口概述
- 2、Set主要实现类:HashSet
- 2.1、HashSet概述
- 2.2、HashSet中添加元素的过程
- 2.3、重写 hashCode() 方法的基本原则
- 2.4、重写equals()方法的基本原则
- 3、Set实现类之二:LinkedHashSet
- 4、Set实现类之三:TreeSet
- 六、Map接口
- 1、Map接口概述
- 2、Map中key-value特点
- 3、Map接口的常用方法
- 4、Map的主要实现类:HashMap
- 5、Map实现类之二:LinkedHashMap
- 6、Map实现类之三:TreeMap
- 7、Map实现类之四:Hashtable
- 8、Map实现类之五:Properties
- 七、Collections工具类
- 1、常用方法
- 2、举例
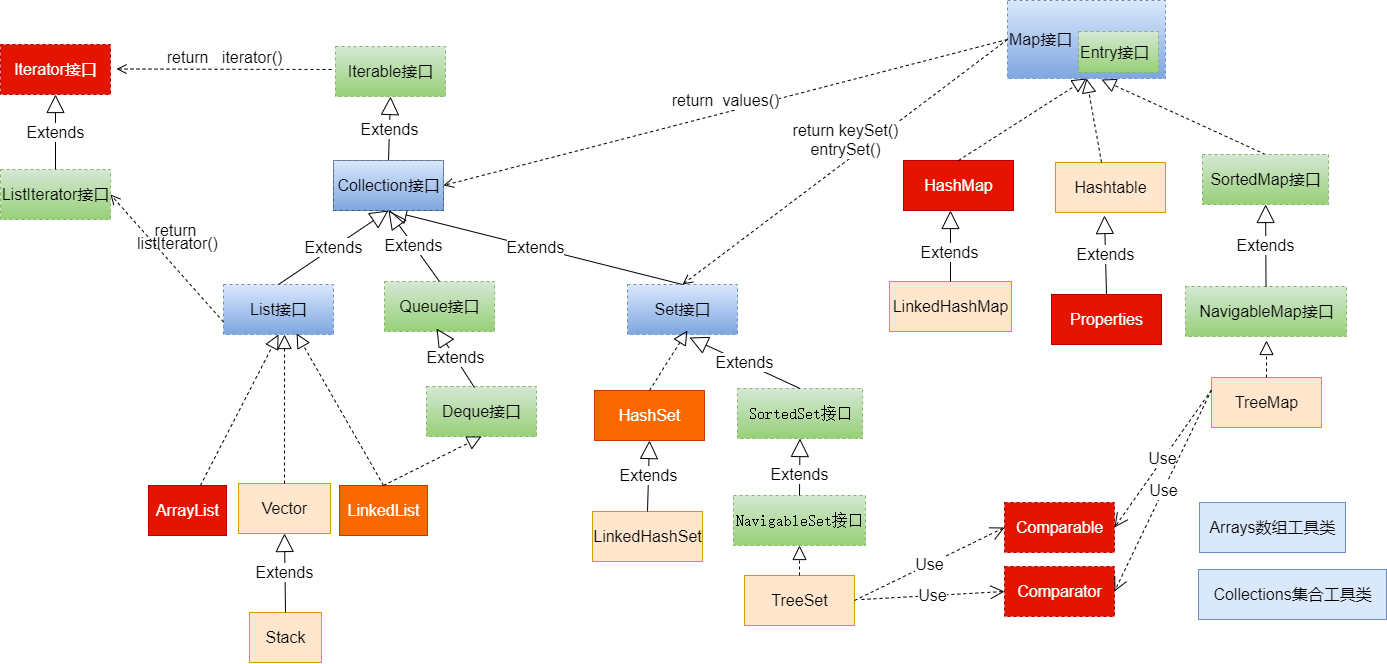
一、Java集合框架体系
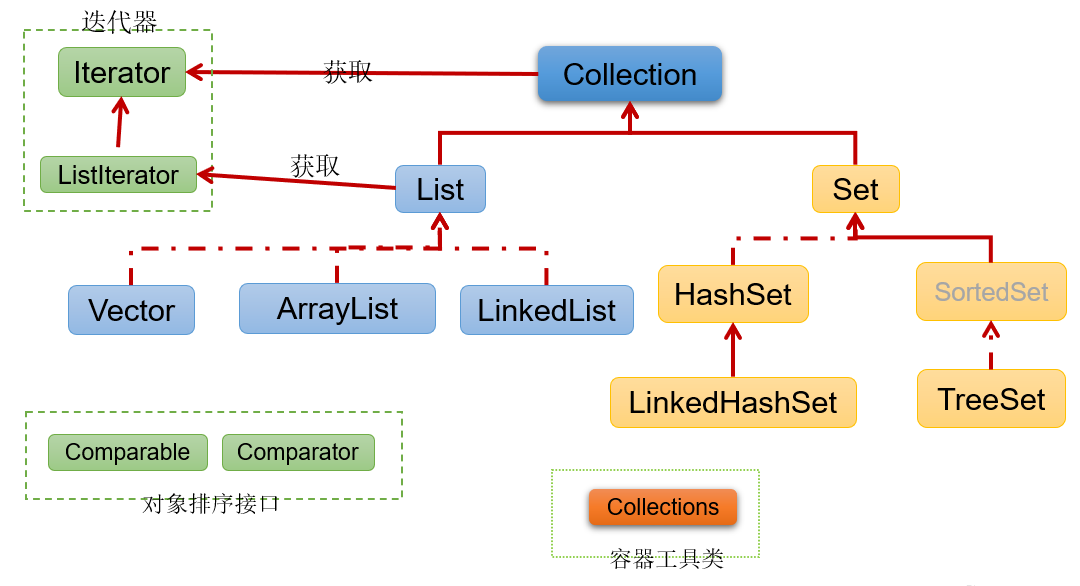
Java 集合可分为 Collection 和 Map 两大体系
- Collection接口:用于存储一个一个的数据,也称单列数据集合
- List子接口:用来存储有序的、可以重复的数据(主要用来替换数组,"动态"数组)
- 实现类:ArrayList(主要实现类)、LinkedList、Vector
- Set子接口:用来存储无序的、不可重复的数据(类似于高中讲的"集合")
- 实现类:HashSet(主要实现类)、LinkedHashSet、TreeSet
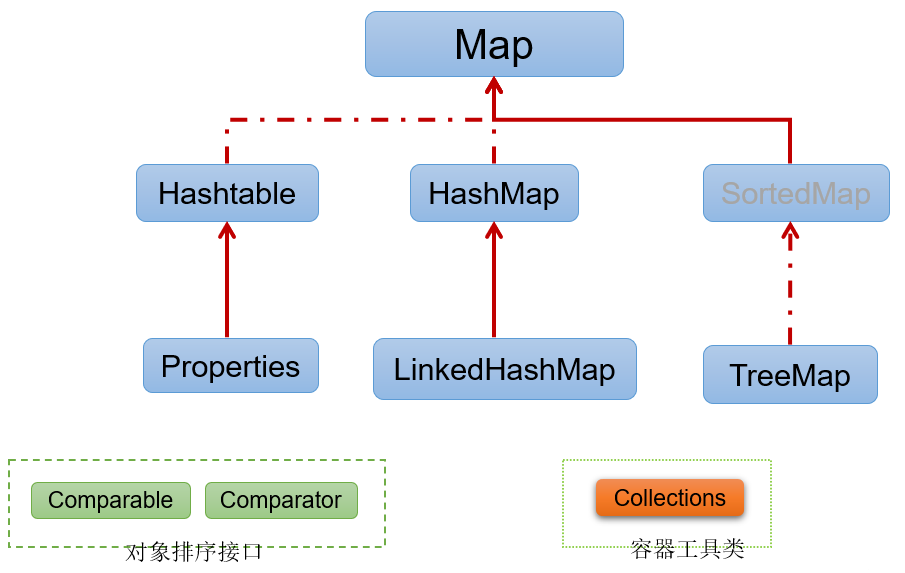
- Map接口:用于存储具有映射关系“key-value对”的集合,即一对一对的数据,也称双列数据集合
- HashMap(主要实现类)、LinkedHashMap、TreeMap、Hashtable、Properties
集合框架全图
Collection接口继承树
Map接口继承树
二、Collection接口及方法
- JDK不提供此接口的任何直接实现,而是提供更具体的子接口(如:Set和List)去实现
- Collection 接口是 List和Set接口的父接口,该接口里定义的方法既可用于操作 Set 集合,也可用于操作 List 集合
1、添加
- add(E obj):添加元素对象到当前集合中
- addAll(Collection other):添加other集合中的所有元素对象到当前集合中
@Test public void test1(){ Collection coll = new ArrayList(); //add() coll.add("AA"); coll.add(123);//自动装箱 coll.add("么么哒"); System.out.println(coll); // [AA, 123, 么么哒] //addAll(Collection other) Collection coll1 = new ArrayList(); coll1.add("BB"); coll1.add(456); coll.addAll(coll1); System.out.println(coll); // [AA, 123, 么么哒, BB, 456] coll.add(coll1); System.out.println(coll); // [AA, 123, 么么哒, BB, 456, [BB, 456]] }2、判断
