深度解析:数据结构二叉树(1)
✅作者简介:大家好,我是再无B~U~G,一个想要与大家共同进步的男人😉😉
🍎个人主页:
再无B~U~G-CSDN博客
目标
1.
掌握树的基本概念
2.
掌握二叉树概念及特性
3.
掌握二叉树的基本操作
VPS购买请点击我 1. 树型结构
1.1 概念
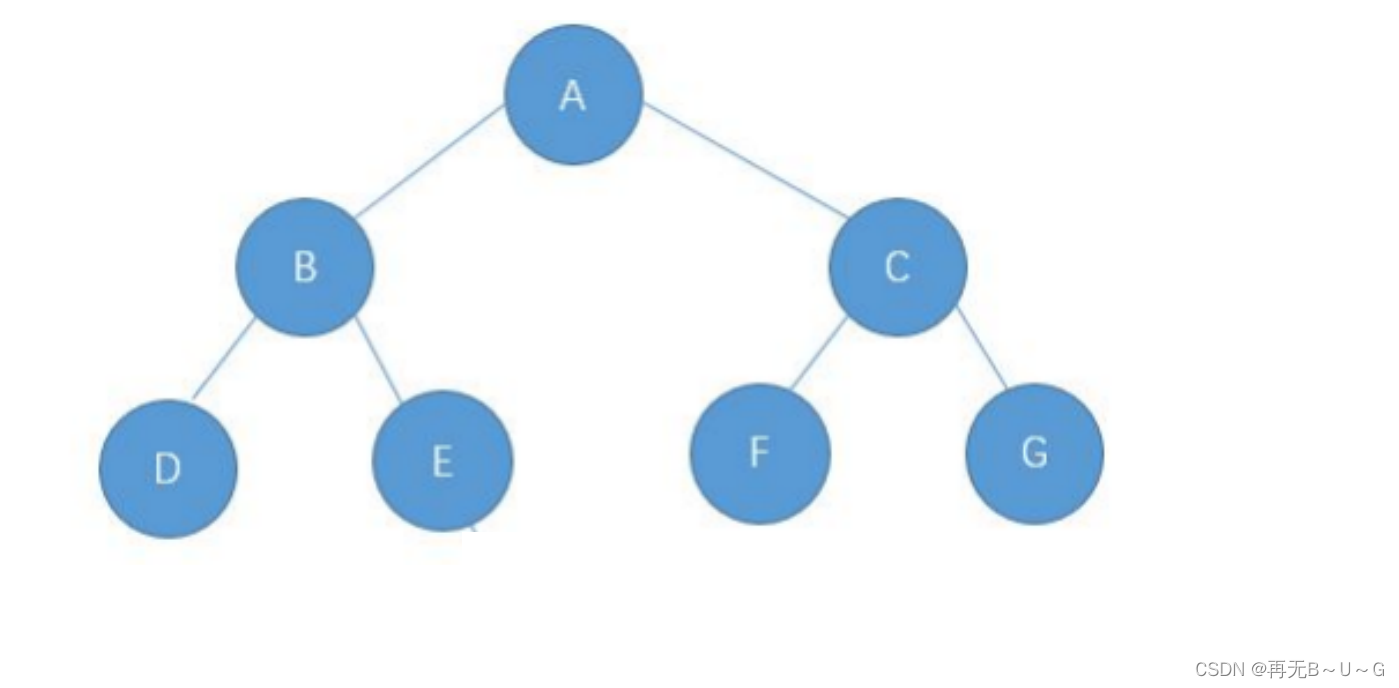
树是一种 非线性 的数据结构,它是由 n ( n>=0 )个有限结点组成一个具有层次关系的集合。 把它叫做树是因为它看 起来像一棵倒挂的树,也就是说它是根朝上,而叶朝下的 。它具有以下的特点:- 有一个特殊的结点,称为根结点,根结点没有前驱结点
