中电金信:技术实践|Flink维度表关联方案解析
导语:Flink是一个对有界和无界数据流进行状态计算的分布式处理引擎和框架,主要用来处理流式数据。它既可以处理有界的批量数据集,也可以处理无界的实时流数据,为批处理和流处理提供了统一编程模型。
维度表可以看作是用户来分析数据的窗口,它区别于事实表业务真实发生的数据,通常用来表示业务属性,以便为分析者提供有用的信息。在实际场景中,由于数据是实时变化的,因此需要通过将维度表进行关联,来保证业务的时效性和稳定性。本文主要围绕Flink维度表关联方案进行论述,分析不同关联方案的作用和特点,与各位读者共飨。
维度表与事实表的关联是数据分析中常见的一种分析方式,在传统数仓系统中,由于数据是有界的,因此关联实现相对简单。但是在实时系统或实时数仓中,数据是无界的,关联时需要考虑的问题就会复杂很多,如数据迟到导致的关联结果不准确、缓存数据消耗资源过大等等。
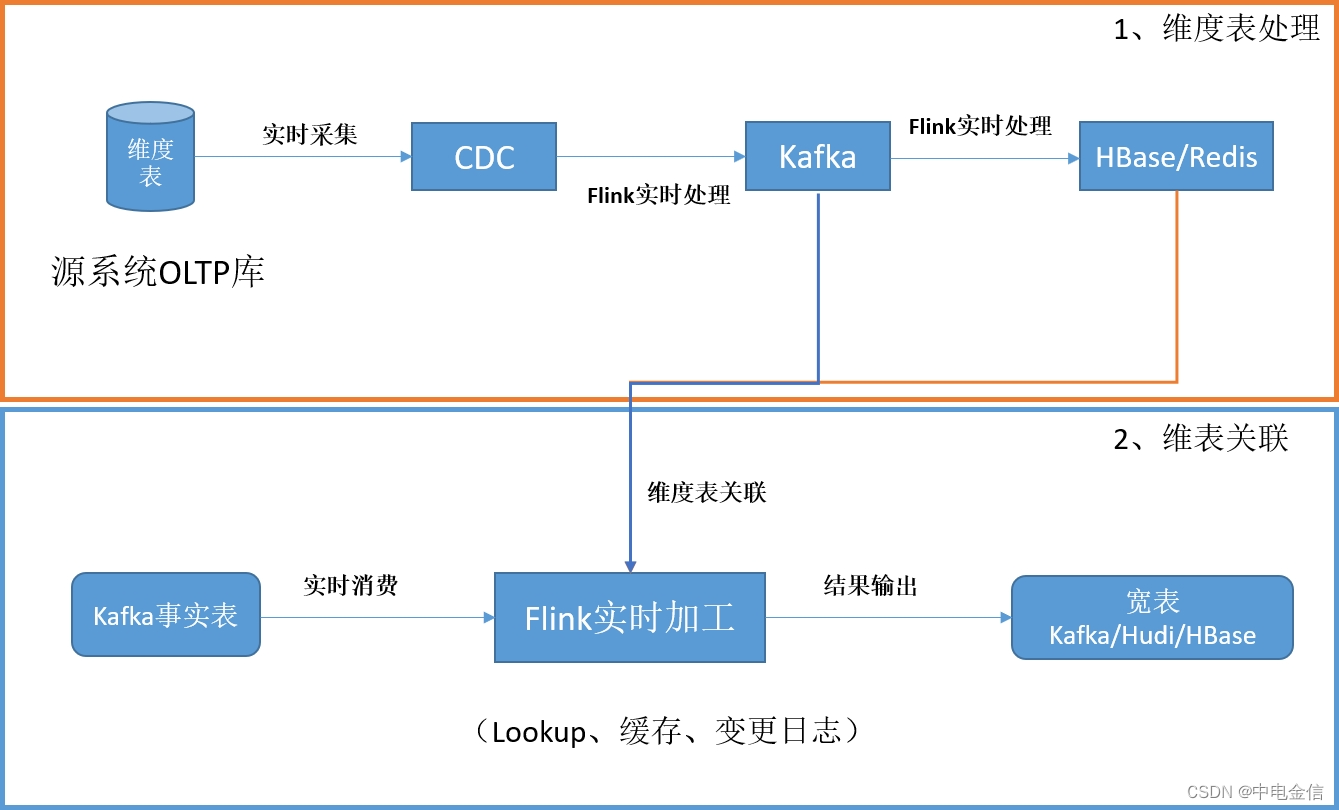
在典型的实时系统中,维表数据一般来源于源系统的OLTP数据库中,采用CDC技术将维表数据实时采集到Kafka或其他消息队列,最后保存到HBase、Hudi、Redis等组件中供数据分析使用。一个比较常见的架构图如下:
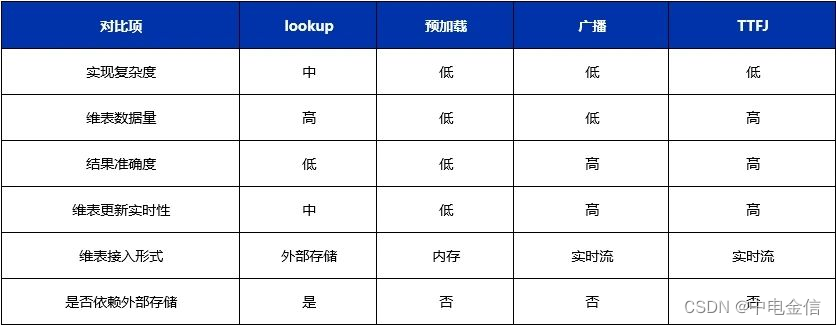
Flink维度表关联有多种方案,包括实时lookup数据库关联、预加载维表关联、广播维度表、Temporal Table Function Join等。每种方案都有各自的特点,需要结合实际情况综合判断,维表关联方案主要考虑的因素有如下几个方面:
■ 实现复杂度:实现维表关联复杂度越低越好
■ 数据库负载:随着事实表数据量增大,数据库吞吐量能否满足,数据库负载能否支撑
■ 维表更新实时性:维表更新后,新的数据能否及时被应用到
■ 内存消耗:是否占用太多内存
■ 横向扩展:随着数据量增大,能否横向扩展
■ 结果确定性:结果的正确性是否能够保证
01 实时lookup数据库关联
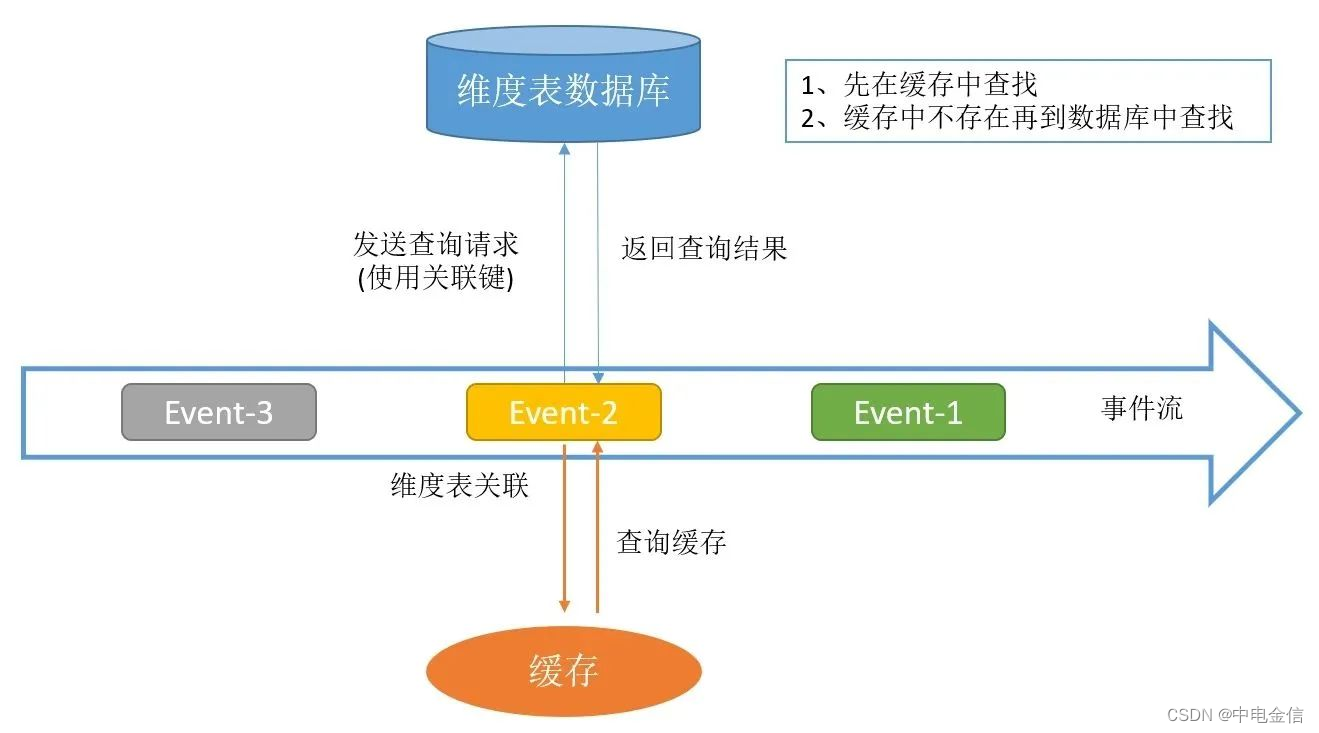
所谓实时lookup数据库关联,就是在用户自定义函数中通过关联字段直接访问数据库实现关联的方式。每条事实表数据都会根据关联键,到存储维度表的数据库中查询一次。
实时lookup数据库关联的特点是实现简单,但数据库压力较大,无法支撑大数据量的维度数据查询,并且在查询时只能根据当时的维度表数据查询,如果事实表数据重放或延迟,查询结果的正确性无法得到保证,且多次查询结果可能不一致。
实时lookup数据库关联还可以再细分为三种方式:同步lookup数据库关联、异步lookup数据库关联和带缓存的数据库lookup关联。
1.1 同步lookup数据库关联
同步实时数据库lookup关联实现最简单,只需要在一个RichMapFunction或者RichFlat-MapFunction中访问数据库,处理好关联逻辑后将结果数据输出即可。上游每输入一条数据就会前往外部表中查询一次,等待返回后输出关联结果。
同步lookup数据库关联的参考代码如下:
创建类并继承RichMapFunction抽象类。
public class HBaseMapJoinFun extends RichMapFunction {
在open方法中实现连接数据库(该数据库存储了维度表信息)。
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration hconf= HBaseConfiguration.create();