- int size():获取当前集合中实际存储的元素个数
- boolean isEmpty():判断当前集合是否为空集合
- boolean contains(Object obj):判断当前集合中是否存在一个与obj对象equals返回true的元素
- boolean containsAll(Collection coll):判断coll集合中的元素是否在当前集合中都存在。即coll集合是否是当前集合的“子集”
- boolean equals(Object obj):判断当前集合与obj是否相等
3、删除
- void clear():清空集合元素
- boolean remove(Object obj) :从当前集合中删除第一个找到的与obj对象equals返回true的元素
- boolean removeAll(Collection coll):从当前集合中删除所有与coll集合中相同的元素
4、其它
- Object[] toArray():返回包含当前集合中所有元素的数组
- hashCode():获取集合对象的哈希值
- iterator():返回迭代器对象,用于集合遍历
@Test public void test2(){ Collection coll = new ArrayList(); coll.add("AA"); coll.add("AA"); Person p1 = new Person("Tom",12); coll.add(p1); coll.add(128);//自动装箱 //集合 ---> 数组 Object[] arr = coll.toArray(); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); // [AA, AA, Person{name='Tom', age=12}, 128] //hashCode(): System.out.println(coll.hashCode()); // -912175978 }三、Iterator(迭代器)接口
1、Iterator接口
- JDK专门提供了一个接口java.util.Iterator遍历集合中的所有元素
- Collection接口与Map接口主要用于存储元素
- Iterator,被称为迭代器接口,本身并不提供存储对象的能力,主要用于遍历Collection中的元素
- Collection接口继承了java.lang.Iterable接口
- 该接口有一个iterator()方法,那么所有实现了Collection接口的集合类都有一个iterator()方法,用以返回一个实现了Iterator接口的对象
- public Iterator iterator(): 获取集合对应的迭代器,用来遍历集合中的元素的
- 集合对象每次调用iterator()方法都得到一个全新的迭代器对象,默认游标都在集合的第一个元素之前
- Iterator接口的常用方法如下
- public E next():返回迭代的下一个元素
- public boolean hasNext():如果仍有元素可以迭代,则返回 true
