【哈希】闭散列的线性探测和开散列的哈希桶解决哈希冲突(C++两种方法模拟实现哈希表)(2)

🎉博主首页: 有趣的中国人
🎉专栏首页: C++进阶
🎉其它专栏: C++初阶 | Linux | 初阶数据结构
小伙伴们大家好,本片文章将会讲解 哈希函数与哈希 之 哈希桶解决哈希冲突 的相关内容。
如果看到最后您觉得这篇文章写得不错,有所收获,麻烦点赞👍、收藏🌟、留下评论📝。您的支持是我最大的动力,让我们一起努力,共同成长!
🎉系列文章: 1. 闭散列的线性探测实现哈希表
文章目录
- `0. 前言`
- `1. 何为开散列`
- ==🎧1.1 开散列的概念🎧==
- ==🎧1.2 开散列哈希表图示🎧==
- `2. 开散列哈希表的实现`
- ==🎧2.1 开散列哈希表的结构🎧==
- ==🎧2.2 哈希桶插入Insert🎧==
- ==🎧2.3 哈希桶查找Find🎧==
- ==🎧2.4 哈希桶删除Erase🎧==
- `3. 字符串哈希与仿函数`
- `4.哈希桶实现哈希表完整代码`
0. 前言
在上一篇文章中我们详细描述了如何用 开放寻址法(闭散列)的线性探测 的方法来实现哈希表。此篇文章我们将用 开散列的哈希桶 来实现哈希表。
1. 何为开散列
🎧1.1 开散列的概念🎧
开散列法又叫链地址法(开链法),首先对关键码集合用 散列函数计算散列地址,具有相同地址的关键码归于同一子集合,每一个子集合称为一个桶,各个桶中的元素通过一个单链表链接起来,各链表的头结点存储在哈希表中。
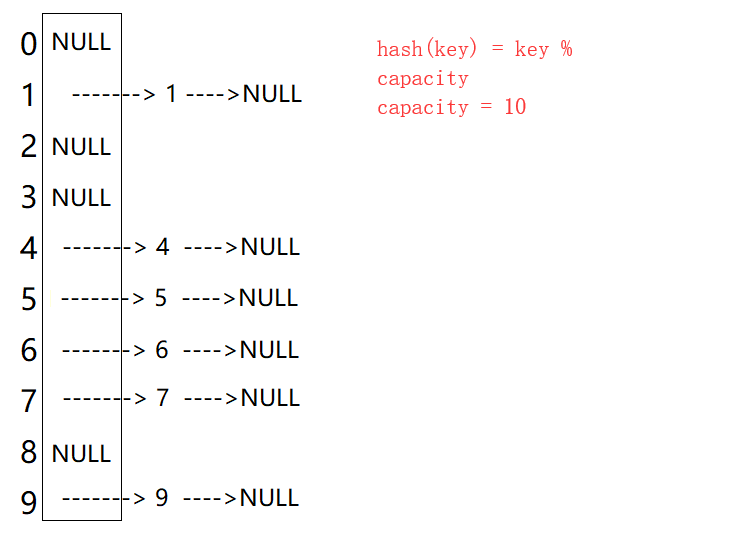
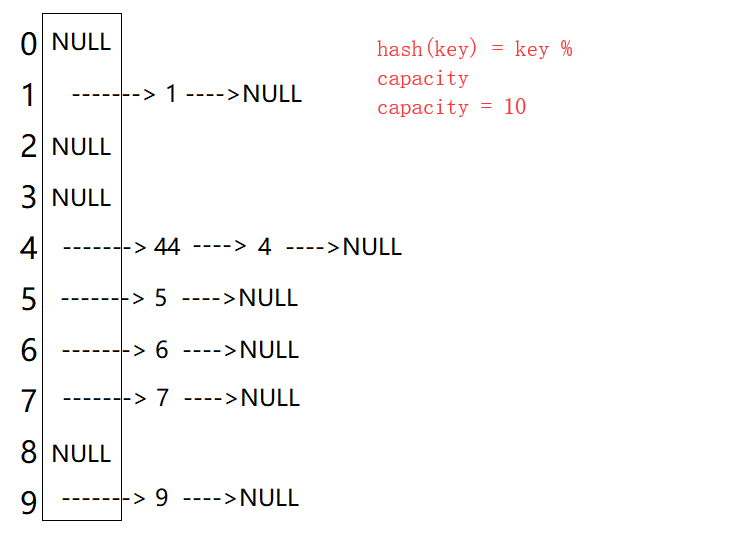
🎧1.2 开散列哈希表图示🎧
插入元素44
从上图可以看出,开散列中每个桶中放的都是发生哈希冲突的元素。
2. 开散列哈希表的实现
🎧2.1 开散列哈希表的结构🎧
很明显,这个哈希表中存储了一个指针数组,我们可以用vector来实现,数组中的每个位置存储了一个节点类型的指针,每个节点相当于是链表的一个节点,即:节点中有一个链表类型的指针,还有一个存放值的位置。
哈希节点和哈希表结构代码:
// 定义节点类型 template struct HashNode { // 存储值的位置 pair _kv; // 节点类型指针 HashNode* _next; HashNode(const pair& kv) :_kv(kv) ,_next(nullptr) {} }; // 定义哈希表,第三个模板类型是仿函数,上一篇文章讲过 template class HashTable { public: typedef HashNode Node; HashTable(size_t n = 10) { _tables.resize(n); } private: // 指针数组 vector _tables; // 存储的元素个数 size_t _n = 0; };🎧2.2 哈希桶插入Insert🎧
插入元素的思路:
- 利用 哈希函数 计算出 要插入的值应该存放在哪个桶里面;
- 之后在对应的桶中进行链表的头插:
- 首先new一个哈希表的节点newnode;
- 让 newnode->_next= _tables[i];
- 再让newnode当作头:_tables[i] = newnode;
- ++_n;
关于哈希桶的扩容:
在线性探测中,当负载因子 load_factor 在 0.75 0.75 0.75 左右的时候就要进行扩容,但是在哈希桶中,我们可以适当让负载因子大一点,在STL库中,哈希桶的扩容是当负载因子等于 1 1 1 的时候进行扩容,即: n = = t a b l e . s i z e ( ) n == table.size() n==table.size()。
注意:哈希桶中的负载因子是可以大于1的,因为一个桶中可能存储的不止一个值。
扩容思路1:
我们可以继续利用在线性探测的扩容思路:
- 新定义一个HashTable的对象newht,表的容量还是两倍;
- 遍历原始的HashTable中的vector _tables:
- 如果_tables[i]不为空,那么就调用newht.Insert()函数;
- 定义一个节点类型的指针Node* cur = _tables[i];
- 调用newht.Insert(cur->_kv);
- 再让cur = cur->_next;
- 如果_tables[i]为空,就让i++;
- 直到 i == _tables.size(),则newht插入完成;
- 最后两个_tables进行交换:_tables.swap(newht._tables);
- 如果_tables[i]不为空,那么就调用newht.Insert()函数;
但是这样扩容虽然可以,但是会很麻烦,因为:
- 由于每个哈希节点是new出来的,因此不能直接使用vector的析构函数,要自己写一个析构函数,不然会有内存泄漏;
- 每次调用newht.Insert()的时候都会重新new一个节点,原始的节点都会被释放,因此这样操作就会很麻烦编译器。
扩容代码(version1):
