springboot系列九: 接收参数相关注解
文章目录
- 基本介绍
- 接收参数相关注解应用实例
- @PathVariable
- @RequestHeader
- @RequestParam
- @CookieValue
- @RequestBody
- @RequestAttribute
- @SessionAttribute
- 复杂参数
- 基本介绍
- 应用实例
- 自定义对象参数-自动封装
- 基本介绍
- 应用实例
基本介绍
1.SpringBoot 接收客户端提交数据 / 参数会使用到相关注解.
2.详细学习 @PathVariable, @RequestHeader, @ModelAttribute, @RequestParam, @CookieValue, @RequestBody
接收参数相关注解应用实例
●需求:
演示各种方式提交数据/参数给服务器, 服务器如何使用注解接收
@PathVariable
1.创建src/main/resources/public/index.html
JavaWeb系列十: web工程路径专题
跟着老韩学springboot
基本注解:
@PathVariable-路径变量 monster/100/king2.创建src/main/java/com/zzw/springboot/controller/ParameterController.java
url占位符回顾
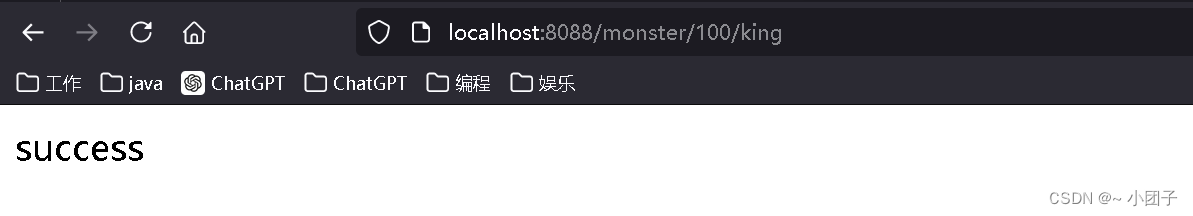
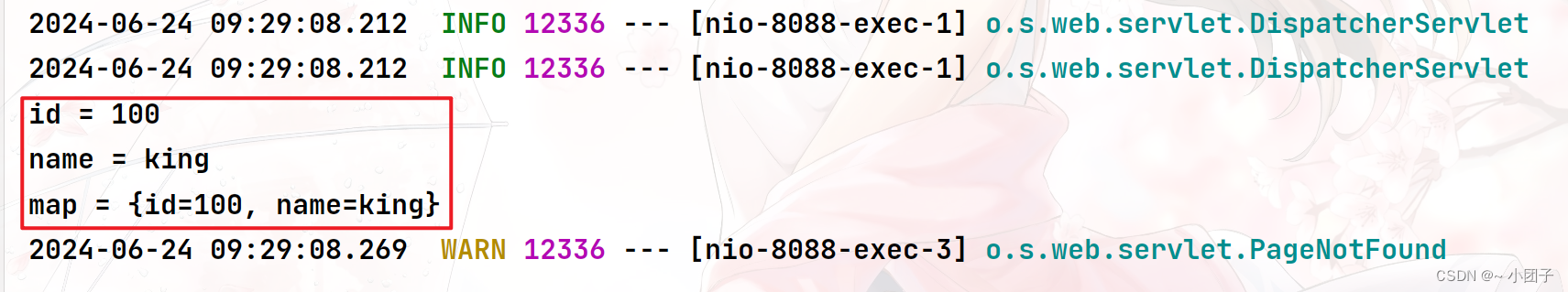
@RestController public class ParameterController { /** * 1./monster/{id}/{name} 构成完整请求路径 * 2.{id} {name} 就是占位变量 * 3.@PathVariable("name"): 这里 name 和 {name} 命名保持一致 * 4.String name_ 这里自定义, 这里韩老师故意这么写 * 5.@PathVariable Map map 把所有传递的值传入map * 6.可以看下@pathVariable源码 * @return */ @GetMapping("/monster/{id}/{name}") public String pathVariable(@PathVariable("id") Integer id, @PathVariable("name") String name, @PathVariable Map map) { System.out.println("id = " + id + "\nname = " + name + "\nmap = " + map); return "success"; } }3.测试 http://localhost:8088https://blog.csdn.net/monster/100/king
@RequestHeader
需求: 演示@RequestHeader使用.