- 注意:在调用it.next()方法之前必须要调用it.hasNext()进行检测。若不调用,且下一条记录无效,直接调用it.next()会抛出NoSuchElementException异常
@Test public void test3(){ Collection coll = new ArrayList(); coll.add("小李广"); coll.add("扫地僧"); coll.add("石破天"); Iterator iterator = coll.iterator(); //获取迭代器对象 while(iterator.hasNext()) { //判断是否还有元素可迭代 System.out.println(iterator.next()); //取出下一个元素 } }- 使用Iterator迭代器删除元素:java.util.Iterator迭代器中有一个方法:void remove()
@Test public void test4(){ Collection coll = new ArrayList(); coll.add(1); coll.add(2); coll.add(3); coll.add(4); coll.add(5); coll.add(6); Iterator iterator = coll.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()){ Integer element = (Integer) iterator.next(); if(element % 2 == 0){ iterator.remove(); } } System.out.println(coll); // [1, 3, 5] }2、迭代器的执行原理
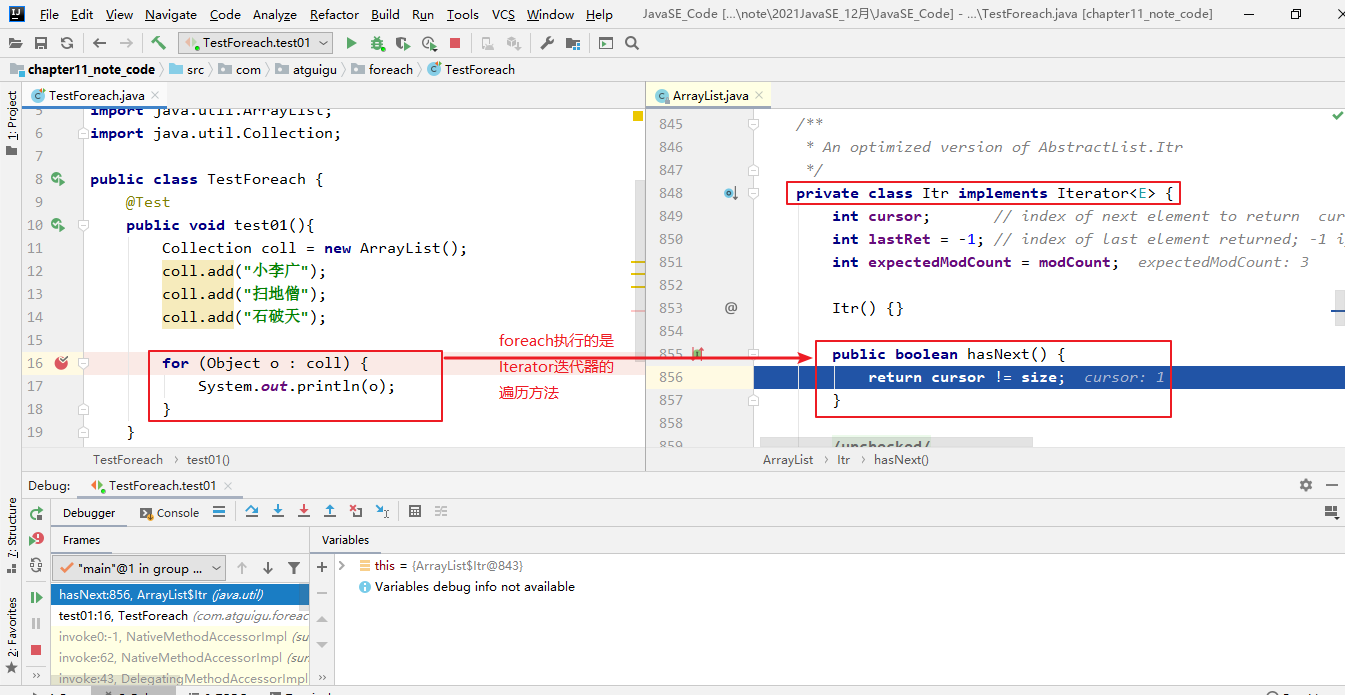
- Iterator迭代器对象在遍历集合时,内部采用指针的方式来跟踪集合中的元素
- 接下来通过一个图例来演示Iterator对象迭代元素的过程
3、foreach循环
- foreach循环(也称增强for循环)是 JDK5.0 中定义的一个高级for循环,专门用来遍历数组和集合的
- foreach循环的语法格式:
for(元素的数据类型 局部变量 : Collection集合或数组){ //操作局部变量的输出操作 } //这里局部变量就是一个临时变量,自己命名就可以举例:
@Test public void test5(){ Collection coll = new ArrayList(); coll.add("小李广"); coll.add("扫地僧"); coll.add("石破天"); //foreach循环其实就是使用Iterator迭代器来完成元素的遍历的。 for (Object o : coll) { System.out.println(o); } }- 对于集合的遍历,增强for的内部原理其实是个Iterator迭代器
- 它用于遍历Collection和数组。通常只进行遍历元素,不要在遍历的过程中对集合元素进行增删操作
public class InterviewTest { @Test public void testFor() { String[] arr1 = new String[]{"AA", "CC", "DD"}; //赋值操作1 // for(int i = 0;i- 赋值操作1结果:[MM, MM, MM]