InputStream hbaseConf = DimSource.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("hbase-site.xml");
InputStream hdfsConf = DimSource.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("hdfs-site.xml");
InputStream coreConf = DimSource.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("core-site.xml");
hconf.addResource(hdfsConf);
hconf.addResource(hbaseConf);
hconf.addResource(coreConf);
if (User.isHBaseSecurityEnabled(hconf)){
String userName = "dl_rt";
String keyTabFile = "/opt/kerberos/kerberos-keytab/keytab";
LoginUtil.setJaasConf(ZOOKEEPER_DEFAULT_LOGIN_CONTEXT_NAME, userName, keyTabFile);
}else {
LOG.error("conf load error!");
}
connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(hconf);
}
在map方法中实现关联操作,并返回结果。
@Override
public Tuple3 map(Tuple2 stringStringTuple2) throws Exception
LOG.info("Search hbase data by key .");
String row_key = stringStringTuple2.f1;
String p_name = stringStringTuple2.f0;
byte[] familyName = Bytes.toBytes("cf");
byte[] qualifier = Bytes.toBytes("city_name");
byte[] rowKey = Bytes.toBytes(row_key);
table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(table_name));
Get get = new Get(rowKey);
get.addColumn(familyName,qualifier);
Result result = table.get(get);
for (Cell cell : result.rawCells()){
LOG.info("{}:{}:{}",Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneRow(cell)),Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneFamily(cell)),
Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneQualifier(cell)),
Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneValue(cell)));
}