// 手动进行析构 ~HashTable() { for (size_t i = 0; i _next; delete cur; cur = next; } } } // 扩容代码 if (_n == _tables.size()) { // 方法1:新定义一个对象 size_t newsize = 2 * _tables.size(); HashTable newht(newsize); for (size_t i = 0; i _next; newht.Insert(cur->_kv); cur = next; } } _tables.swap(newht._tables); }扩容思路2:
- 定义一个新表vector newtables,表的容量还是两倍;
- 遍历旧表,如果当前位置不为空,在新表中进行插入,思路如下:
- 定义一个哈希节点指针Node* cur = _tables[i];
- 通过cur->_kv.first 和 哈希函数 计算出 应该插入到新表的哪个桶中(hashi);
- 由于插入之后会找不到下一个节点的位置,所以应该再定义一个Node* next = cur->next;
- 在新表中头插cur,还是同样的思路:
- 让cur->_next = newtables[hashi](cur的下一个指向原始的头节点);
- 接着让 newtables[hashi] = cur(让cur当头);
- 插入完成让cur = next;
- 直到cur == nullptr,说明此桶中的节点都在新表中插入完成;
- 让旧表中的_tables[i] = nullptr; (这部也可以不做,因为表不会调用析构函数,但是最好还是置空一下)
- 如果当前位置为空,则i++;
- 直到 i == _tables.size(),说明此表的所有元素在新表中插入完成;
- 最后两表进行交换:_tables.swap(newtables);
扩容代码(version2):
if (_n == _tables.size()) { vector newtable; // 两倍的旧表容量 size_t newsize = 2 * _tables.size(); newtable.resize(newsize); for (size_t i = 0; i _next; // 计算在新表中的位置 size_t hashi = cur->_kv.first % newtable.size(); // cur的下一个位置指向原来的头 cur->_next = newtable[hashi]; // cur当头 newtable[hashi] = cur; // 更新cur的位置 cur = next; } // 旧表置空 _tables[i] = nullptr; } _tables.swap(newtable); }完整的插入逻辑代码:
bool Insert(const pair& kv) { // 这边就是上一篇文章的仿函数 HashFunc hf; // 查找思路待会实现 if (Find(kv.first)) { return false; } // 判断负载因子扩容 // 负载因子为1扩容 if (_n == _tables.size()) { // 方法1:新定义一个对象 /*size_t newsize = 2 * _tables.size(); HashTable newht(newsize); for (size_t i = 0; i _next; newht.Insert(cur->_kv); cur = next; } } _tables.swap(newht._tables);*/ // 方法2:新定义一个表 vector newtable; size_t newsize = 2 * _tables.size(); newtable.resize(newsize); for (size_t i = 0; i _next; size_t hashi = hf(cur->_kv.first) % newtable.size(); cur->_next = newtable[hashi]; newtable[hashi] = cur; cur = next; } _tables[i] = nullptr; } _tables.swap(newtable); } size_t hashi = hf(kv.first) % _tables.size(); Node* newnode = new Node(kv); // 头插 newnode->_next = _tables[hashi]; _tables[hashi] = newnode; ++_n; return true; }🎧2.3 哈希桶查找Find🎧
查找实现思路如下:
- 根据 key 和 哈希函数计算出对应的桶(hashi);
- 在此桶中进行寻找:
- 定义一个哈希节点类型的指针Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
- 一直向后寻找,直到找到或者 cur == nullptr(没有此元素)。
- 找到返回此位置的指针,找不到返回空。
完整的查找逻辑代码:
Node* Find(const K& key) { HashFunc hf; // 根据 `key` 和 哈希函数计算出对应的桶(`hashi`) size_t hashi = hf(key) % _tables.size(); Node* cur = _tables[hashi]; while (cur) { if (cur->_kv.first == key) { return cur; } else { cur = cur->_next; } } return nullptr; }🎧2.4 哈希桶删除Erase🎧
删除实现思路如下:
- 根据 key 和 哈希函数计算出对应的桶(hashi);
- 在此桶中进行查找,这里要考虑要删除的节点的前一个节点是否为空;
- 如果前一个节点不为空,直接让prev->_next = cur->_next;
- 如果前一个节点为空,就让 _tables[i] = cur->_next;
- delete cur; cur = nullptr;
- 如果一直到 cur == nullptr 最后都未曾找到,则返回false;
- 最后 --_n。
完整的删除逻辑代码:
bool Erase(const K& key) { HashFunc hf; // 根据 `key` 和 哈希函数计算出对应的桶(`hashi`); size_t hashi = hf(key) % _tables.size(); Node* cur = _tables[hashi]; Node* prev = nullptr; while (cur) { if (cur->_kv.first == key) { // 如果前一个节点为空,就让 `_tables[i] = cur->_next`; if (prev == nullptr) { _tables[hashi] = cur->_next; } // 如果前一个节点为空,就让 `_tables[i] = cur->_next` else { prev->_next = cur->_next; } delete cur; return true; } else { prev = cur; cur = cur->_next; } } return false; }3. 字符串哈希与仿函数
字符串哈希我们上一篇文章讲过::
- 当我们插入数字的类型,例如:double、float、int、 char、unsigned用的是一种类型的哈希函数;
- 当我们插入字符串类型string的时候用的是另一种类型的哈希函数;
- 🔎遇到这种情况的时候我们一般用仿函数来解决问题!!!🔍
因此我们要加一个仿函数的模板参数:class HashFunc
对于数字类型的仿函数代码:
template struct Hash { size_t operator()(const K& key) { // 强转即可 return (size_t)key; } };对于string类型的仿函数代码:
这里先写一下,待会再细谈:
struct StringFunc { size_t operator()(const string& str) { size_t ret = 0; for (auto& e : str) { ret *= 131; ret += e; } return ret; } };由于string类型的哈希我们经常用,因此可以用模板的特化,并将此模板用缺省参数的形式传递,这样我们就不用在每次用的时候传入仿函数了。
template struct Hash { size_t operator()(const K& key) { return (size_t)key; } }; template struct Hash { size_t operator()(const string& str) { size_t ret = 0; for (auto& e : str) { ret *= 131; ret += e; } return ret; } };4.哈希桶实现哈希表完整代码
🎧有需要的小伙伴自取哈,博主已经检测过了,无bug🎧
🎨博主gitee链接: Jason-of-carriben 哈希桶实现哈希表完整代码
#pragma once #include #include using namespace std; template struct HashFunc { size_t operator()(const K& key) { return (size_t)key; } }; template struct HashFunc { size_t operator()(const string& str) { size_t hash_value = 0; for (auto& e : str) { hash_value = hash_value * 131 + e; } return hash_value; } }; namespace hash_bucket { template struct HashNode { pair _kv; HashNode* _next; HashNode(const pair& kv) :_kv(kv) ,_next(nullptr) {} }; template class HashTable { public: typedef HashNode Node; HashTable(size_t n = 