- 除根结点外,其余结点被分成M(M > 0)个互不相交的集合T1、T2、......、Tm,其中每一个集合Ti (1
根的左子树
--->
根的右子树。
(根左右)
LNR
:中序遍历
(Inorder Traversal)——
根的左子树
--->
根节点
--->根的右子树。
(左根右)
LRN
:后序遍历
(Postorder Traversal)——
根的左子树
--->
根的右子树
--->根节点。
(左右根)
// 前序遍历
void preOrder ( Node root ); // 中序遍历 void inOrder ( Node root ); // 后序遍历 void postOrder ( Node root )下面主要分析前序递归遍历,中序与后序图解类似,同学们可自己动手绘制。
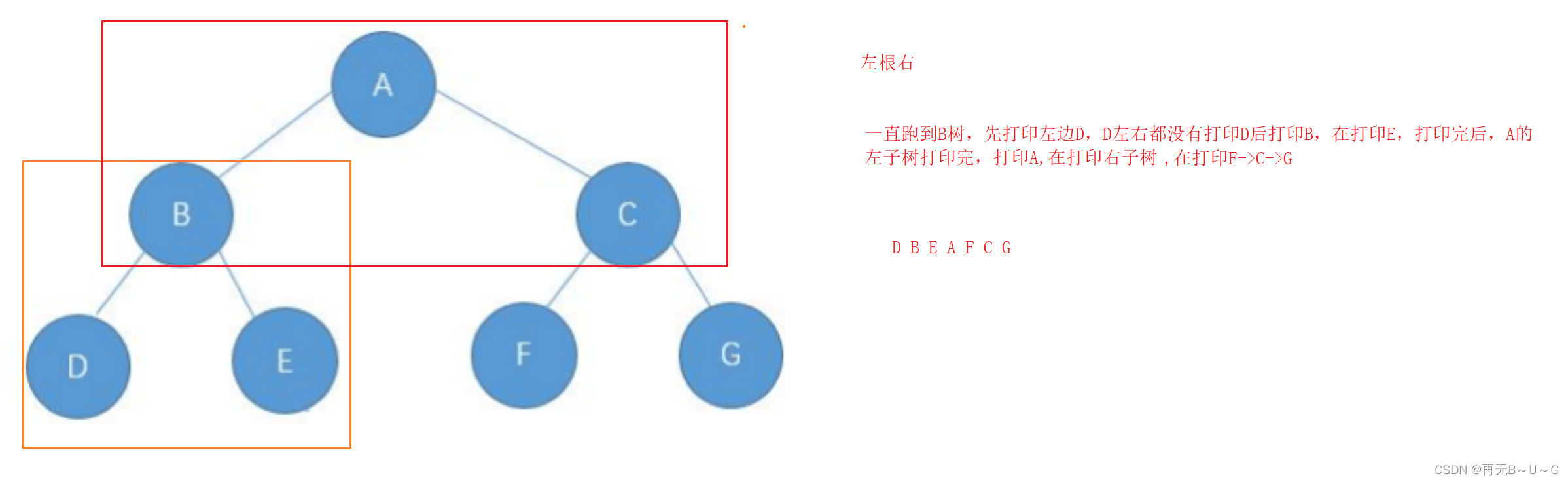
前序遍历结果:ABCDEFG 分析: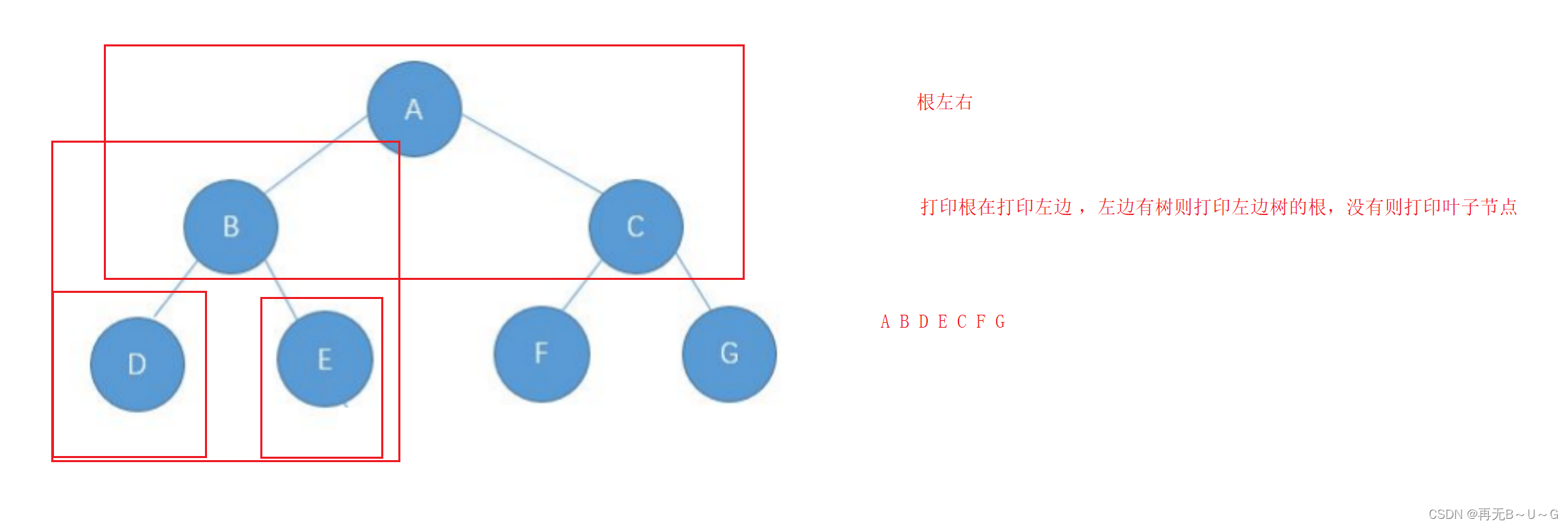 中序遍历结果:DBEAFCG
中序遍历结果:DBEAFCG
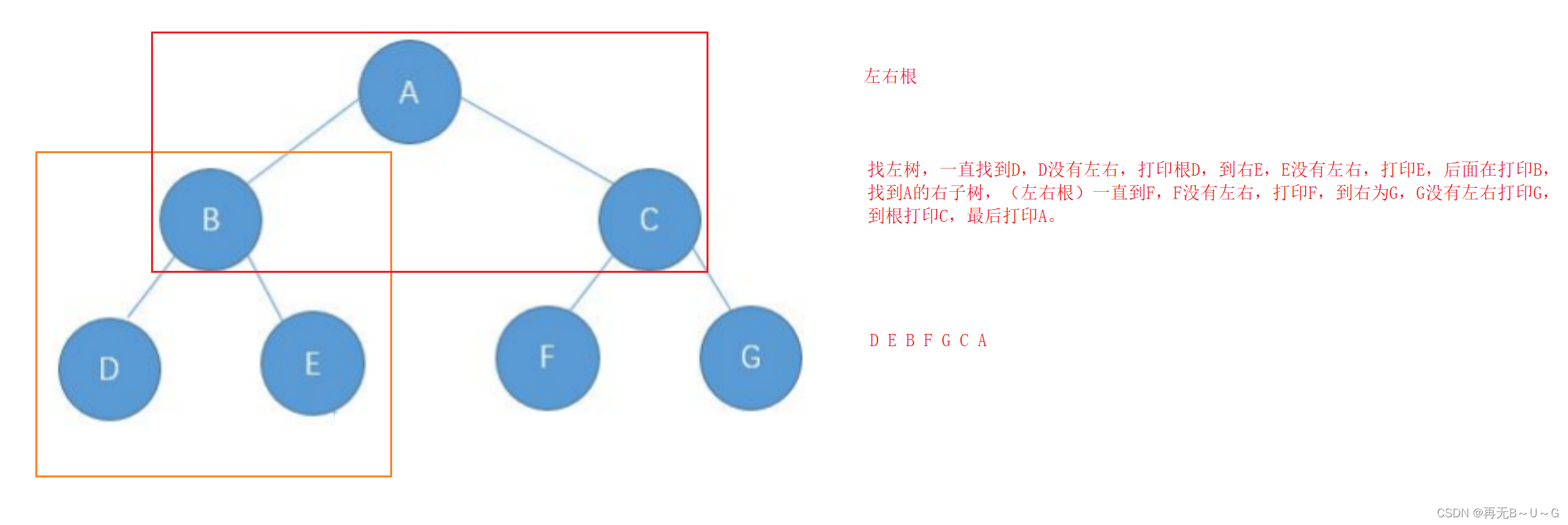
 后序遍历结果:DEBFGCA
后序遍历结果:DEBFGCA