- 赋值操作2结果:[AA, CC, DD]
四、Collection子接口1:List
1、List接口特点
- 鉴于Java中数组用来存储数据的局限性,我们通常使用java.util.List替代数组
- List集合类中元素有序、且可重复,集合中的每个元素都有其对应的顺序索引
- JDK API中List接口的实现类常用的有:ArrayList、LinkedList和Vector
2、List接口方法
List除了从Collection集合继承的方法外,List 集合里添加了一些根据索引来操作集合元素的方法
- 插入元素
- void add(int index, Object ele):在index位置插入ele元素
- boolean addAll(int index, Collection eles):从index位置开始将eles中的所有元素添加进来
- 获取元素
- Object get(int index):获取指定index位置的元素
- List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex):返回从fromIndex到toIndex位置的子集合
- 获取元素索引
- int indexOf(Object obj):返回obj在集合中首次出现的位置
- int lastIndexOf(Object obj):返回obj在当前集合中末次出现的位置
- 删除和替换元素
- Object remove(int index):移除指定index位置的元素,并返回此元素
- Object set(int index, Object ele):设置指定index位置的元素为ele
举例:
public class TestListMethod { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建List集合对象 List list = new ArrayList(); // 往 尾部添加 指定元素 list.add("图图"); list.add("小美"); list.add("不高兴"); System.out.println(list); // [图图, 小美, 不高兴] // 往指定位置添加 list.add(1,"没头脑"); System.out.println(list); // [图图, 没头脑, 小美, 不高兴] // 删除指定位置元素 返回被删除元素 System.out.println(list.remove(2)); System.out.println(list); // [图图, 没头脑, 不高兴] // 在指定位置 进行 元素替代(改) // 修改指定位置元素 list.set(0, "三毛"); System.out.println(list); // [三毛, 没头脑, 不高兴] } }3、List接口主要实现类:ArrayList
- ArrayList 是 List 接口的主要实现类
- 本质上,ArrayList是对象引用的一个”变长”数组
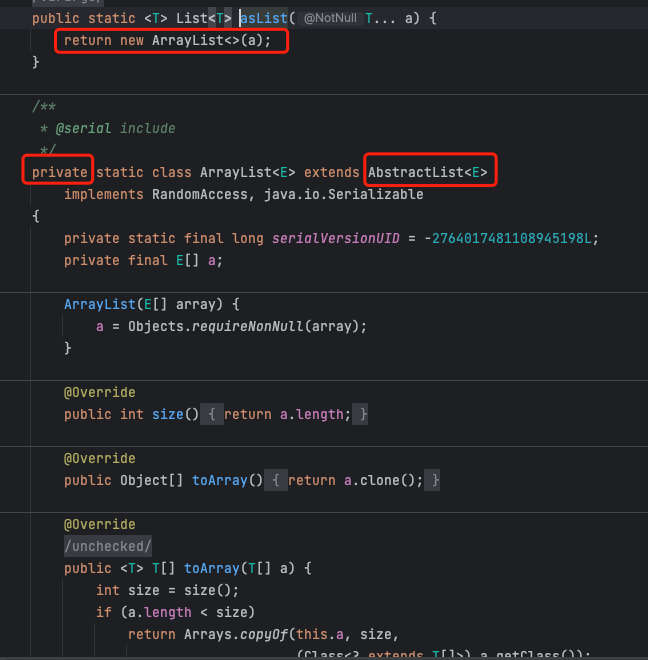
Arrays.asList(…) 方法创建集合