1.修改src/main/resources/public/index.html
@RequestHeader-获取http请求头
2.修改ParameterController.java
JavaWeb系列八: WEB 开发通信协议(HTTP协议)
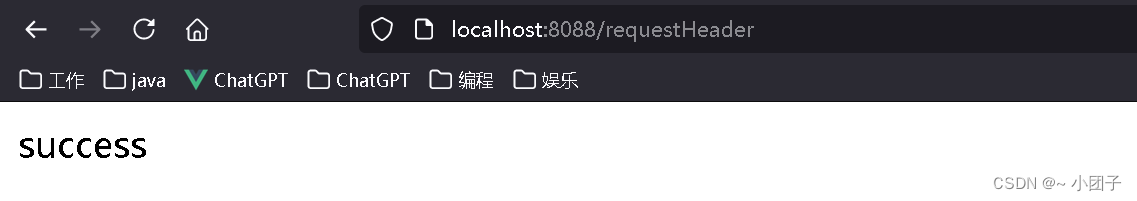
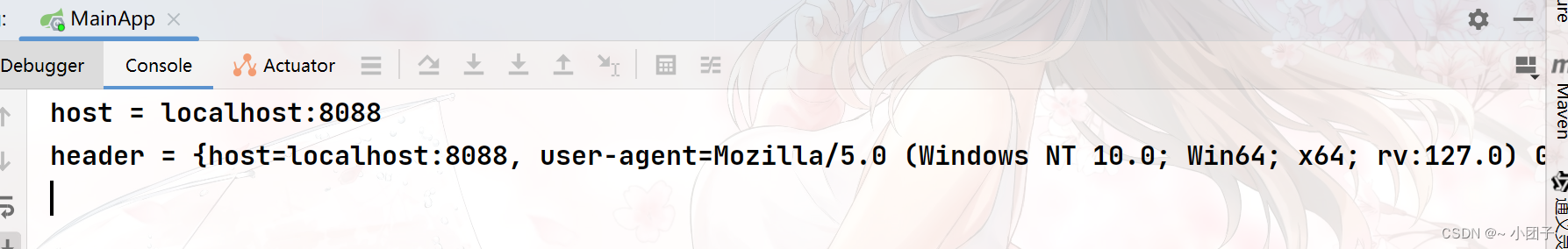
/** * 1. @RequestHeader("Cookie") 获取http请求头的 cookie信息 * 2. @RequestHeader Map header 获取到http请求的所有信息 */ @GetMapping("https://blog.csdn.net/requestHeader") public String requestHeader(@RequestHeader("Host") String host, @RequestHeader Map header) { System.out.println("host = " + host + "\nheader = " + header); return "success"; }3.测试
@RequestParam
需求: 演示@RequestParam使用.