选择题
1. 某完全二叉树按层次输出(同一层从左到右)的序列为 ABCDEFGH 。该完全二叉树的前序序列为 () A: ABDHECFG B: ABCDEFGH C: HDBEAFCG D: HDEBFGCA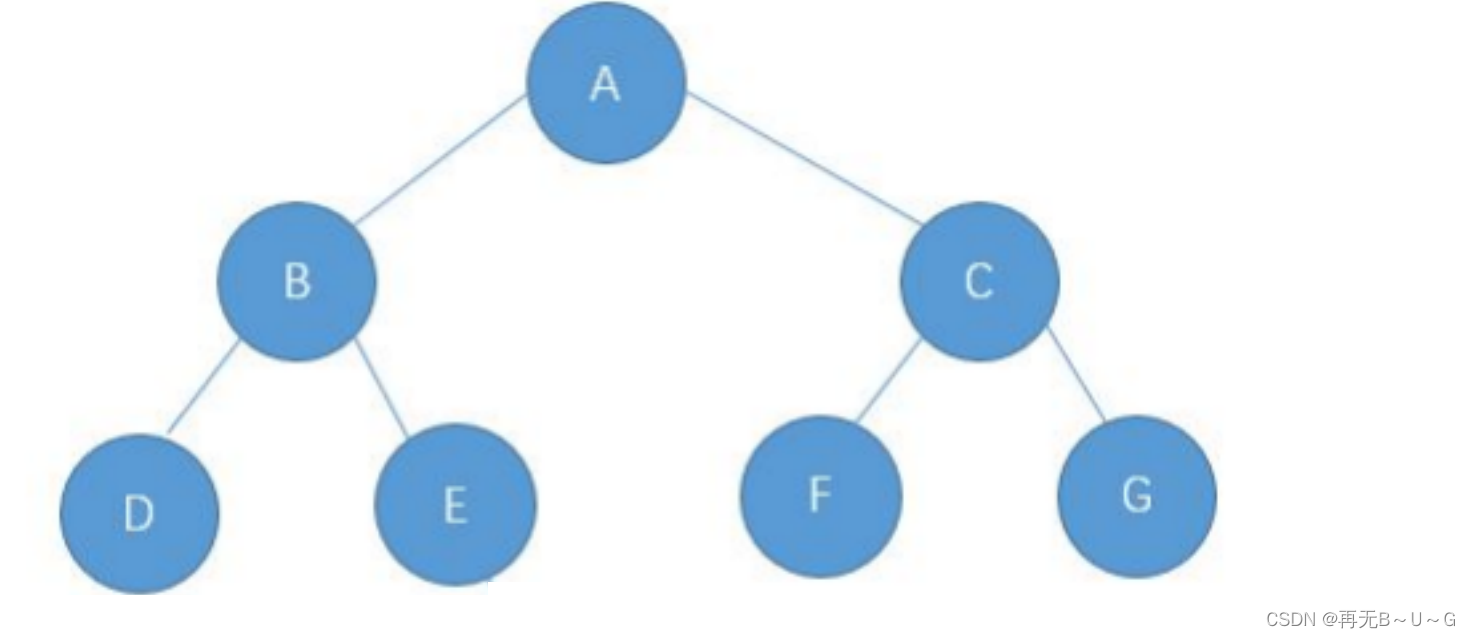 2.
二叉树的先序遍历和中序遍历如下:先序遍历:
EFHIGJK;
中序遍历:
HFIEJKG.
则二叉树根结点为
()
A: E B: F C: G D: H
2.
二叉树的先序遍历和中序遍历如下:先序遍历:
EFHIGJK;
中序遍历:
HFIEJKG.
则二叉树根结点为
()