- Arrays.asList(…) 方法返回的 List 集合,既不是 ArrayList 实例,也不是 Vector 实例
- Arrays.asList(…) 返回值是一个固定长度的 List 集合
- 返回值对象Arrays.ArrayList,Arrays工具类的内部类ArrayList
- 继承AbstractList也就是实现List接口
- 但是Arrays.ArrayList没有重写add方法
- 所以返回的此集合不能新增
- 私有内部类,所以返回值用父类List表示,而不能用Arrays.ArrayList
public abstract class AbstractList extends AbstractCollection implements List { protected AbstractList() { } public boolean add(E e) { add(size(), e); return true; } ... public void add(int index, E element) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } }例子:
@Test public void test6(){ List list = Arrays.asList("1", "2", "3"); list.add("a"); }输出结果:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException at java.util.AbstractList.add(AbstractList.java:148) at java.util.AbstractList.add(AbstractList.java:108)
4、List的实现类之二:LinkedList
- 对于频繁的插入或删除元素的操作,建议使用LinkedList类,效率较高
- 这是由底层采用链表(双向链表)结构存储数据决定的
- 特有方法
- void addFirst(Object obj)
- void addLast(Object obj)
- Object getFirst()
- Object getLast()
- Object removeFirst()
- Object removeLast()
5、List的实现类之三:Vector
- Vector 是一个古老的集合,JDK1.0就有了
- 大多数操作与ArrayList相同,区别之处在于Vector是线程安全的
- 在各种List中,最好把ArrayList作为默认选择
- 当插入、删除频繁时,使用LinkedList
- Vector总是比ArrayList慢,所以尽量避免使用
- 特有方法:
- void addElement(Object obj)
- void insertElementAt(Object obj,int index)
- void setElementAt(Object obj,int index)
- void removeElement(Object obj)
- void removeAllElements()
五、Collection子接口2:Set
1、Set接口概述
- Set接口是Collection的子接口,Set接口相较于Collection接口没有提供额外的方法
