动态内存管理(1)
文章目录
- 目录
- 1. 为什么存在动态内存分配
- 2. 动态内存函数的介绍
- 2.1 malloc 和 free
- 2.2 calloc
- 2.3 realloc
- 3. 常见的动态内存错误
- 3.1 对NULL指针的解引用操作
- 3.2 对动态开辟空间的越界访问
- 3.3 对非动态开辟内存使用free释放
- 3.4 使用free释放一块动态开辟内存的一部分
- 3.5 对同一块动态内存多次释放
- 3.6 动态开辟内存忘记释放(内存泄漏)
目录
- 为什么存在动态内存分配
- 动态内存函数的介绍
- 常见的动态内存错误
- 几个经典的笔试题
- 柔性数组
1. 为什么存在动态内存分配
我们已经掌握的内存开辟方式有:
int main() { int a = 10;//变量 int arr[10];//数组 return 0; }但是上述的开辟空间的方式有两个特点:
- 空间开辟大小是固定的。
- 数组在申明的时候,必须指定数组的长度,它所需要的内存在编译时分配。
但是对于空间的需求,不仅仅是上述的情况,有时候我们需要的空间大小在程序运行的时候才能知道,那数组的编译时开辟空间的方式就不能满足了,这时候就只能试试动态内存开辟了。
2. 动态内存函数的介绍
2.1 malloc 和 free
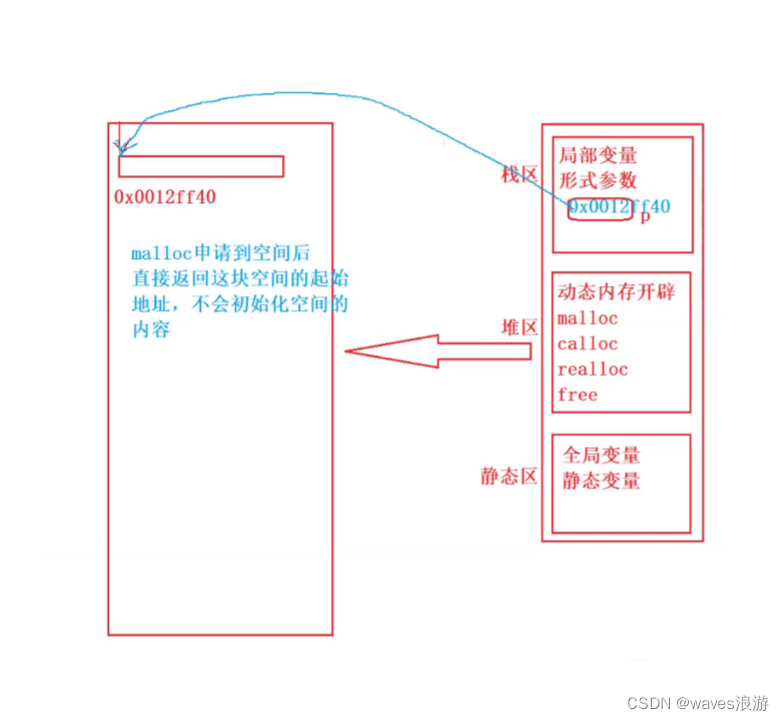
malloc - memory alloc 内存开辟
C语言提供了一个动态内存开辟的函数:
void* malloc (size_t size);
这个函数向内存申请一块连续可用的空间,并返回指向这块空间的指针。
- 如果开辟成功,则返回一个指向开辟好空间的指针。
- 如果开辟失败,则返回一个NULL指针,因此malloc的返回值一定要做检查。
- 返回值的类型是 void* ,所以malloc函数并不知道开辟空间的类型,具体在使用的时候使用者自己来决定。
- 如果参数 size 为0,malloc的行为是标准是未定义的,取决于编译器。
注: malloc 申请的内存空间,当程序退出时,还给操作系统;当程序不退出,动态申请的内存,不会主动释放的,需要使用 free 函数来释放。
C语言提供了另外一个函数free,专门是用来做动态内存的释放和回收的,函数原型如下:
void free (void* ptr);
free函数用来释放动态开辟的内存:
- 如果参数 ptr 指向的空间不是动态开辟的,那free函数的行为是未定义的。
- 如果参数 ptr 是NULL指针,则函数什么事都不做。
注: malloc 和 free 都声明在 stdlib.h 的头文件中。
#include #include int main() { //int arr[10]; int* p = (int*)malloc(40); if (NULL == p) { perror("malloc"); return 1; } //开辟成功 int i = 0; for (i = 0; i2.2 calloc
C语言还提供了一个函数叫calloc,calloc函数也用来动态内存分配。原型如下:
void* calloc (size_t num, size_t size);
- 函数的功能是为 num 个大小为 size 的元素开辟一块空间,并且把空间的每个字节初始化为0。
- 与函数 malloc 的区别只在于 calloc 会在返回地址之前把申请的空间的每个字节初始化为全0。
#include #include int main() { int* p = (int*)calloc(10, sizeof(int)); if (NULL == p) { perror("calloc"); return 1; } //打印数据 int i = 0; for (i = 0; i#include #include int main() { int* p = (int*)calloc(INT_MAX, sizeof(int)); if (NULL == p) { perror("calloc"); return 1; } //打印数据 int i = 0; for (i = 0; i所以,如果我们对申请的内存空间的内容要求初始化,那么可以很方便的使用calloc函数来完成任务。
2.3 realloc