String cityName = Bytes.toString(result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("cf"),Bytes.toBytes("city_name")));
return new Tuple3(row_key,p_name,cityName);
}
在主类中调用。
//关联维度表 SingleOutputStreamOperator resultStream = dataSource.map(new HBaseMapJoinFun()); resultStream.print().setParallelism(1);
1.2 异步lookup数据库关联
异步实时数据库lookup关联需要借助AsyncIO来异步访问维表数据。AsyncIO可以充分利用数据库提供的异步Client库并发处理lookup请求,提高Task并行实例的吞吐量。
相较于同步lookup,异步方式可大大提高数据库查询的吞吐量,但相应的也会加大数据库的负载,并且由于查询只能查当前时间点的维度数据,因此可能造成数据查询结果的不准确。
AsyncIO提供lookup结果的有序和无序输出,由用户自己选择是否保证event的顺序。
示例代码参考如下:
创建Join类并继承RichAsyncFunction抽象类。
public class HBaseAyncJoinFun extends RichAsyncFunction {
在open方法中实现连接数据库(存储了维度表的信息)。
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration hconf= HBaseConfiguration.create();
InputStream hbaseConf = DimSource.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("hbase-site.xml");
InputStream hdfsConf = DimSource.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("hdfs-site.xml");
InputStream coreConf = DimSource.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("core-site.xml");
hconf.addResource(hdfsConf);
hconf.addResource(hbaseConf);
hconf.addResource(coreConf);
if (User.isHBaseSecurityEnabled(hconf)){
String userName = "dl_rt";
String keyTabFile = "/opt/kerberos/kerberos-keytab/keytab";
LoginUtil.setJaasConf(ZOOKEEPER_DEFAULT_LOGIN_CONTEXT_NAME, userName, keyTabFile);
}else {
LOG.error("conf load error!");
}
final ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2,
new ExecutorThreadFactory("hbase-aysnc-lookup-worker", Threads.LOGGING_EXCEPTION_HANDLER));