- Set 集合不允许包含相同的元素,如果试把两个相同的元素加入同一个 Set 集合中,则添加操作失败
- Set集合支持的遍历方式和Collection集合一样:foreach和Iterator
- Set的常用实现类有:HashSet、TreeSet、LinkedHashSet
2、Set主要实现类:HashSet
2.1、HashSet概述
- HashSet 是 Set 接口的主要实现类,大多数时候使用 Set 集合时都使用这个实现类
- HashSet 按 Hash 算法来存储集合中的元素,因此具有很好的存储、查找、删除性能
- HashSet 具有以下特点:
- 不能保证元素的排列顺序
- HashSet 不是线程安全的
- 集合元素可以是 null
- HashSet 集合判断两个元素相等的标准:
- 两个对象通过 hashCode() 方法得到的哈希值相等
- 并且两个对象的 equals() 方法返回值为true
- 对于存放在Set容器中的对象,对应的类一定要重写hashCode()和equals(Object obj)方法,以实现对象相等规则。即:“相等的对象必须具有相等的散列码”
- HashSet集合中元素的无序性,不等同于随机性。这里的无序性与元素的添加位置有关
- 具体来说:我们在添加每一个元素到数组中时
- 具体的存储位置是由元素的hashCode()调用后返回的hash值决定的
- 导致在数组中每个元素不是依次紧密存放的,表现出一定的无序性
2.2、HashSet中添加元素的过程
- 第1步:当向 HashSet 集合中存入一个元素时
- HashSet 会调用该对象的 hashCode() 方法得到该对象的 hashCode值
- 然后根据 hashCode值
- 通过某个散列函数决定该对象在 HashSet 底层数组中的存储位置
- 第2步:如果要在数组中存储的位置上没有元素,则直接添加成功
- 第3步:如果要在数组中存储的位置上有元素,则继续比较
- 如果两个元素的hashCode值不相等,则添加成功
- 如果两个元素的hashCode()值相等,则会继续调用equals()方法
- 如果equals()方法结果为false,则添加成功
- 如果equals()方法结果为true,则添加失败
- 第3步两种添加成功的操作,由于该底层数组的位置已经有元素了,则会通过链表的方式继续链接,存储
2.3、重写 hashCode() 方法的基本原则
- 在程序运行时,同一个对象多次调用 hashCode() 方法应该返回相同的值
- 当两个对象的 equals() 方法比较返回 true 时,这两个对象的 hashCode() 方法的返回值也应相等
- 对象中用作 equals() 方法比较的 Field,都应该用来计算 hashCode 值
注意:如果两个元素的 equals() 方法返回 true,但它们的 hashCode() 返回值不相等,hashSet 将会把它们存储在不同的位置,但依然可以添加成功
2.4、重写equals()方法的基本原则
- 重写equals方法的时候一般都需要同时复写hashCode方法
- 通常参与计算hashCode的对象的属性也应该参与到equals()中进行计算
- 为什么用Eclipse/IDEA复写hashCode方法,有31这个数字?