10) { _tables.resize(n); } ~HashTable() { for (size_t i = 0; i _next; delete cur; cur = next; } } } bool Insert(const pair& kv) { HashFunc hf; if (Find(kv.first)) { return false; } // 判断负载因子扩容 // 负载因子为1扩容 if (_n == _tables.size()) { // 方法1:新定义一个对象 /*size_t newsize = 2 * _tables.size(); HashTable newht(newsize); for (size_t i = 0; i _next; newht.Insert(cur->_kv); cur = next; } } _tables.swap(newht._tables);*/ // 方法2:新定义一个表 vector newtable; size_t newsize = 2 * _tables.size(); newtable.resize(newsize); for (size_t i = 0; i _next; size_t hashi = hf(cur->_kv.first) % newtable.size(); cur->_next = newtable[hashi]; newtable[hashi] = cur; cur = next; } _tables[i] = nullptr; } _tables.swap(newtable); } size_t hashi = hf(kv.first) % _tables.size(); Node* newnode = new Node(kv); // 头插 newnode->_next = _tables[hashi]; _tables[hashi] = newnode; ++_n; return true; } Node* Find(const K& key) { HashFunc hf; size_t hashi = hf(key) % _tables.size(); Node* cur = _tables[hashi]; while (cur) { if (cur->_kv.first == key) { return cur; } else { cur = cur->_next; } } return nullptr; /*for (size_t i = 0; i _next; if (cur->_kv.first == key) { return cur; } else { cur = next; } } } return nullptr;*/ } bool Erase(const K& key) { HashFunc hf; size_t hashi = hf(key) % _tables.size(); Node* cur = _tables[hashi]; Node* prev = nullptr; while (cur) { if (cur->_kv.first == key) { if (prev == nullptr) { _tables[hashi] = cur->_next; } else { prev->_next = cur->_next; } delete cur; return true; } else { prev = cur; cur = cur->_next; } } return false; //for (size_t i = 0; i _kv.first == key) // { // if (prev == nullptr) // { // _tables[i] = cur->_next; // } // else // { // prev->_next = cur->_next; // } // delete cur; // return true; // } // else // { // prev = cur; // cur = cur->_next; // } // } //} //return false; } private: vector _tables; size_t _n = 0; }; void HashTest1() { int a[] = { 10001,11,55,24,19,12,31,93,67,26 }; HashTable ht; for (auto e : a) { ht.Insert(make_pair(e, e)); } ht.Insert(make_pair(32, 32)); //ht.Insert(make_pair(32, 32)); ht.Erase(31); ht.Erase(10001); } void HashTest2() { string arr[] = { "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉","苹果","草莓", "苹果","草莓" }; HashTable countMap; for (auto& e : arr) { countMap.Insert(make_pair(e, e)); } } }