1.修改src/main/resources/public/index.html
@RequestParam-获取请求参数
2.修改ParameterController.java
SpringMVC系列五: SpringMVC映射请求数据
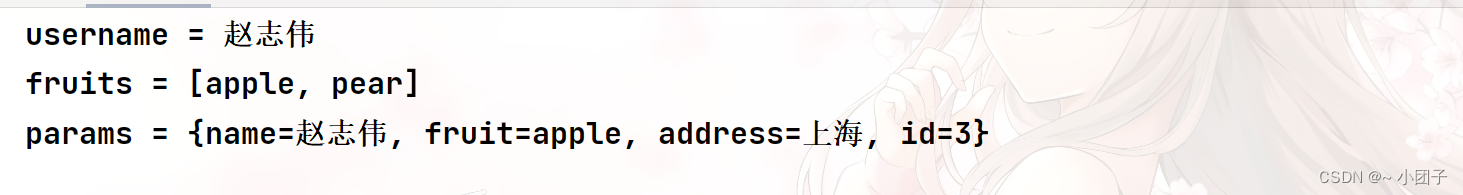
/** * 如果我们希望将所有的请求参数的值都获取到, 可以通过 * @RequestParam Map params */ @GetMapping("/hi") public String hi(@RequestParam(value = "name") String username, @RequestParam(value = "fruit") List fruits, @RequestParam Map params) { System.out.println("username = " + username + "\nfruits = " + fruits + "\nparams = " + params); return "success"; }3.测试
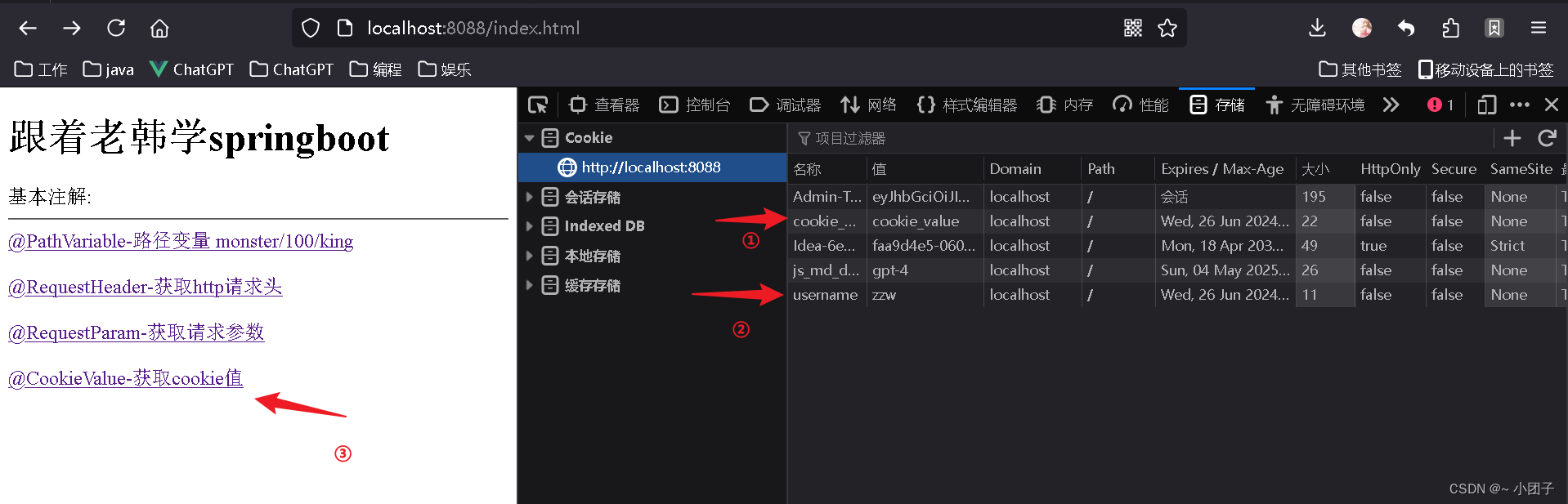
@CookieValue
需求: 演示@CookieValue使用.