try{
connection = ConnectionFactory.createAsyncConnection(hconf).get();
table=connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(table_name),threadPool);
}catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e){
LOG.error("Exception while creating connection to HBase.",e);
throw new RuntimeException("Cannot create connection to HBase.",e);
}
在AsyncInvoke方法中实现异步关联,并返回结果。
@Override
public void asyncInvoke(Tuple2 input, ResultFuture resultFuture) throws Exception {
LOG.info("Search hbase data by key .");
String row_key = input.f1;
String p_name = input.f0;
byte[] familyName = Bytes.toBytes("cf");
byte[] qualifier = Bytes.toBytes("city_name");
byte[] rowKey = Bytes.toBytes(row_key);
Get get = new Get(rowKey);
get.addColumn(familyName,qualifier);
CompletableFuture responseFuture = table.get(get);
responseFuture.whenCompleteAsync(
(result, throwable) -> {
if (throwable != null){
if (throwable instanceof TableNotFoundException){
LOG.error("Table '{}' not found", table_name,throwable);
resultFuture.completeExceptionally(
new RuntimeException("HBase table '"+table_name+"' not found.",throwable)
);
}else {
LOG.error(String.format("HBase asyncLookup error,retry times = %d",1),throwable);
responseFuture.completeExceptionally(throwable);
}
}else{
List list = new ArrayList();
if (result.isEmpty()){
String cityName="";
list.add(new Tuple3(row_key,p_name,cityName));
resultFuture.complete(list);
}else{
String cityName = Bytes.toString(result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("cf"),Bytes.toBytes("city_name")));