- 首先,选择系数的时候要选择尽量大的系数。因为如果计算出来的hash地址越大,所谓的“冲突”就越少,查找起来效率也会提高。(减少冲突)
- 其次,31只占用5bits,相乘造成数据溢出的概率较小
- 再次,31可以 由i*31== (i String name; int age; public Person() { } public Person(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { System.out.println("Person equals()..."); if (this == o) return true; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; Person person = (Person) o; return age == person.age && Objects.equals(name, person.name); } @Override public int hashCode() { System.out.println("Person hashCode()..."); return Objects.hash(name, age); } } Set set = new HashSet(); set.add("AA"); set.add(123); set.add("BB"); set.add(new Person("Tom",12)); set.add(new Person("Tom",12)); Iterator iterator = set.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()){ System.out.println(iterator.next()); } } name='Tom', age=12} LinkedHashSet set = new LinkedHashSet(); set.add("张三"); set.add("张三"); set.add("李四"); set.add("王五"); set.add("王五"); set.add("赵六"); System.out.println("set = " + set);//不允许重复,体现添加顺序 } TreeSet set = new TreeSet(); set.add("MM"); set.add("CC"); set.add("AA"); set.add("DD"); set.add("ZZ"); //set.add(123); //报ClassCastException的异常 System.out.println(set); // [AA, CC, DD, MM, ZZ] } String name; int age; public User() { } public User(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } /* 举例:按照age从小到大的顺序排列,如果age相同,则按照name从大到小的顺序排列 * */ public int compareTo(Object o) { if(this == o){ return 0; } if(o instanceof User){ User user = (User)o; int value = this.age - user.age; if(value != 0){ return value; } return -this.name.compareTo(user.name); } throw new RuntimeException("输入的类型不匹配"); } } TreeSet set = new TreeSet(); set.add(new User("Tom",12)); set.add(new User("Rose",23)); set.add(new User("Jerry",2)); set.add(new User("Eric",18)); set.add(new User("Tommy",44)); set.add(new User("Jim",23)); set.add(new User("Maria",18)); //set.add("Tom"); Iterator iterator = set.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()){ System.out.println(iterator.next()); } System.out.println(set.contains(new User("Jack", 23))); //true } //按照User的姓名的从小到大的顺序排列 Comparator comparator = new Comparator() { @Override public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) { if(o1 instanceof User && o2 instanceof User){ User u1 = (User)o1; User u2 = (User)o2; return u1.name.compareTo(u2.name); } throw new RuntimeException("输入的类型不匹配"); } }; TreeSet set = new TreeSet(comparator); set.add(new User("Tom",12)); set.add(new User("Rose",23)); set.add(new User("Jerry",2)); set.add(new User("Eric",18)); set.add(new User("Tommy",44)); set.add(new User("Jim",23)); set.add(new User("Maria",18)); Iterator iterator = set.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()){ System.out.println(iterator.next()); } } //创建 map对象 HashMap map = new HashMap(); //添加元素到集合 map.put("黄晓明", "杨颖"); map.put("李晨", "李小璐"); map.put("李晨", "范冰冰"); map.put("邓超", "孙俪"); System.out.println(map); //删除指定的key-value System.out.println(map.remove("黄晓明")); System.out.println(map); //查询指定key对应的value System.out.println(map.get("邓超")); System.out.println(map.get("黄晓明")); } HashMap map = new HashMap(); map.put("许仙", "白娘子"); map.put("董永", "七仙女"); map.put("牛郎", "织女"); map.put("许仙", "小青"); System.out.println("所有的key:"); Set keySet = map.keySet(); for (Object key : keySet) { System.out.println(key); } System.out.println("所有的value:"); Collection values = map.values(); for (Object value : values) { System.out.println(value); } System.out.println("所有的映射关系:"); Set entrySet = map.entrySet(); for (Object mapping : entrySet) { //System.out.println(entry); Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) mapping; System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "-" + entry.getValue()); } } Map map = new HashMap(); map.put(null,null); map.put("Tom",23); map.put("CC",new Date()); map.put(34,"AA"); System.out.println(map); // {null=null, CC=Sat