A: E B: F C: G D: H
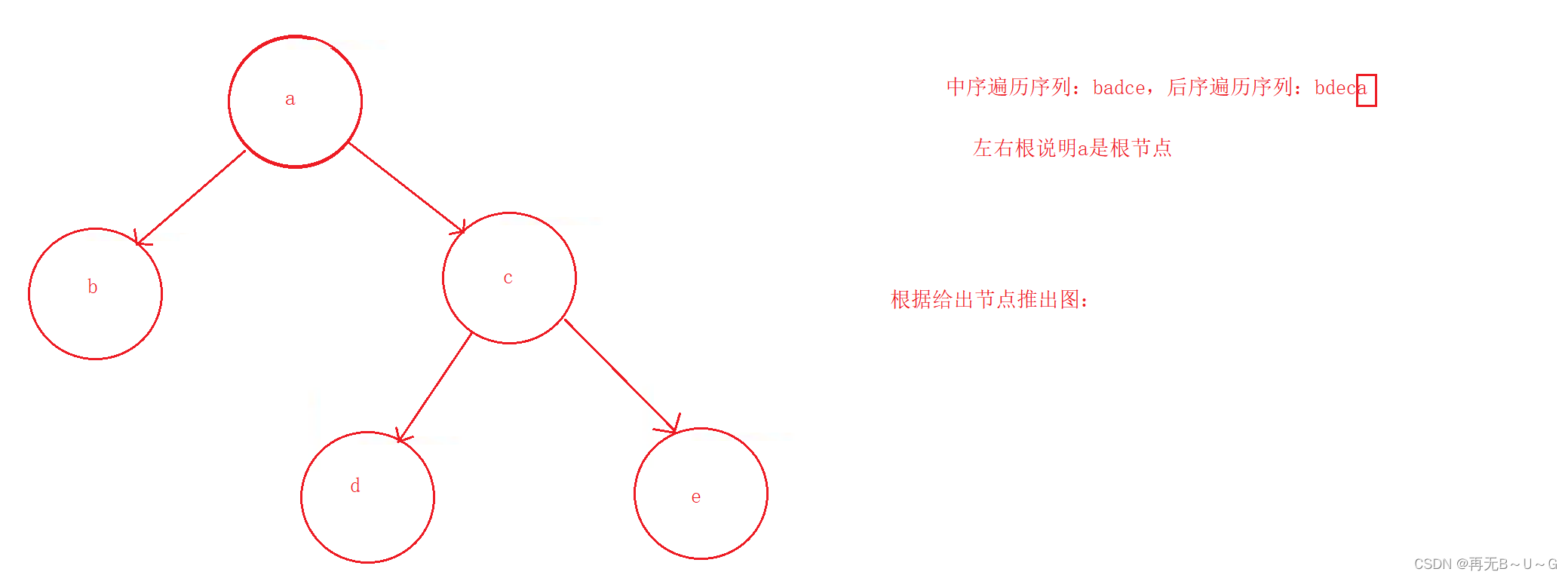
 3.
设一课二叉树的中序遍历序列:
badce
,后序遍历序列:
bdeca
,则二叉树前序遍历序列为
()
A: adbce B: decab C: debac D: abcde
3.
设一课二叉树的中序遍历序列:
badce
,后序遍历序列:
bdeca
,则二叉树前序遍历序列为
()
A: adbce B: decab C: debac D: abcde
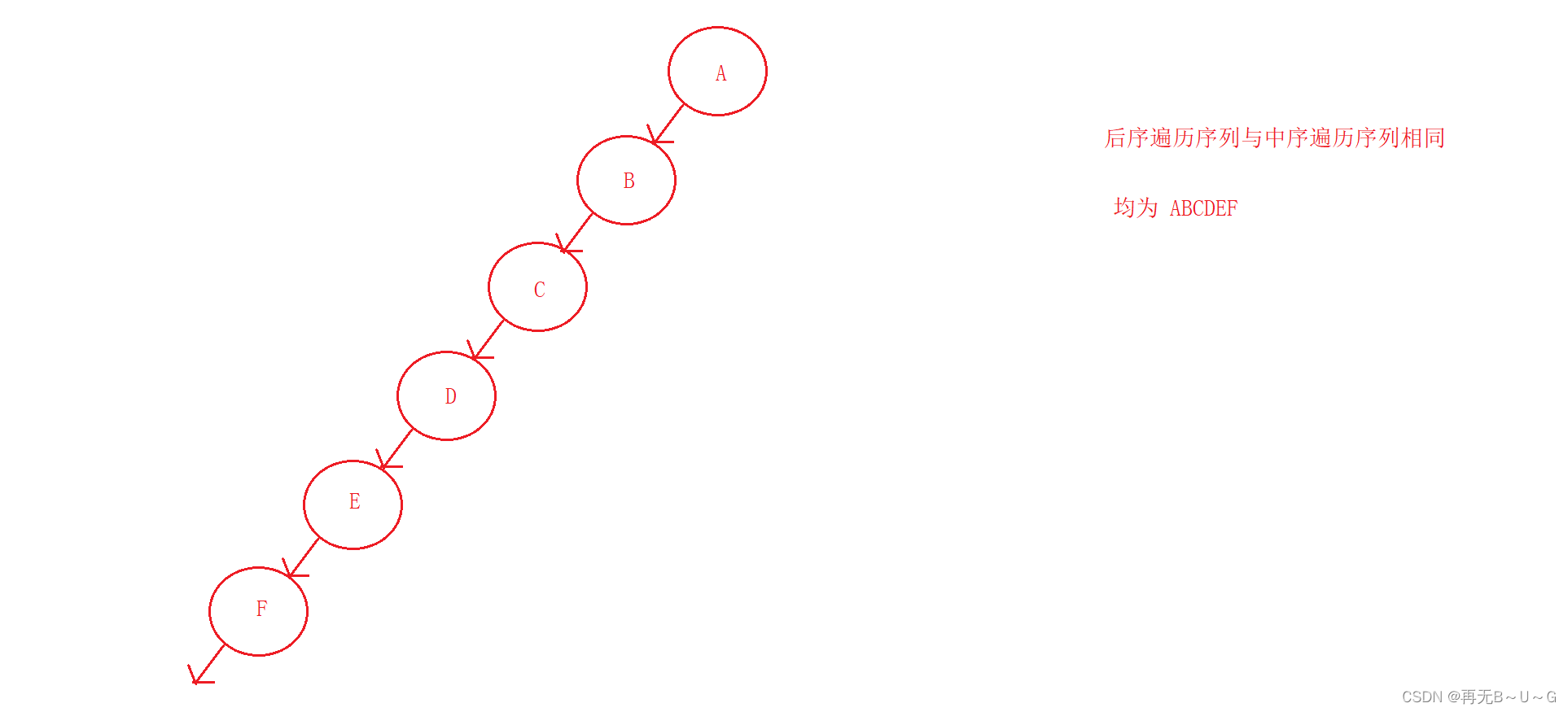
 4.