list.add(new Tuple3(row_key,p_name,cityName));
resultFuture.complete(list);
}
}
}
);
}
在主方法中调用。
//异步关联维度表
DataStream unorderedResult = AsyncDataStream.unorderedWait(dataSource, new HBaseAyncJoinFun(),
5000L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,2).setParallelism(2);
unorderedResult.print();
此处使用unorderedWait方式,允许返回结果存在乱序。
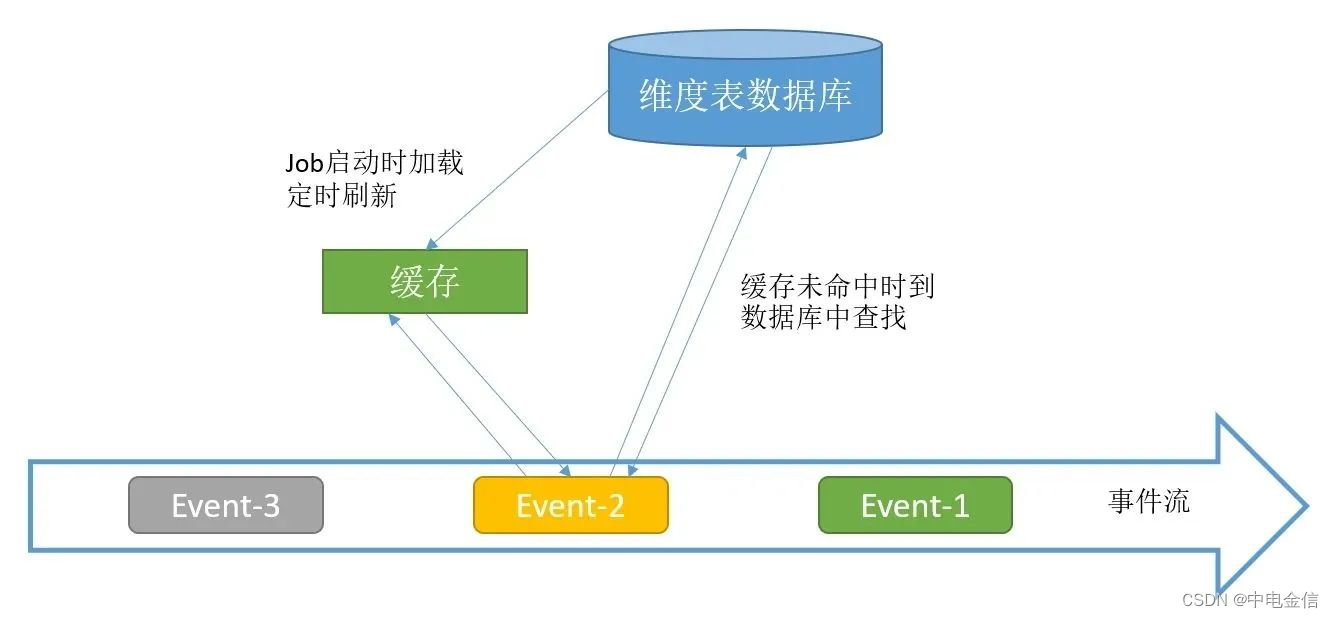
1.3 带缓存的数据库lookup关联
带缓存的数据库lookup关联是对上述两种方式的优化,通过增加缓存机制来降低查询数据库的请求数量,而且缓存不需要通过 Checkpoint 机制持久化,可以采用本地缓存,例如Guava Cache可以比较轻松的实现。
此种方式的问题在于缓存的数据无法及时更新,可能会造成关联数据不正确的问题。
02 预加载维表关联
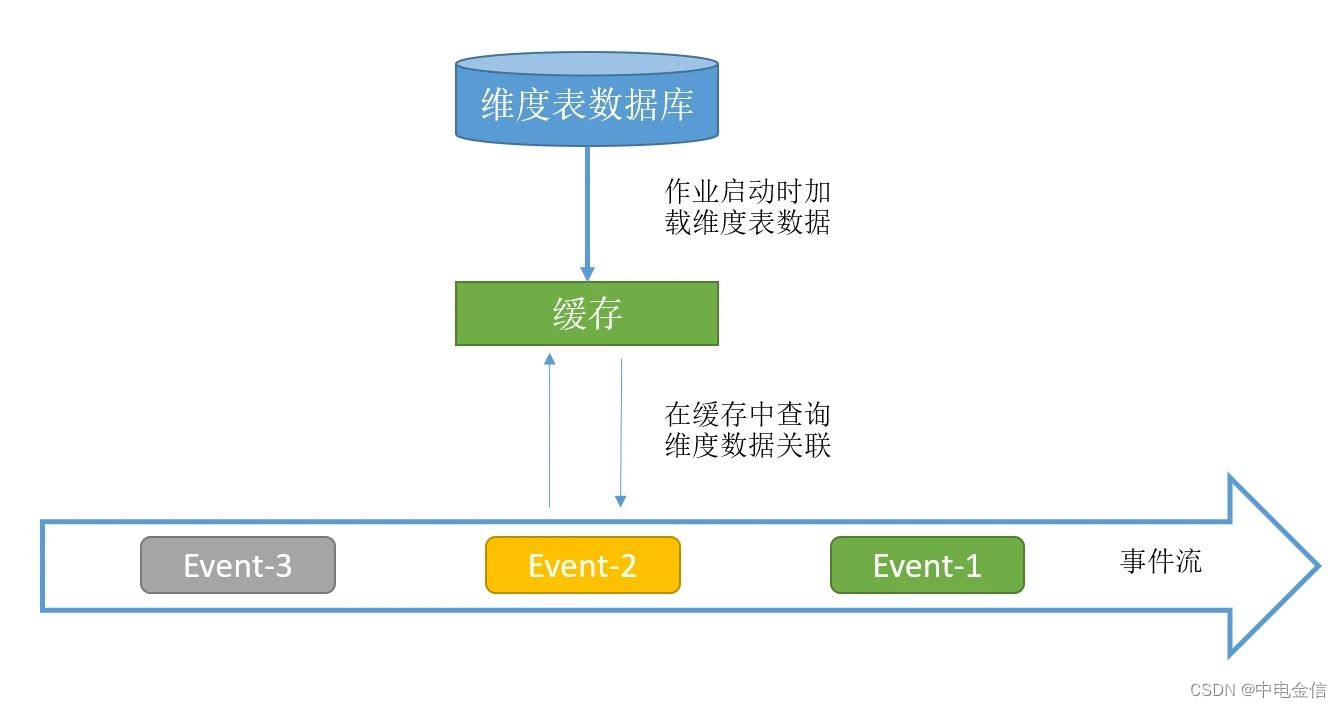
预加载维表关联是在作业启动时就把维表全部加载到内存中,因此此种方式只适用于维度表数据量不大的场景。相较于lookup方式,预加载维表可以获得更好的性能。
预加载维表关联还可以再细分为四种方式:启动时预加载维表、启动时预加载分区维表、启动时预加载维表并定时刷新和启动时预加载维表并实时lookup数据库。
预加载维表的各种细分方案可根据实际应用场景进行结合应用,以此来满足不同的场景需求。
2.1 启动时预加载维表
启动时预加载维表实现比较简单,作业初始化时,在用户函数的open方法中读取数据库的维表数据放到内存中,且缓存的维表数据不作为State,每次重启时open方法都被再次执行,从而加载新的维表数据。
此方法需要占用内存来存储维度表数据,不支持大数据量的维度表,且维度表加载入内存后不能实时更新,因此只适用于对维度表更新要求不高且数据量小的场景。
2.2 启动时预加载分区维表
对于维表比较大的情况,可以在启动预加载维表基础之上增加分区功能。简单来说就是将数据流按字段进行分区,然后每个Subtask只需要加在对应分区范围的维表数据。此种方式一定要自定义分区,不要用KeyBy。
2.3 启动时预加载维表并定时刷新
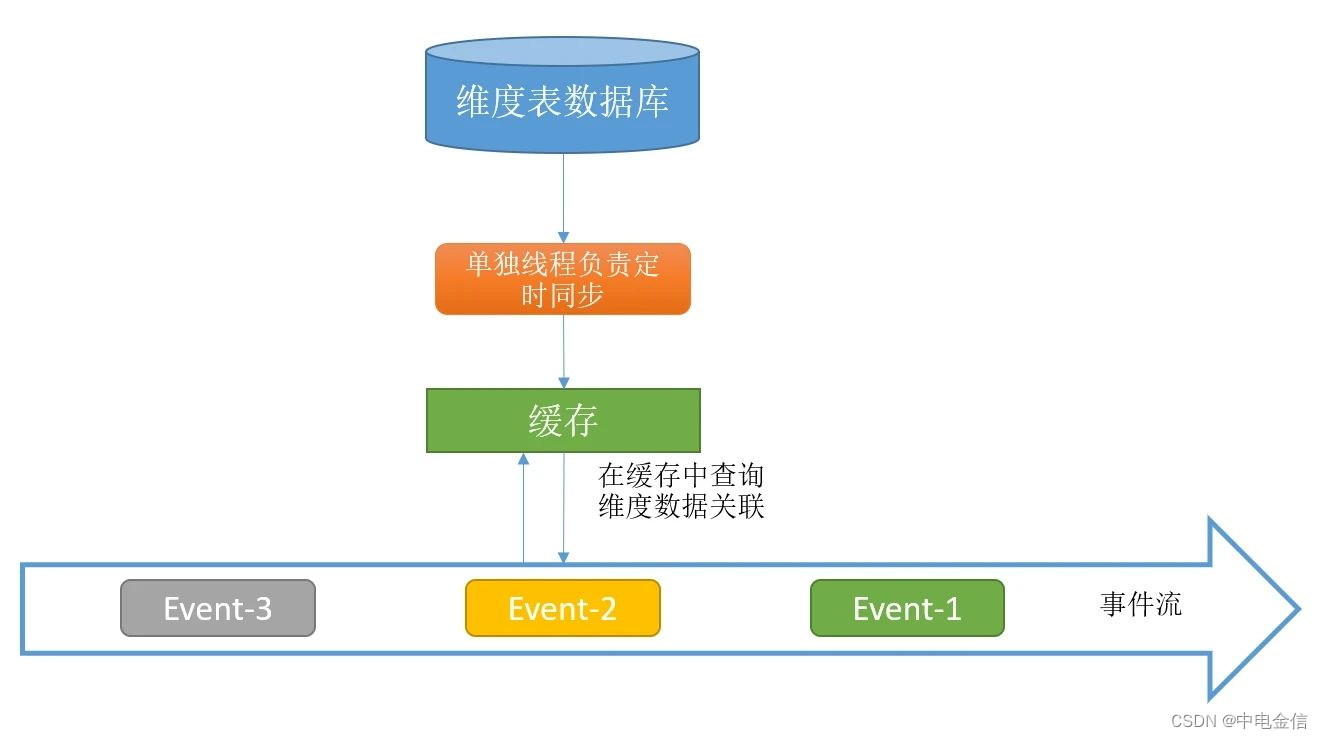
预加载维度数据只有在Job启动时才会加载维度表数据,这会导致维度数据变更无法被识别,在open方法中初始化一个额外的线程来定时更新内存中的维度表数据,可以一定程度上缓解维度表更新问题,但无法彻底解决。
示例代码参考如下:
public class ProLoadDimMap extends RichMapFunction {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ProLoadDimMap.class.getName());
ScheduledExecutorService executor = null;
private Map cache;
@Override
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
executor.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