1.修改src/main/resources/public/index.html
@CookieValue-获取cookie值
2.修改ParameterController.java
JavaWeb系列十一: Web 开发会话技术(Cookie, Session)
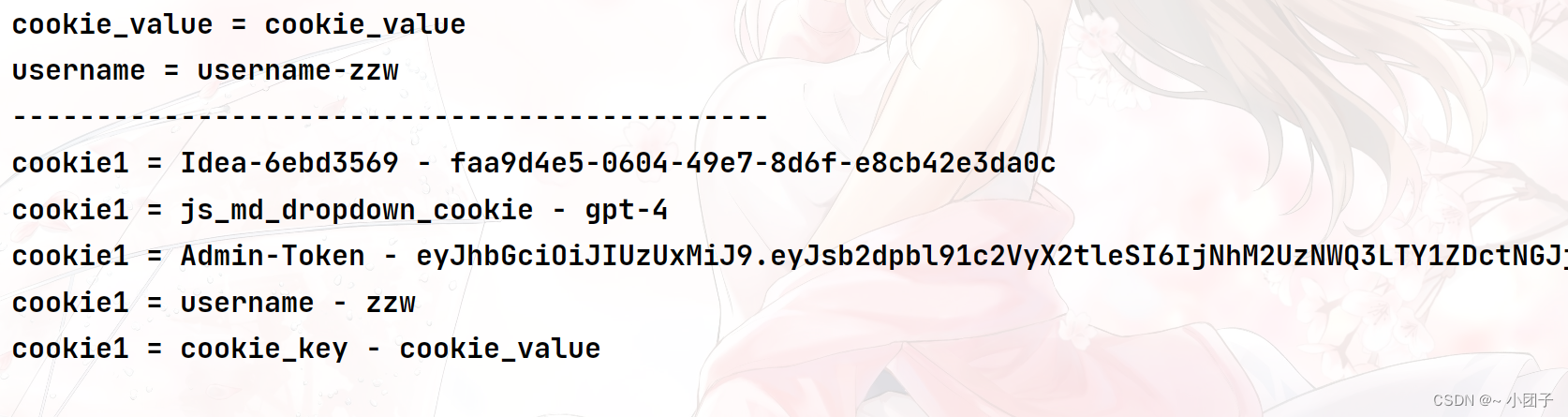
/** * 因为我们的浏览器目前没有cookie, 我们可以自己设置cookie * 如果要测试, 可以先写一个方法, 在浏览器创建对应的cookie * 说明: * 1. value = "cookie_key" 表示接收名字为 cookie_key的cookie * 2. 如果浏览器携带来对应的cookie, 那么后面的参数是String, 则接收到的是对应的value * 3. 后面的参数是Cookie, 则接收到的是封装好的对应的cookie */ @GetMapping("https://blog.csdn.net/cookie") public String cookie(@CookieValue(value = "cookie_key") String cookie_value, @CookieValue(value = "username") Cookie cookie, HttpServletRequest request) { System.out.println("cookie_value = " + cookie_value + "\nusername = " + cookie.getName() + "-" + cookie.getValue()); Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies(); for (Cookie cookie1 : cookies) { System.out.println("cookie1 = " + cookie1.getName() + "-" + cookie1.getValue()); } return "success"; }3.测试
@RequestBody
需求: 演示@RequestBody使用.
1.修改src/main/resources/public/index.html
测试@RequestBody获取数据: 获取POST请求体
名字:
年龄:2.修改ParameterController.java
SpringMVC系列十: 中文乱码处理与JSON处理
/** * @RequestBody 是整体取出Post请求内容 */ @PostMapping("/save") public String postMethod(@RequestBody String content) { System.out.println("content = " + content);//content = name=zzw&age=23 return "sucess"; }3.测试
content = name=zzw&age=123
@RequestAttribute
需求: 演示@RequestAttribute使用. 获取request域的属性.
1.修改src/main/resources/public/index.html
@RequestAttribute-获取request域属性
2.创建RequestController.java
SpringMVC系列十: 中文乱码处理与JSON处理
@Controller public class RequestController { @RequestMapping("https://blog.csdn.net/login") public String login(HttpServletRequest request) { request.setAttribute("user", "赵志伟");//向request域中添加的数据 return "forward:/ok";//请求转发到 /ok } @GetMapping("/ok") @ResponseBody public String ok(@RequestAttribute(value = "user", required = false) String username, HttpServletRequest request) { //获取到request域中的数据 System.out.println("username--" + username); System.out.println("通过servlet api 获取 username-" + request.getAttribute("user")); return "success"; //返回字符串, 不用视图解析器 } }3.测试…
@SessionAttribute
需求: 演示@SessionAttribute使用. 获取session域的属性.