Apr 22 17:51:16 CST 2023, 34=AA, Tom=23} } LinkedHashMap map = new LinkedHashMap(); map.put("Tom",23); map.put("CC","test"); map.put(34,"AA"); System.out.println(map); // {Tom=23, CC=test, 34=AA} } TreeMap map = new TreeMap(); map.put("CC",45); map.put("MM",78); map.put("DD",56); map.put("GG",89); System.out.println(map); // {CC=45, DD=56, GG=89, MM=78} } //按照User的姓名的从小到大的顺序排列 TreeMap map = new TreeMap(new Comparator() { @Override public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) { if(o1 instanceof User && o2 instanceof User){ User u1 = (User)o1; User u2 = (User)o2; return u1.name.compareTo(u2.name); } throw new RuntimeException("输入的类型不匹配"); } }); map.put(new User("Tom",12),67); map.put(new User("Rose",23),"87"); map.put(new User("Jerry",2),88); map.put(new User("Eric",18),45); map.put(new User("Tommy",44),77); map.put(new User("Jim",23),88); map.put(new User("Maria",18),34); System.out.println(map); } Properties pros = new Properties(); pros.load(new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties")); String user = pros.getProperty("user"); System.out.println(user); } List list = Arrays.asList(45, 43, 65, 6, 43, 2, 32, 45, 56, 34, 23); //reverse(List):反转 List 中元素的顺序 // Collections.reverse(list); // [23, 34, 56, 45, 32, 2, 43, 6, 65, 43, 45] //shuffle(List):对 List 集合元素进行随机排序,每次不一样 // Collections.shuffle(list); // [65, 32, 34, 23, 45, 45, 2, 43, 43, 56, 6] //sort(List):根据元素的自然顺序对指定 List 集合元素按升序排序 // Collections.sort(list); // [2, 6, 23, 32, 34, 43, 43, 45, 45, 56, 65] //sort(List,Comparator):根据指定的 Comparator 产生的顺序对 List 集合元素进行排序 Collections.sort(list, new Comparator() { @Override public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) { if(o1 instanceof Integer && o2 instanceof Integer){ Integer i1 = (Integer) o1; Integer i2 = (Integer) o2; // return i1 - i2; return -(i1.intValue() - i2.intValue()); } throw new RuntimeException("类型不匹配"); } }); // [65, 56, 45, 45, 43, 43, 34, 32, 23, 6, 2] System.out.println(list); } List list = Arrays.asList(45, 43, 65, 6, 43, 2, 32, 45, 56, 34, 23); System.out.println(list); Object max = Collections.max(list); Object max1 = Collections.max(list,new Comparator() { @Override public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) { if(o1 instanceof Integer && o2 instanceof Integer){ Integer i1 = (Integer) o1; Integer i2 = (Integer) o2; // return i1 - i2; return -(i1.intValue() - i2.intValue()); } throw new RuntimeException("类型不匹配"); } }); System.out.println(max); // 65 System.out.println(max1); // 2 int count = Collections.frequency(list, 45); System.out.println("45出现了" + count + "次"); // 45出现了2次 } List src = Arrays.asList(45, 43, 65, 6, 43, 2, 32, 45, 56, 34, 23); //void copy(List dest,List src):将src中的内容复制到dest中 //错误的写法: // List dest = new ArrayList(); //正确的写法: List dest = Arrays.asList(new Object[src.size()]); Collections.copy(dest,src); System.out.println(dest); } //提供了多个unmodifiableXxx()方法,该方法返回指定 Xxx的不可修改的视图。 List list1 = new ArrayList(); //list1可以写入数据 list1.add(34); list1.add(12); list1.add(45); List list2 = Collections.unmodifiableList(list1); //此时的list2只能读,不能写 list2.add("AA");//不能写 System.out.println(list2.get(0));//34 } //Collections 类中提供了多个 synchronizedXxx() 方法 List list1 = new ArrayList(); //返回的list2就是线程安全的 List list2 = Collections.synchronizedList(list1); list2.add(123); HashMap map1 = new HashMap(); //返回的map2就是线程安全的 Map map2 = Collections.synchronizedMap(map1); }
- 第1步:当向 HashSet 集合中存入一个元素时
- 特有方法
- 私有内部类,所以返回值用父类List表示,而不能用Arrays.ArrayList
- 插入元素
- 它用于遍历Collection和数组。通常只进行遍历元素,不要在遍历的过程中对集合元素进行增删操作
- 对于集合的遍历,增强for的内部原理其实是个Iterator迭代器
- 使用Iterator迭代器删除元素:java.util.Iterator迭代器中有一个方法:void remove()
- JDK专门提供了一个接口java.util.Iterator遍历集合中的所有元素
- HashMap(主要实现类)、LinkedHashMap、TreeMap、Hashtable、Properties
- List子接口:用来存储有序的、可以重复的数据(主要用来替换数组,"动态"数组)
- Collection接口:用于存储一个一个的数据,也称单列数据集合
文章版权声明:除非注明,否则均为主机测评原创文章,转载或复制请以超链接形式并注明出处。