load();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},5,5, TimeUnit.MINUTES);//每隔 5 分钟拉取一次维表数据
}
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
}
@Override
public Tuple2 map(Tuple2 stringIntegerTuple2) throws Exception {
String username = stringIntegerTuple2.f0;
Integer city_id = stringIntegerTuple2.f1;
String cityName = cache.get(city_id.toString());
return new Tuple2(username,cityName);
}
public void load() throws Exception {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://172.XX.XX.XX:XX06/yumd?useSSL=false&characterEncoding=UTF-8", "root", "Root@123");
PreparedStatement statement = con.prepareStatement("select city_id,city_name from city_dim;");
ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery();
//全量更新维度数据到内存
while (rs.next()) {
String cityId = rs.getString("city_id");
String cityName = rs.getString("city_name");
cache.put(cityId, cityName);
}
con.close();
}
}
2.4 启动时预加载维表并实时lookup数据库
此种方案就是将启动预加载维表和实时look两种方式混合使用,将预加载的维表作为缓存给实时lookup使用,未命中则到数据库里查找。该方案可解决关联不上的问题。
03 广播维度表
广播维度表方案是将维度表数据用流的方式接入Flink Job 程序,并将维度表数据进行广播,再与事件流数据进行关联,此种方式可以及时获取维度表的数据变更,但因数据保存在内存中,因此支持的维度表数据量较小。
示例代码参考如下:
首先将维度表进行广播。
//维度数据源
DataStream dimSource = env.addSource(new DimSource1());
// 生成MapStateDescriptor
MapStateDescriptor dimState = new MapStateDescriptor("dimState",
BasicTypeInfo.INT_TYPE_INFO,BasicTypeInfo.STRING_TYPE_INFO);
BroadcastStream broadcastStream = dimSource.broadcast(dimState);
实现BroadcastProcessFunction类的processElement方法处理事实流与广播流的关联,并返回关联结果。
SingleOutputStreamOperator output = dataSource.connect(broadcastStream).process(