某二叉树的
后序遍历序列与中序遍历序列相同
,均为
ABCDEF
,则按层次输出
(
同一层从左到右
)
的序列为
()
A: FEDCBA B: CBAFED C: DEFCBA D: ABCDEF
4.
某二叉树的
后序遍历序列与中序遍历序列相同
,均为
ABCDEF
,则按层次输出
(
同一层从左到右
)
的序列为
()
A: FEDCBA B: CBAFED C: DEFCBA D: ABCDEF
 【参考答案】
1.A 2.A 3.D 4.A
【参考答案】
1.A 2.A 3.D 4.A
前序遍历代码:
//前序遍历 void preOrder(BTNode root) { if (root == null) { return; } System.out.print(root.ch + " "); //递归遍历左子树 preOrder(root.left); //递归遍历右子树 preOrder(root.right); }中序遍历代码:
//中序遍历 void inOrder(BTNode root) { if (root == null) { return; } //递归遍历左子树 inOrder(root.left); System.out.print(root.ch + " "); //递归遍历右子树 inOrder(root.right); }后序遍历代码:
//后序遍历 void postOrder(BTNode root){ if(root == null){ return; } //递归遍历左子树 postOrder(root.left); //递归遍历右子树 postOrder(root.right); System.out.print(root.ch + " "); }2.5.3 二叉树的基本操作
// 获取树中节点的个数 int size(BTNode root){ if(root == null){ return 0; } //递归遍历左子树 //递归遍历右子树 int ret = size(root.left) + size(root.right) + 1; return ret; } // 获取叶子节点的个数 int getLeafNodeCount(BTNode root){ if(root == null){ return 0; } if(root.left == null && root.right == null){ return 1; } return getLeafNodeCount(root.left) + getLeafNodeCount(root.right); } // 子问题思路-求叶子结点个数 // 获取第K层节点的个数 int getKLevelNodeCount(BTNode root,int k){ if(root == null) { return 0; } if(k == 1) { return 1; } return getKLevelNodeCount(root.left,k-1) + getKLevelNodeCount(root.right,k-1); } // 获取二叉树的高度 int getHeight(BTNode root){ if(root == null) { return 0; } int leftHeight = getHeight(root.left); int rightHeight = getHeight(root.right); return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight+1:rightHeight+1; } // 检测值为value的元素是否存在 BTNode find(BTNode root,char val){ if(root == null) { return null; } if(root.ch == val) { return root; } //左边找 BTNode ret = find(root.left,val); if(ret != null) { return ret; } //右边找 ret = find(root.right,val); if(ret != null) { return ret; } return null; } //层序遍历 void levelOrder(BTNode root){ //双向列表当列队 Queue queue = new LinkedList(); if(root == null) { return; } queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { BTNode cur = queue.poll(); System.out.print(cur.ch+" "); if(cur.left != null) { queue.offer(cur.left); } if(cur.right != null) { queue.offer(cur.right); } } System.out.println(); } // 判断一棵树是不是完全二叉树 boolean isCompleteTree(BTNode root){ Queue queue = new LinkedList(); if(root == null) return true; queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { BTNode cur = queue.poll(); if(cur == null) { break; } queue.offer(cur.left); queue.offer(cur.right); } while (!queue.isEmpty()) { BTNode node = queue.peek(); if(node != null) { return false; }else { queue.poll(); } } return true; }好了,今天就到这里了,感谢观看。
文章版权声明:除非注明,否则均为主机测评原创文章,转载或复制请以超链接形式并注明出处。