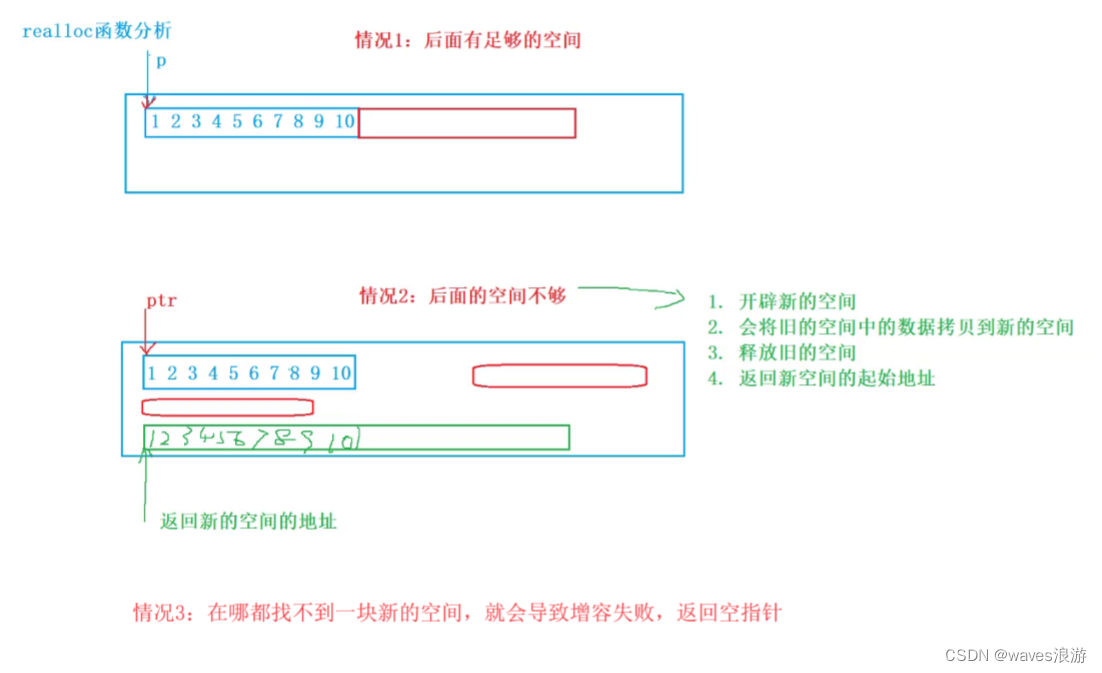
- realloc函数的出现让动态内存管理更加灵活。
- 有时我们会发现过去申请的空间太小了,有时候我们又会觉得申请的空间过大了,那为了合理的调整内存,我们一定会对内存的大小做灵活的调整,那 realloc 函数就可以做到对动态开辟内存大小的调整。
函数原型如下:
void* realloc (void* ptr, size_t size);
- ptr 是要调整的内存地址(Pointer to a memory block previously allocated with malloc, calloc or realloc.)
- 当 ptr 为空指针时,它的功能和 malloc 是一样的(Alternatively, this can be a null pointer, in which case a new block is allocated (as if malloc was called).)
- size 是调整之后的新大小
- 返回值为调整之后的内存起始位置
#include #include int main() { int* p = (int*)malloc(40); if (NULL == p) { perror("malloc"); return 1; } //初始化为1~10 int i = 0; for (i = 0; i3. 常见的动态内存错误
3.1 对NULL指针的解引用操作
void test() { int *p = (int *)malloc(INT_MAX/4); *p = 20;//如果p的值是NULL,就会有问题 free(p); }解决方法:要对 p 进行判断,看它是否为空指针
3.2 对动态开辟空间的越界访问
#include #include int main() { int* p = (int*)malloc(40); if (NULL == p) { perror("malloc"); return 1; } int i = 0; //对动态开辟空间的越界访问 for (i = 0; i3.3 对非动态开辟内存使用free释放
#include #include int main() { int a = 10; int* p = &a; printf("%d\n", *p); free(p); p = NULL; return 0; }3.4 使用free释放一块动态开辟内存的一部分
#include #include int main() { int* p = (int*)malloc(40); if (NULL == p) { perror("malloc"); return 1; } int i = 0; for (i = 0; i3.5 对同一块动态内存多次释放
#include #include int main() { int* p = (int*)malloc(40); if (NULL == p) { return 1; } //使用 //释放 free(p); free(p);//err p = NULL; return 0; }#include #include int main() { int* p = (int*)malloc(40); if (NULL == p) { return 1; } //使用 //释放 free(p); p = NULL; free(p);//这样写没有问题,因为p为空指针时,free什么都不干 return 0; }3.6 动态开辟内存忘记释放(内存泄漏)
#include #include void test() { int* p = (int*)malloc(100); if (NULL != p) { *p = 20; } } int main() { test(); while (1); return 0; }主函数在调用test函数之后,申请了100个字节的空间,并把地址传给了p,但是test函数结束之后,p由于出了作用域,被销毁了,导致找不到这100个字节的空间了,而程序之后又进入了死循环,这就导致我申请了100个字节的内存空间,但是我又用不上,又释放不了,造成了内存泄漏。
注: 动态申请的内存空间,不会因为出了作用域自动销毁(还给操作系统)!只有2种方式销毁: free 或者 程序结束(退出)