Android 性能优化之启动优化
文章目录
- Android 性能优化之启动优化
- 启动状态
- 冷启动
- 温启动
- 热启动
- 耗时检测
- 检测手段
- TraceView
- 使用方式
- 缺点
- Systrace
- 环境配置
- 使用方式
- TraceView和Systrace比较
- AOP统计耗时
- 环境配置
- 使用
- 优化
- 白屏优化
- 异步加载优化
- 环境配置
- 使用
- 延迟加载优化
- AppStartup
- 源码下载
Android 性能优化之启动优化
启动状态
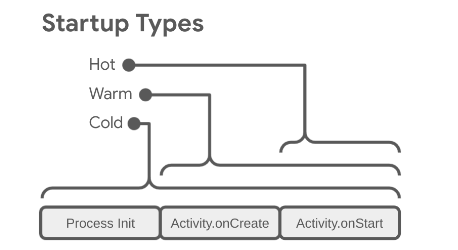
冷启动
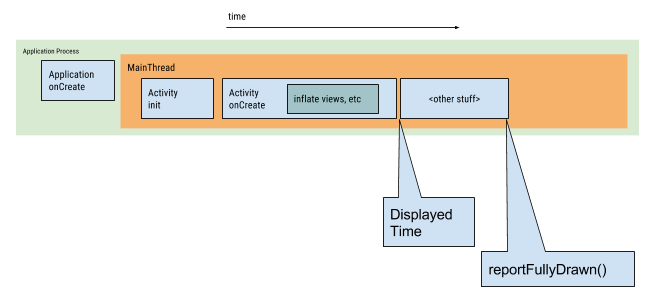
冷启动是应用程序启动的默认方式。当用户首次启动应用程序时,或者系统彻底杀死了应用程序进程后再次启动应用程序时,会经历冷启动。在冷启动过程中,系统需要创建一个新的进程,并初始化所有必要的资源。这包括加载应用程序的代码、数据,以及初始化应用程序的环境。冷启动的时间相对较长,因为系统需要执行一系列初始化操作。用户能感受到明显的等待时间,这段时间从点击应用图标到看到应用程序主界面出现。
在冷启动开始时,系统有以下三项任务:
- 加载并启动应用。
- 在启动后立即显示应用的空白启动窗口。
- 创建应用进程。
系统一创建应用进程,应用进程就负责后续阶段:
- 创建应用对象。
- 启动主线程。
- 创建主 activity。
- 膨胀视图。
- 创建屏幕布局。
- 执行初步绘制。
温启动
温启动是指应用程序已经在后台运行,但由于系统资源紧张等原因被系统终止。当用户再次启动应用程序时,系统会重新加载应用程序。与冷启动相比,温启动不需要重新创建进程,因此启动时间较短。
热启动
热启动是指应用程序处于前台运行状态,用户通过返回键或应用程序内部的逻辑退到后台,然后又重新显示到前台。在这种情况下,应用程序的进程仍然在运行,所以不需要进行任何初始化操作。热启动是最快的启动方式,因为系统只需要恢复应用程序的前台状态。
耗时检测
检测手段
- TraceView
- Systrace
- AOP统计耗时
TraceView
TraceView 是 Android SDK 中提供的性能分析工具,它可以帮助开发者分析应用程序的方法调用和线程活动。TraceView 专注于应用程序的内部行为,提供了方法执行时间、调用次数、CPU 使用率等详细信息。它通常用于分析应用程序的特定部分或特定场景。
使用方式
public class BaseApp extends Application { @Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); // TraceView开始 Debug.startMethodTracing("myTrace001"); initRefresh(); initTitleBar(); initToast(); initActivites(); // TraceView结束 Debug.stopMethodTracing(); } }运行程序后生成文件:/sdcard/Android/data/com.example.android_performance_optimization/files/myTrace001.trace
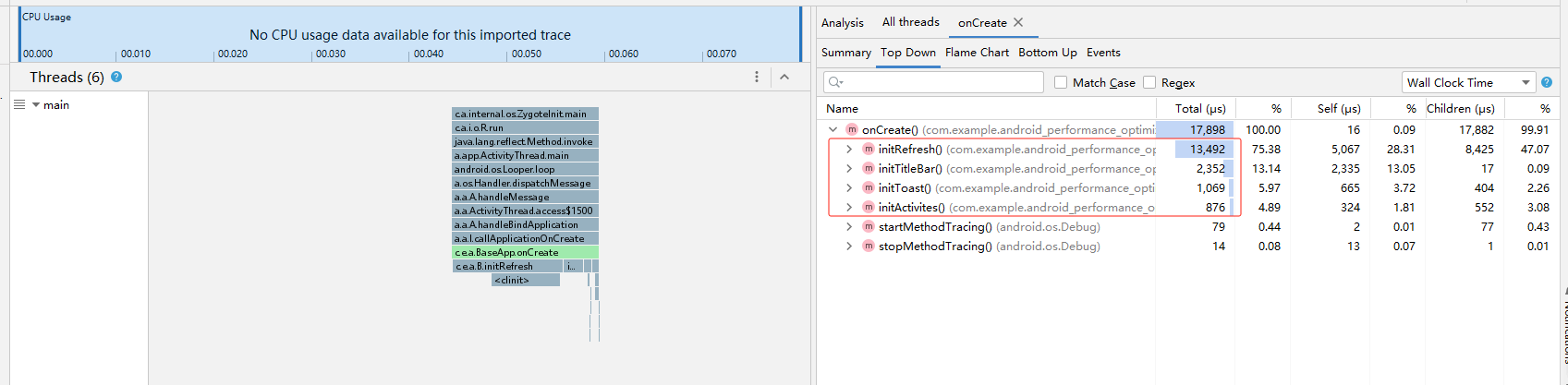
将 trace 文件到处,用 AndroidStudio的 Profiler 工具打开,可以清楚看到各个方法的执行时间:
缺点
- 运行时开销严重,整体会变慢。
- 可能带偏优化方向。
Systrace
Systrace 是 Android SDK 中提供的另一个性能分析工具,它提供了系统级别的跟踪信息,包括内核调度、硬件I/O、进程/线程调度等。Systrace 专注于整个 Android 系统的行为,帮助开发者了解系统资源的使用情况和潜在的瓶颈。
环境配置
https://blog.csdn.net/Donald_Zhuang/article/details/118771191
https://blog.csdn.net/jdsjlzx/article/details/134179374
使用方式
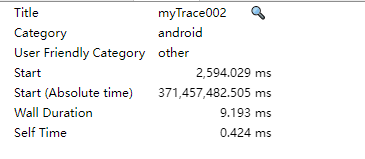
public class BaseApp extends Application { @Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); // Systrace开始 Trace.beginSection("myTrace002"); initRefresh(); initTitleBar(); initToast(); initActivites(); // Systrace结束 Trace.endSection(); } }先执行命令:python D:\dev\AndroidSDK\platform-tools\systrace\systrace.py -t 10 -o mytrace.html -a com.example.android_performance_optimization sched freq idle am wm gfx view binder_driver hal dalvik camera input res
然后运行程序,大概10秒后会生成 mytrace.html 文件。
打开 html 文件过滤相关信息后可以看到 Wall Duration 耗时:
TraceView和Systrace比较
性能消耗:
- TraceView:由于它收集所有方法的耗时信息和嵌套关系,因此本身的性能消耗很大,可能会影响到实际的运行环境,统计的耗时可能不准确。