new BroadcastProcessFunction() {
@Override
public void processElement(Tuple2 input, ReadOnlyContext readOnlyContext, Collector collector) throws Exception {
ReadOnlyBroadcastState state = readOnlyContext.getBroadcastState(dimState);
String name = input.f0;
Integer city_id = input.f1;
String city_name="NULL";
if (state.contains(city_id)){
city_name=state.get(city_id);
collector.collect("result is : "+name+" ,"+city_id+" ,"+city_name);
}
}
实现BroadcastProcessFunction类的processBroadcastElement方法处理广播流数据,将新的维度表数据进行广播。
@Override
public void processBroadcastElement(Tuple2 input, Context context, Collector collector) throws Exception {
LOG.info("收到广播数据:"+input);
context.getBroadcastState(dimState).put(input.f0,input.f1);
}
04 Temporal Table Function Join
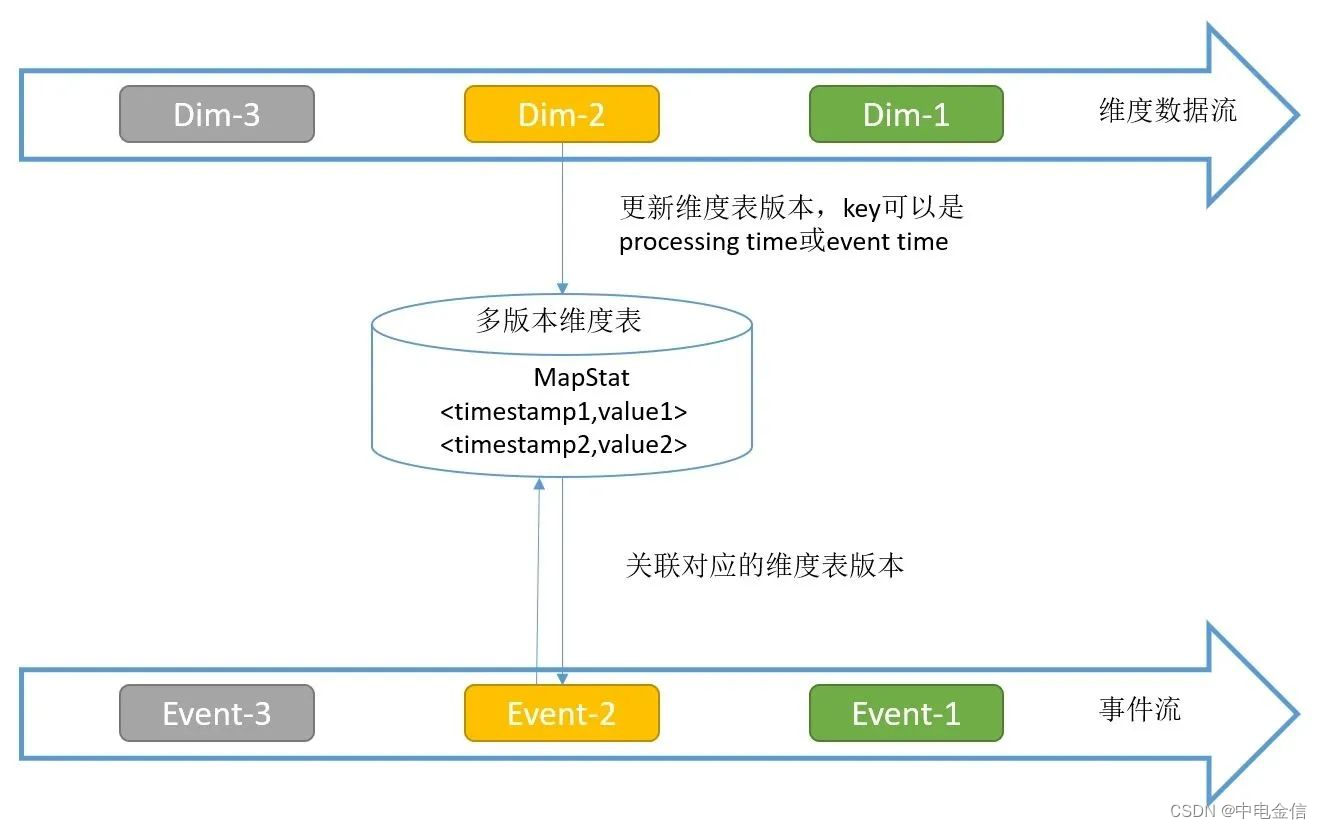
Temporal Table Function Join仅支持在Flink SQL API中使用,需要将维度表数据作为流的方式传入Flink Job。该种方案可支持大数据量的维度表,且维度表更新及时,关联数据准确性更高,缺点是会占用状态后端和内存的资源,同时自行实现的代码复杂度过高。
Temporal Table是持续变化表上某一时刻的视图,Temporal Table Function是一个表函数,传递一个时间参数,返回Temporal Table这一指定时刻的视图。可以将维度数据流映射为Temporal Table,主流与这个Temporal Table进行关联,可以关联到某一个版本(历史上某一个时刻)的维度数据。
示例代码参考如下:
public class TemporalFunTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(TimeCharacteristic.EventTime);
EnvironmentSettings bsSettings = EnvironmentSettings.newInstance().inStreamingMode().build();
StreamTableEnvironment tableEnv = StreamTableEnvironment.create(env, bsSettings);
env.setParallelism(1);
//定义主流
DataStream dataSource = env.addSource(new EventSource2())
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(new BoundedOutOfOrdernessTimestampExtractor(Time.seconds(0)){