1.修改src/main/resources/public/index.html
@SessionAttribute-获取session域属性
2.创建RequestController.java
JavaWeb系列十一: Web 开发会话技术(Cookie, Session)
@Controller public class RequestController { @RequestMapping("https://blog.csdn.net/login") public String login(HttpServletRequest request, HttpSession session) { request.setAttribute("user", "赵志伟");//向request域中添加的数据 session.setAttribute("mobile", "黑莓");//向session域中添加的数据 return "forward:/ok";//请求转发到 /ok } @GetMapping("/ok") @ResponseBody public String ok(@RequestAttribute(value = "user", required = false) String username, HttpServletRequest request, @SessionAttribute(value = "mobile", required = false) String mobile, HttpSession session) { //获取到request域中的数据 System.out.println("username--" + username); System.out.println("通过servlet api 获取 username-" + request.getAttribute("user")); //获取session域中的数据 System.out.println("mobile--" + mobile); System.out.println("通过HttpSession 获取 mobile-" + session.getAttribute("mobile")); return "success"; //返回字符串, 不用视图解析器 } }3.测试…
复杂参数
基本介绍
1.在开发中, SpringBoot在相应客户端请求时, 也支持复杂参数
2.Map, Model, Errors/BindingResult, RedirectAttributes, ServletResponse, SessionStatus, UriComponentsBuilder, ServletUriComponentBuilder, HttpSession.
3.Map, Model,数据会被放在request域, 到时Debug一下.
4.RedirectAttribute 重定向携带数据
应用实例
说明: 演示复杂参数的使用.
重点: Map, Model, ServletResponse
●代码实现
1.修改src/main/java/com/zzw/springboot/controller/RequestController.java
SpringMVC系列六: 模型数据
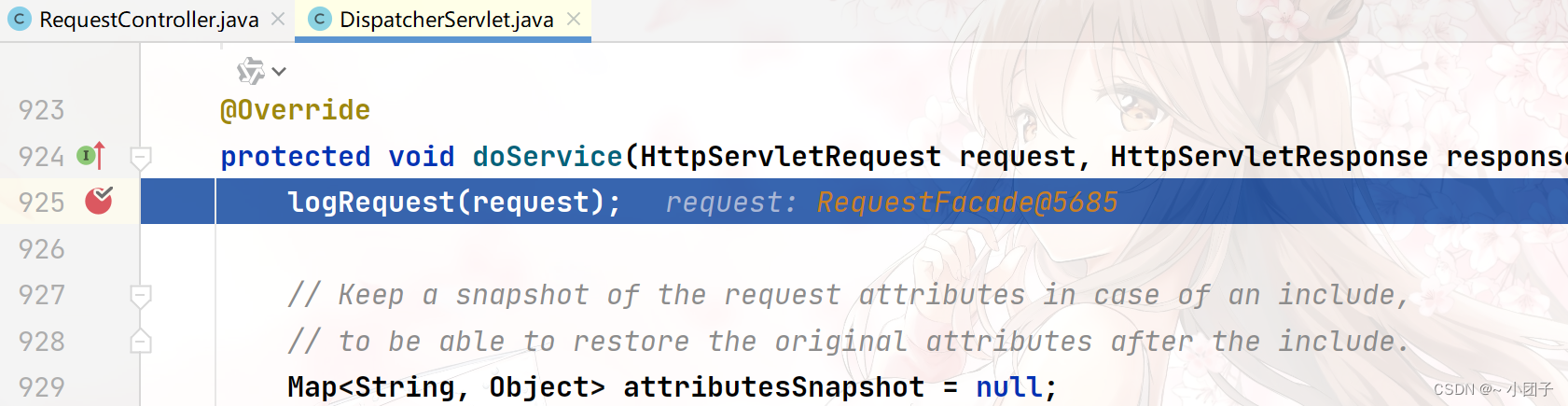
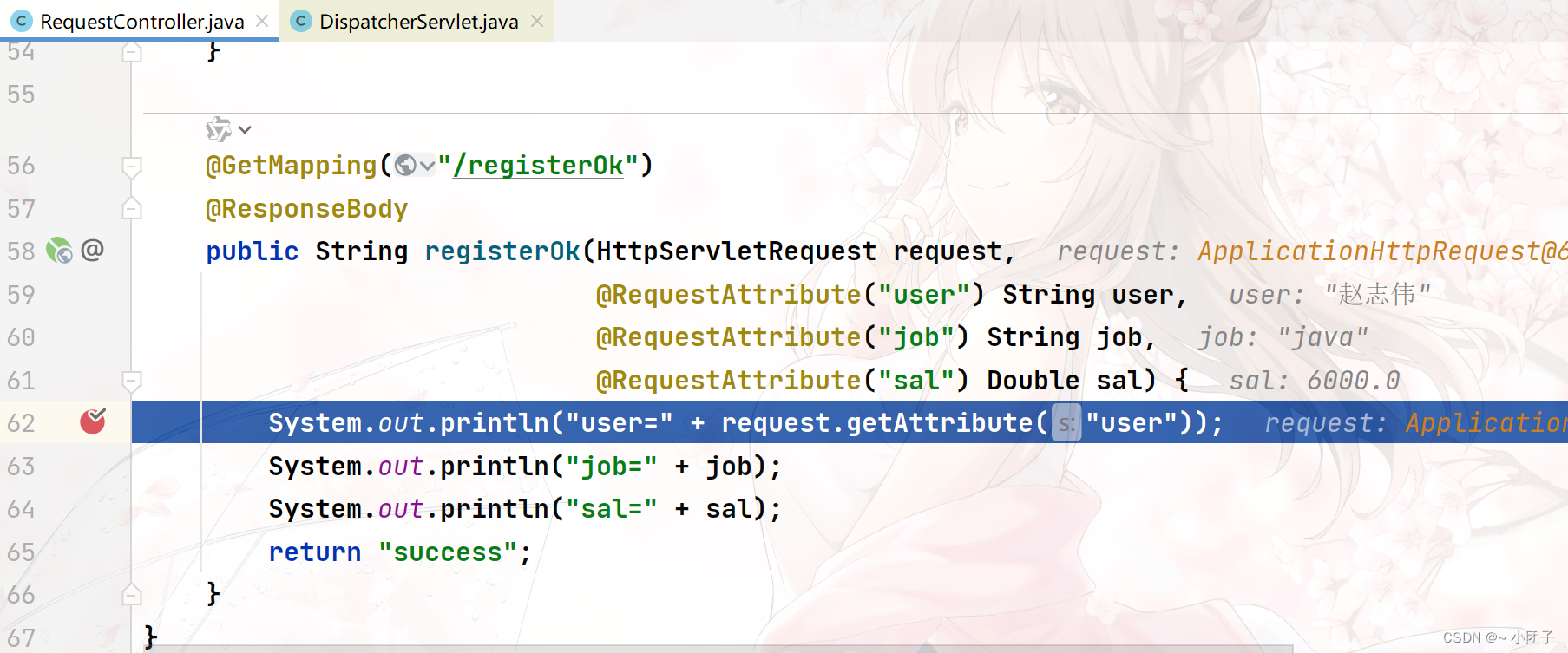
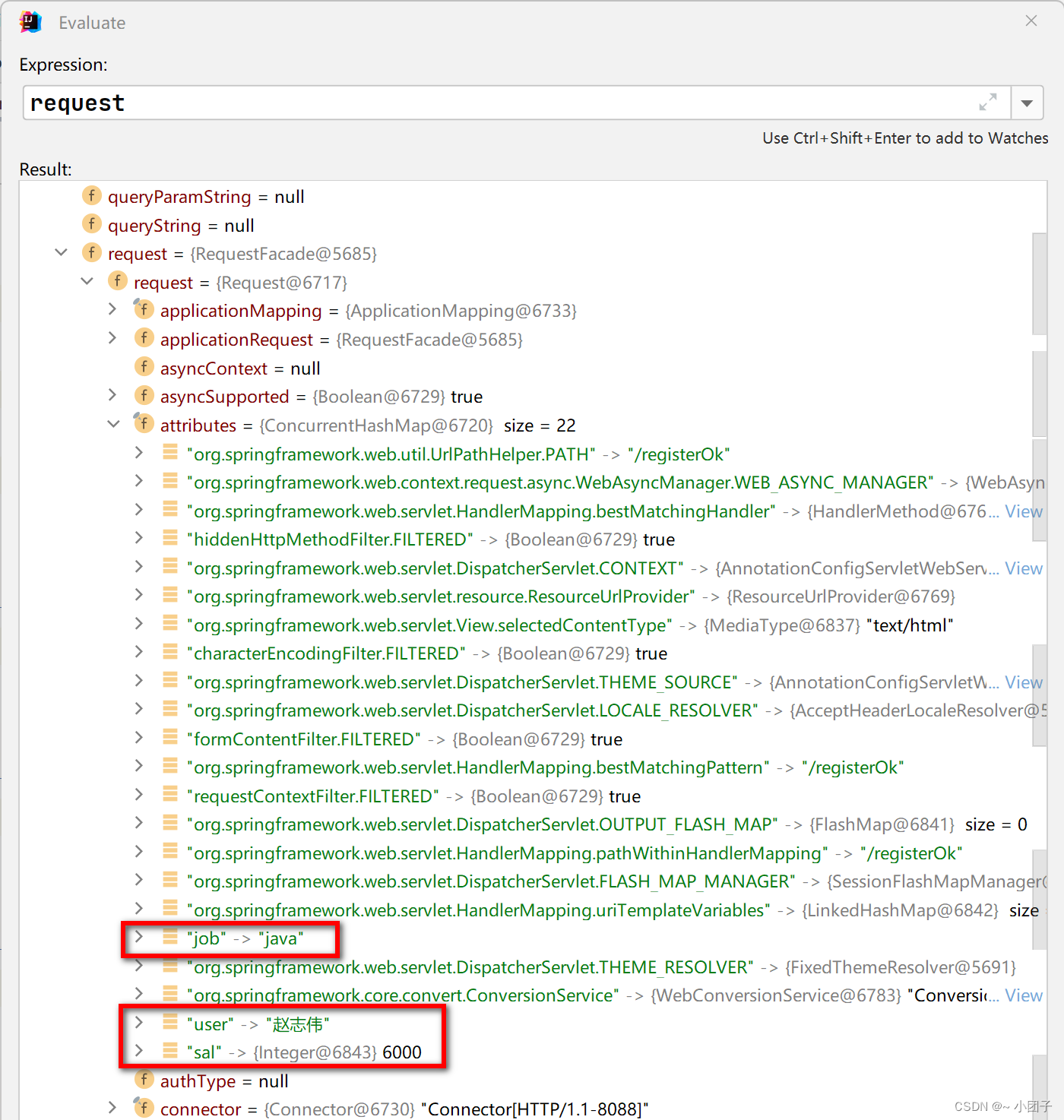
//响应一个注册请求 @GetMapping("/register") public String register(Map map, Model model, HttpServletRequest request) { //如果一个注册请求, 会将注册数据封装到map或者model //map中的数据和model中的数据, 会被放入到request域中 map.put("user", "赵志伟"); map.put("job", "java"); model.addAttribute("sal", 6000); //一会我们再测试response使用 //请求转发 return "forward:/registerOk"; } @GetMapping("/registerOk") @ResponseBody public String registerOk(HttpServletRequest request, @RequestAttribute("user") String user, @RequestAttribute("job") String job, @RequestAttribute("sal") Double