- Systrace:采用了不同的思路,通过有限的Label先粗略统计出一个阶段的耗时,定位到问题后再进一步细化和测算分析。这种方式相对于TraceView来说,对性能的影响较小。
适用范围:
- TraceView:更适用于从软件跟踪的角度分析应用程序的性能。
- Systrace:则更侧重于从系统整体的角度分析Android系统的性能,包括各个关键子系统和服务的运行情况。
AOP统计耗时
环境配置
这里使用第三方框架:https://github.com/FlyJingFish/AndroidAOP
添加依赖库:
implementation 'io.github.FlyJingFish.AndroidAop:android-aop-core:1.8.8' implementation 'io.github.FlyJingFish.AndroidAop:android-aop-annotation:1.8.8' annotationProcessor 'io.github.FlyJingFish.AndroidAop:android-aop-processor:1.8.8'
使用
定义注解:
@AndroidAopPointCut(CostTimePointcut.class) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.METHOD) public @interface CostTime { }定义切面类:
public class CostTimePointcut implements BasePointCut { @Nullable @Override public Object invoke(@NonNull ProceedJoinPoint proceedJoinPoint, @NonNull CostTime costTime) { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); proceedJoinPoint.proceed(); // 继续执行原方法 long time = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime; Class targetClass = proceedJoinPoint.getTargetClass(); String className = targetClass.getName(); AopMethod targetMethod = proceedJoinPoint.getTargetMethod(); String methodName = targetMethod.getName(); String builder = className + "#" + methodName + " [" + time + "ms" + "] "; Log.e("CostTime", builder); return null; } }使用AOP:
public class BaseApp extends Application { @CostTime @Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); initRefresh(); initTitleBar(); initToast(); initActivites(); } @CostTime private void initActivites() { ActivityManager.getInstance().init(instance); } @CostTime private void initToast() { ToastUtils.init(instance, new ToastStyle()); ToastUtils.setDebugMode(AppConfig.isDebug()); ToastUtils.setInterceptor(new ToastLogInterceptor()); } @CostTime private void initTitleBar() { TitleBar.setDefaultStyle(new TitleBarStyle()); } @CostTime private void initRefresh() { SmartRefreshLayout.setDefaultRefreshHeaderCreator(new DefaultRefreshHeaderCreator() { @Override public RefreshHeader createRefreshHeader(Context context, RefreshLayout layout) { layout.setPrimaryColorsId(R.color.black, android.R.color.white);//全局设置主题颜色 return new ClassicsHeader(context); } }); SmartRefreshLayout.setDefaultRefreshFooterCreator(new DefaultRefreshFooterCreator() { @Override public RefreshFooter createRefreshFooter(Context context, RefreshLayout layout) { return new ClassicsFooter(context).setDrawableSize(20); } }); } }输出:
com.example.android_performance_optimization.BaseApp#initRefresh [1ms] com.example.android_performance_optimization.BaseApp#initTitleBar [0ms] com.example.android_performance_optimization.BaseApp#initToast [0ms] com.example.android_performance_optimization.BaseApp#initActivites [1ms] com.example.android_performance_optimization.BaseApp#onCreate [2ms]
优化
- 白屏优化
- 异步加载优化
- 延迟加载优化
白屏优化
在启动时提供一个简洁的初始界面给用户,增强用户体验。
定义主题:
@drawable/shape_splash true false false true @null true配置AndroidManifest.xml:
异步加载优化
环境配置
这里使用第三方框架:https://github.com/aiceking/AppStartFaster
添加依赖库:
implementation 'com.github.aiceking:AppStartFaster:2.2.0'
使用
public class BaseApp extends Application { private static BaseApp instance; public static BaseApp getInstance() { return instance; } @CostTime @Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); instance = this; AppStartTaskDispatcher.create() .setShowLog(true) .addAppStartTask(new ActivityTask(instance)) .addAppStartTask(new ToastTask(instance)) .addAppStartTask(new TitleBarTask()) .addAppStartTask(new RefreshTask()) .start() .await(); } }延迟加载优化
IdleHandler 是一个用于在主线程(UI 线程)空闲时执行任务的接口。
使用场景:
- 数据预加载。
- 清理资源。
- 日志上传。
- 检查更新。
- 性能分析。
使用:
首先,你需要创建一个实现了IdleHandler接口的类或使用匿名内部类。在queueIdle()方法中定义你希望在空闲时执行的代码逻辑。该方法的返回值决定了IdleHandler的生命周期:
- 返回true表示IdleHandler将继续保留在集合中,下次消息队列空闲时还会再次调用queueIdle()。
- 返回false表示执行完毕后将从集合中移除,不再重复调用。
定义延迟加载启动器:
public class DelayInitDispatcher { private DelayInitDispatcher() { } public static DelayInitDispatcher newInstance() { return new DelayInitDispatcher(); } private LinkedList mDelayTasks = new LinkedList(); private MessageQueue.IdleHandler mIdleHandler = new MessageQueue.IdleHandler() { @Override public boolean queueIdle() { if (mDelayTasks.size() > 0) { Task task = mDelayTasks.poll(); task.run(); } return !mDelayTasks.isEmpty(); } }; public DelayInitDispatcher addTask(Task task) { mDelayTasks.add(task); return this; } public void start() { Looper.myQueue().addIdleHandler(mIdleHandler); } }定义Task接口:
public interface Task extends Runnable{ }定义2个任务:
public class PreloadTask implements Task { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(1000L); Log.e("TAG", "预加载数据"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }public class ClearTask implements Task { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(2000L); Log.e("TAG", "清理资源"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }使用:
DelayInitDispatcher.newInstance() .addTask(new PreloadTask()) .addTask(new ClearTask()) .start();AppStartup
- AppStartup 是一个可以用于加速App启动速度的 Jetpack 组件。
- AppStartup 是借助 ContentProvider 进行提前初始化操作
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_14876133/article/details/119247723
源码下载