@Override
public long extractTimestamp(Tuple3 stringIntegerLongTuple3) {
return stringIntegerLongTuple3.f2;
}
});
//定义维度流
DataStream cityStream = env.addSource(new DimSource())
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(
//指定水位线、时间戳
new BoundedOutOfOrdernessTimestampExtractor(Time.seconds(0)) {
@Override
public long extractTimestamp(Tuple3 element) {
return element.f2;
}
});
//主流,用户流, 格式为:user_name、city_id、ts
Table userTable = tableEnv.fromDataStream(dataSource,"user_name,city_id,ts.rowtime");
//定义城市维度流,格式为:city_id、city_name、ts
Table cityTable = tableEnv.fromDataStream(cityStream,"city_id,city_name,ts.rowtime");
tableEnv.createTemporaryView("userTable", userTable);
tableEnv.createTemporaryView("cityTable", cityTable);
//定义一个TemporalTableFunction
TemporalTableFunction dimCity = cityTable.createTemporalTableFunction("ts", "city_id");
//注册表函数
tableEnv.registerFunction("dimCity", dimCity);
Table u = tableEnv.sqlQuery("select * from userTable");
u.printSchema();
tableEnv.toAppendStream(u, Row.class).print("user streaming receive : ");
Table c = tableEnv.sqlQuery("select * from cityTable");
c.printSchema();
tableEnv.toAppendStream(c, Row.class).print("city streaming receive : ");
//关联查询
Table result = tableEnv
.sqlQuery("select u.user_name,u.city_id,d.city_name,u.ts " +
"from userTable as u " +
", Lateral table (dimCity(u.ts)) d " +
"where u.city_id=d.city_id");
//打印输出
DataStream resultDs = tableEnv.toAppendStream(result, Row.class);
resultDs.print("\t\t join result out:");
env.execute("joinDemo");
}
}