sal) { System.out.println("user=" + request.getAttribute("user")); System.out.println("job=" + job); System.out.println("sal=" + sal); return "success"; }2.浏览器输入 http://localhost:8088/register , 打断点测试
SpringMVC系列十三: SpringMVC执行流程 - 源码分析
进入目标方法
剖析 request 对象
3.继续修改 register()方法
JavaWeb系列十一: Web 开发会话技术(Cookie, Session)
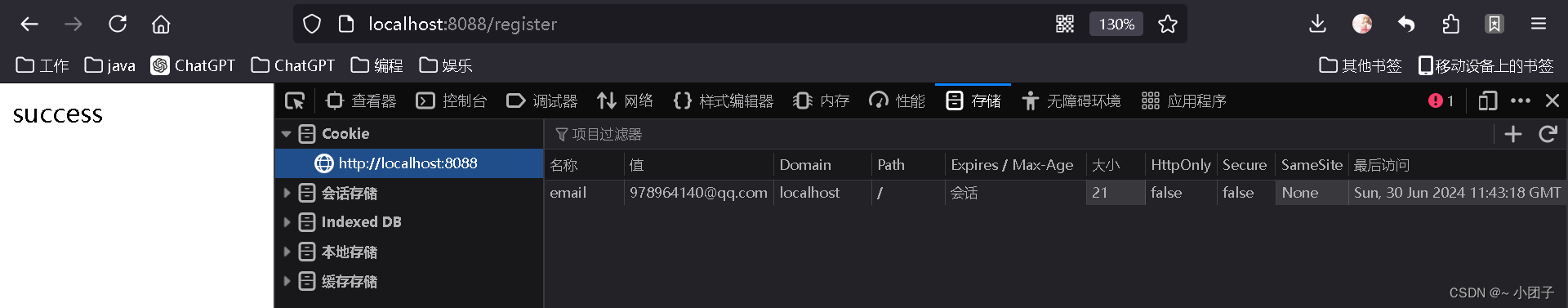
//响应一个注册请求 @GetMapping("/register") public String register(Map map, Model model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws UnsupportedEncodingException { //如果一个注册请求, 会将注册数据封装到map或者model //map中的数据和model中的数据, 会被放入到request域中 map.put("user", "赵志伟"); map.put("job", "java"); model.addAttribute("sal", 6000); //一会我们再测试response使用 //演示创建cookie, 并通过response 添加到浏览器/客户端 Cookie cookie = new Cookie("email", "978964140@qq.com"); response.addCookie(cookie); //请求转发 return "forward:/registerOk"; }4.测试
自定义对象参数-自动封装
基本介绍
1.在开发中, SpringBoot在响应客户端/浏览器请求时, 也支持自定义对象参数
2.完成自动类型转换与格式化
3.支持级联封装
应用实例
●需求说明:
演示自定义对象参数使用,完成自动封装,类型转换。
●代码实现
1.创建public/save.html
添加妖怪 编号:
姓名:
年龄:
婚否:
生日:
坐骑名称:
坐骑价格:2.创建src/main/java/com/zzw/springboot/bean/Car.java
@Data public class Car { private String name; private Double price; }3.创建src/main/java/com/zzw/springboot/bean/Monster.java
@Data public class Monster { private Integer id; private String name; private Integer age; private Boolean maritalStatus; private Date birthday; private Car car; }4.修改ParameterController.java
//处理添加monster的方法 @PostMapping("/saveMonster") public String saveMonster(Monster monster) { System.out.println("monster = " + monster); return "success"; }5.回填public/save.html
编号:
姓名:
年龄:
婚否:
生日:6.自动封装需要用到自定义转换器. 接下来, 继续学习自定义转换器.
🔜 下一篇预告: [即将更新,敬请期待]
📚 目录导航 📚
- springboot系列一: springboot初步入门
- springboot系列二: sprintboot依赖管理
- springboot系列三: sprintboot自动配置
- springboot系列四: sprintboot容器功能
- springboot系列五: springboot底层机制实现 上
- springboot系列六: springboot底层机制实现 下
- springboot系列七: Lombok注解,Spring Initializr,yaml语法
- springboot系列八: springboot静态资源访问,Rest风格请求处理, 接收参数相关注解
…
💬 读者互动 💬
在学习 Spring Boot 静态资源访问和 Rest 风格请求处理的过程中,您有哪些新的发现或疑问?欢迎在评论区留言,让我们一起讨论吧!😊